* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
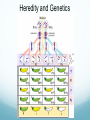
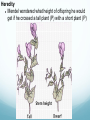
Heredity and Genetics Heredity: Passing of traits from parent to offspring is called Heredity Genetics is the study of DNA and Heredity. The first major contributor to Heredity was Gregor Mendel, the “father of Genetics.” Mendel's Work Mendel studied purebred pea plants in the garden of the monastery where he lived. Purebred organisms produce offspring with the same traits as their parents. Think of purebred dogs: a German Shepard is purebred because if it breeds with another purebred German Shepard, the traits are predictable. Mutts like Sakura have many breeds mixed in them, and have many unpredictable traits. Heredity Mendel noticed that there were patterns in the traits passed from parent to offspring. He dedicated his life studying these patterns. He noticed that parent tall plants (P) which mixed with parent tall plants (P) tended to produce tall offspring and short plants that bred with short plants produced short offspring. Trait versus Characteristic: The plants characteristic is whether it is tall or short. The word trait is used to refer to the plant's height. Heredity Mendel wondered what height of offspring he would get if he crossed a tall plant (P) with a short plant (P) Heredity Mendel noticed that the offspring (F1) were all as tall as the tall plants (because tall was the dominant gene) The offspring (F1) were then self-pollinated and made a second generation (F2) When they grew out, ¾ of the plants were tall, and ¼ of the plants were short. The recessive 'short' genes had shown themselves again! Heredity After many years of trial and error experimentation and mathematical calculation, Mendel compiled his findings: Mendel's Conclusions: Passing of genetic information controls an organisms traits These factors must exist in pairs. One part comes from male, one part comes from female. One factor can hide or 'mask' the other factor (dominant/recessive) Today we call these 'factors' genes. Genes Each plant had a gene which controlled for the plant's height. Alleles are the different forms of a gene. For example, the gene that controls the plants height has two alleles. The F1 generation of mixed tall/short plants had 1 short allele and 1 tall allele. Allelles Dominant alleles (represented with a capital letter), block out recessive alleles (represented as a lowercase letter) T – Tall Plant is dominant to t – Short Plant. There are three ways of referring to the alleles of an organism: TT – Homozygous Dominant Tt – Heterozygous Dominant tt – Homozygous Recessive The prefix 'hetero' means different, 'homo' means the same Think critically: Why do you think there is no heterozygous recessive? Allelles Even though there are three genotypes: TT, Tt, tt There are only two phenotypes: Short and Tall