* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Differentiation
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Spina bifida wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
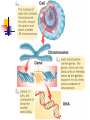
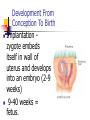
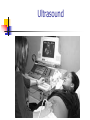
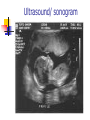
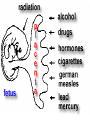
Development From Conception To Birth Conception occurs when a sperm and an ovum unite. A zygote (0-14 days) is produced by union of a sperm and an egg. Development From Conception To Birth The child inherits half of its genetic makeup from each parent through meiosis of 46 chromosomes, 23 from each parent. Development From Conception To Birth Implantation zygote embeds itself in wall of uterus and develops into an embryo (2-9 weeks) 9-40 weeks = fetus. Differentiation development of cells into tissues and organs. controlled by cell's expression of genes with environment. Sexual differentiation From fertilization - six weeks of development, male and female embryos have undifferentiated gonads (sex glands: ovaries or testes). Sexual differentiation a gene on the Y chromosome directs the undifferentiated gonads to become testes. If Y chromosome is not present (as in normal females), undifferentiated gonads will become ovaries (female epigenesist) Fetal period Gestation = pregnancy Full term = 40 weeks Viability = ability to survive outside womb Premature birth = prior to 37 weeks or birth weight of less than 5.5 pounds Development From Conception To Birth Despite protection of mother's body, baby's development may be influenced by mother's diet, physical condition, drugs she may use, including tobacco and alcohol. Prenatal Development Folic acid (vitamin B9 or folate) important in preventing neural tube defects such as spina bifida crucial in development of DNA. plays large role in cell growth and development and tissue formation Prenatal Development 400 micrograms (0.4 milligrams) daily of folic acid Mom needs 350 extra calories daily Maintain normal exercise (unless complications arise) Alphafetoprotein AFP is a protein secreted by the fetal liver and excreted in the mother's blood. Elevated AFP in mother’s blood can indicate neural tube defect in baby such as spina bifida. Lower levels of AFP suggest possible Down’s syndrome or other chromosomal defect. Ultrasound Ultrasound/ sonogram Amniocentesis CV Sampling Chorionic villi are tiny parts of placenta formed from the fertilized egg, having same genes as the fetus. CVS can identify chromosomal problems: Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs disease and sickle cell disease Teratogens Agents capable of causing developmental abnormalities in utero. effect related to type of agent, dose and duration and time of exposure Environmental Insults 1. Malnourishment Malnourished mother = malnourished baby Miscarriages and stillbirths Teratogenic drugs Anti-nausea - thalidomide Prevent miscarriages: Synthetic hormones - diethylstilbestrol (DES)—cancer in children Alcohol – FAS Tetracycline- bone development Environmental Insults 2. Alcohol Migrating cells go TOO FAR F.A.S. Environmental Insults 3. Radiation Cells don’t go far enough After 8 weeks/ problems Mental retardation Growth retardation Environmental Insults 4. Smoking cigarettes Poisons and lack of oxygen Fetus curls up/ trauma Low birth weight/stillbirth Fetal Tobacco Syndrome Teratogens Cocaine, marijuana – reflexes, attention, mood (short-term?) Rubella – heart/brain defects, deafness and cataracts/blindness Stress – LBW, premature, miscarriage HB Pressure – LBW/ constricted blood flow to placenta Development In Infancy Newborn infants are able to recognize voices (audition) and faces (vision), to make appropriate facial reactions to taste and smell, and even to learn.