* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Access Slides
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
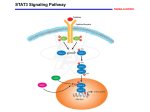
IFNs,Cytokines & the JAKSTAT Signaling Cascade March 10, 2005 Chris Schindler Innate Viral Interfering Activity is Discovered in Cultured Cells (1950s) 1960s 1970s 1980s Initial and intermittent characterization of IFN activity. Purification of “Immune”, “Leukocyte” & “Fibroblast” IFNs yields >10 type I IFNs (a & b) and one type II IFN (IFN-g). Cloned IFNs, the first of many disappointments for biotech industry, is a boon to molecular biologists. An Evolving IFN-a Signaling Paradigm IFN-a PTK-x P P Stat2 IRF-9 Stat1 P P P P antiviral* antiproliferative* chemokine* PKR OAS IP10 iNOS Interferon Stimulated Response Elements (ISREs) ISG54 ISG15 GBP IP10 OAS HLA-A MX TAGTTTCACTTTCCC CAGTTTCGGTTTCCC TACTTTCAGTTTCAT AGGTTTCACTTTCCA TGGTTTCGTTTCCTC CAGTTTCTTTTCTCC GAGTTTCGTTTCTGA Identification of “High IFN Producing Cells” (HIPCs) in vivo A small subset of WBCs produce most of the circulating IFN-Is The IFN-I Autocrine Loop and Toll Like Receptors (TLRs) dsRNA TLR3 IFN-b LPS TLR4 I FN-b ssDNA I FNAR NFkB TLR7 IKKa/b/e CpG IRF-8 ? ? IKKa/b/e IRF-3 St1/St2 IFN-b IRF-7 danger IFN-a’s P TLR9 IRF-7 IRF-7 IFN-a’s danger IFN Type II (a.k.a. IFN-g) Signaling Paradigm IFN-g IFNgR Jak2 Jak1 Y Stat1 Stat1 P P inflammation* macrophage act.* chemokines* IRF1 MIG GBP iNOS CIITA GAS Binding Elements Gene GBP FcgRI ICSBP ICAM-1 c-fos IFP53 IRF-1 IRF-1 Ly6E mig Species human human human human human human human mouse mouse mouse Element ATT AC T CT AAA TTT CC C AG AAA TTT CT C GG AAA TTT CC C GG AAA GTT CC C GT CAA ATT CT C AG AAA TTT CC C CG AAA TTT CC C CG AAA ATT CC T GT AAG CTT AC T AT AAA Tyk2: Member of the Unusual Janus Kinase Family JH7 0 100 JH6 200 JH5 300 400 JH4 500 JH3 600 700 Tyk2 Jak1 Jak2 Jak3 JH2/yK 800 900 JH1/TK 1000 1100 Expressed in all tissues Expressed in hematopoietic tissues 1200 STATs & Four Helix Bundle Cytokines Stat1 Stat2 Stat3 Stat4 Stat5a/b Stat6 IFN-I(a,b,,) & IFN-g IFN-I(a,b,,) IL-10 and IL-6 families IL-12, IL-23, IL-27 Single Chain, IL-2 & IL-3 families IL-4, IL-13 Conserved STAT Domains NH2 0 100 Coil-Coil 200 300 DNA 400 LK 500 SH2 600 Y TAD 700 800 STAT Evolution • STAT homologues have been identified in most model metazoans, including Dictyostelium, C. elegans, Drosophila, Anopheles, Xenopus and zebrafish. • STAT homologues in C. elegans are very distantly related. • The three STAT Dictyostelium homologues are structurally and functionally quite divergent. The Dictyostelium STATs, most closely related to Stat3 & Stat5 may encode the primordial SH2 domain. • Homologues of a STAT (37 % identity to Stat5), JAK (27 % identity to Jak2), cytokine and cytokine receptor have each been identified in Drosophila. This pathway play several important developmental roles. • Zebra fish encodes a Stat1 and Stat3 homologue. The Stat3 homologue is developmentally expressed and syntenic with both murine and human Stat3. The Stat1 homologue is more distantly related and expressed later in life. • Sequence analysis suggests that mammalian STATs evolved from a single syntenic Stat3-Stat5 (murine chromosome 17) tandem cluster that was duplicated to form the Stat1-Stat4 (murine chromosome 2) and Stat2-Stat6 (murine chromosome 12) tandem clusters. This was followed by the duplication of Stat5 into Stat5a and Stat5b. Stat1 • Transduces critical signals for all three classes of IFNs. • Stat1 is activated by several other ligands, but its role appears to be more secondary. • There are two isoforms - Stat1b, which is carboxy terminally truncated before the TAD, is assumed to function as an antagonist of Stat1a. • Generic biological activities include: – Promoting the expression of inflammatory or “danger” signals. – Antagonizing proliferation and/or promoting apoptosis. – Stat3 appears to antagonize both of these activities. • Stat1 is tyrosine phosphorylated on Y701 and serine phosphorylated on S727 (in the TAD). This latter phosphorylation is required for maximal transcription of some genes. • Stat1 has also been reported to be acetylated at K785 and SUMOylated at K703. • Stat1 activity is antagonized by phosphatases directed at the receptor and JAKs, and directly by one or more nuclear phosphatases. • Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 (SOCS-1), a Stat1 target gene, directs an important negative feed back loop to suppress IFNg-Stat1 dependent signals. Type I IFN Signaling Tyk2 P Jak1 Y Y Y P Stat2 IRF-9 Stat1 P P P P P P P P Stat2 • Transduces critical signals for type I IFNs and -IFNs. • Murine and Human Stat2 are functionally analogous but uncharacteristically divergent in sequence, especially in the TAD. • Human Stat2 is tyrosine phosphorylated on Y690 and murine Stat2 on Y689. Other modifications have not been reported, although it is likely to be serine phosphorylated. • Stat2 is the only STAT that does not appear to homodimerize and bind DNA directly. • Stat2 activity is antagonized by phosphatases directed at the receptor and JAKs, and directly by one or more nuclear phosphatases. • In contrast to Stat1 and Stat3, the distribution of Stat2 is unstimulated cells is almost exclusively cytoplasmic. Murine Coil-Coil DNA SH2 Y689 TAD 923 aa 76 % Homology Human 851 aa Coil-Coil DNA Divergent SH2 Y690 TAD Stat3 • Transduces signals for type I IFNs,-IFNs, the critical signals for the extended IL-10 family and the extended IL-6 families. • There are two isoforms, Stat3a & Stat3b. Like Stat1b, Stat3b is carboxy terminally truncated before the TAD, but has been shown to direct the expression of a unique set of genes through association with other transcription factors. Generic biological activities include: • – Promoting cell growth associated with cell transformation. – Antagonizing the expression of inflammatory or “danger” signals. – Stat1 antagonizes both of these activities (a ying-yang relationship). • Stat3 is the only STAT that is essential for development (i.e., the knockout is embryonic lethal). Tissues specific knockouts reveal an important roles in protecting tissues form inflammation and suppressing transformation. • Stat3 is tyrosine phosphorylated at Y705, serine phosphorylated at S727 and acetylated at K785. • Stat3 activity is antagonized by phosphatases directed at the receptor and JAKs, and directly by one or more nuclear phosphatases. • In response to stimulation by the IL-6 family of ligands, Stat3 activity is directly suppressed by SOCS-3, a Stat3 target gene. Endocytosis IL-6 Signaling Cytoplasm IL-6 IL-6Ra gp130 Jak2 Cytoplasm Y Y Y Stat3 P Jak1 P Jak2 Jak1 Stat3 SHP-2 P P MAPK ERK Cytoplasm Endosome Nucleus P P Gene Expression Jak2 Jak1 Stat5a and Stat5b • Transduce critical signals for all members of the IL-2, IL-3 and single chain cytokine receptor families, i.e. is Stat5 is functionally pleiotropic like its ancestral partner Stat3. • Consistent with their significant level of homology, Stat5a & Stat5b can functionally overlap, especially in hematopoietic tissues (e.g., in response to IL-2 and IL-3 family ligands). • However, gene targeting studies have underscored a specificity for Stat5a in prolactin response and a specificity for Stat5b in GH response. • Stat5 has been implicated in the development of some hematopoietic tumors and the regulation of some stem cell populations. • SOCS-2 specifically antagonizes Stat5b activation in response to GH (i.e., SOCS-2 knockout mice exhibit gigantism). Stat4 & Stat6 • Stat4 and Stat6 exhibit a the most ligand specificity. – Stat4 transduces signals for members of the IL-12 family. (IFN-Is can also promote a partial activation of Stat4). – Stat6 transduces signals for closely related IL-4 and IL-13. • Stat4, Stat6 and their activating ligands play an essential role in the development of effector CD4+ T-helper cells. – Stat4 directs the development of Th1 cells. – Stat6 directs the development of Th2 cells. • Full Stat4 activation requires both tyrosine phosphorylation at Y689 and serine phosphorylation at S721. • The ability of IL-18 to direct Stat4 serine phosphorylation accounts for its ability to synergize with some Stat4 activating ligands (e.g., IFN-Is) to direct the activation to Th1 cells. Cytokines and the Th1-Th2 Paradigm Ag iDC Flt-3L GM-CSF IFN-a DC IFN-a IL-12 Th1 Stat4 Stat6 Th2 Th0 IFN-g IL-2 TNF IL-4 IL-5 IL-6 IL-10 TGF-b The Four (a)-Helix Bundle Family of Cytokines - There are ~50 members; a.k.a - hematopoietins They play important roles in development/activation of lymphocytes & myelocytes. They all transduce pivotal signals through JAKs and STATs They can be divided into two families based on the receptors they bind: Cytokines that bind type I cytokine receptors: The gC Family IL-2 family includes IL-2, IL-7, TSLP, IL-9, IL-15, IL-21 (Stat5) IL-4 family includes IL-4 and IL-13 (Stat6) The IL-3 family includes IL-3, IL-5 and GM-CSF (Stat5) The Extended gp130 Family- (Stat3) IL6-gp130 family includes IL-6, IL-11, CNTF, LIF, OSM, CT-1, NP, NNT1/BSF3 (Stat3) gp130-like family includes OSM, IL-31, G-CSF, Leptin IL-12 family includes IL-12, IL-23, IL-27, IL-30 (Stat4*) The single chain family includes Epo, GH, PRL, Tpo (Stat5) Cytokines that bind type II cytokine receptors: The human Type I IFN Family includes 12 a-IFNs, IFN-b, IFN-, limitin(Stat1-3) Type II IFN Family includes only IFN-g (Stat1) -IFN family includes IL-28a, IL-28b, IL-29 (Stat1-3) IL-10 family includes IL-10, IL-19, IL-20, IL-22, IL-24, IL-26 (Stat3)