* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File 1-pedigree
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
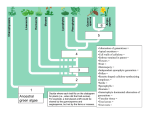
What is a Pedigree… And Nooooo it’s not Dogfood. Biology I Searcy Ninth Grade Center It is a diagram that shows how a trait is inherited through several generations. Pedigree for the Albino Trait Pedigree for a Sex Linked Trait Human geneticists illustrate the inheritance of a gene within a family by using a pedigree chart. • Squares = males • Circles = females • Shaded = individual has the • • • • trait or condition Unshaded = individual does not have trait or condition Horizontal line = marriage Vertical line = offspring, arranged from left to right in order of birth Roman numerals - label different generations = unaffected female = affected female = female carrier = unaffected male = male affected by one trait = male carrier And more... Patterns of Inheritance By analyzing patterns of inheritance, biologists can learn about genetic diseases. If a trait is autosomal, it will appear in both sexes equally and if it is sexlinked, it is usually seen only in males. The major use of pedigree analysis is in clinical evaluation and counseling of patients with inherited abnormalities. Patterns of Recessive Traits • May appear to “skip” generations • Most children of normal and affected parents are normal • AA x aa ---> Aa • All children of two affected parents will be affected • aa x aa ---> aa Patterns of Recessive Traits • Normal parents may produce affected offspring • Aa x Aa ---> 3/4 normal; 1/4 affected Patterns of Dominant Traits • Trait tends to appear each generation • Normal and affected individual expected to produce normal and affected children (approximate 1:1 ratio) • Affected individuals generally heterozygous if rare trait • Aa x aa ---> 1/2 Aa; 1/2 aa Patterns of Dominant Traits • At least one parent must be affected in order for children to be affected • Aa x aa • Normal parents will always produce normal offspring • aa x aa ---> aa