* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Child Birth
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Miscarriage wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
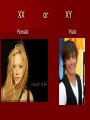
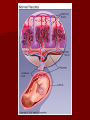
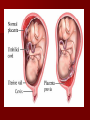
Pregnancy and Childbirth Lesson #24 Conception / Fertilization: union of an ovum and a sperm. Takes place in the upper 1/3 of the fallopian tube Heredity: passing of characteristics from biological parents to their children. Chromosome: carries genes. Gene: unit of hereditary material – 46 Chromosomes (23 from father, 23 from the mother) – Female: X chromosome – Male: X or Y chromosome – XX = female – XY = male XX Female or XY Male Sex-linked characteristics: hereditary characteristics transmitted on the sex chromosomes. Amniotic Sac: pouch of fluid that surrounds a fetus. Endometrium: Inner lining of the uterus. Embryo: Conception to 2nd month of growth. Fetus: 9th week to birth Placenta: Anchors the embryo to the uterus. Umbilical Cord: Ropelike structure that connects the embryo to the placenta. Tools to determine if the baby is developing correctly Ultrasound: provide an image of the developing baby Amniocentesis: the use of a needle (inserted into the uterus to get fluid from the amniotic sac) Pregnancy 1st sign of pregnancy – Woman will miss her period Labor: Process of childbirth – Dilation of the cervix – Delivery of the baby – Delivery of the placenta Complications Ectopic Pregnancy Miscarriage Cesarean Section Stillbirth After the Baby is Born Apgar Score: rating of the baby 1 to 5 minutes after birth. Postpartum period: Hormones produce changes in the mother’s body.