* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sex Linked Genes
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Sexual dimorphism wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
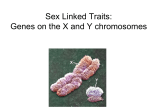
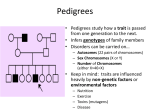
Sex Linked Genes Sex Linked Genes • Found on 23rd chromosome. • If a gene is found only on the X chromosome and not the Y chromosome, it is said to be a sex-linked trait. • Sex linkage is linked to the gender of the individual. X Chromosome Y Chromosome XR XR XR How we see sex linked genes • Look at XX or XY chromosomes – Place superscript letter above X chromosome. • Female Homozygous (Dominant) – XHXH • Female Heterozygous (Carrier) – XHXh • Female Homozygous (Recessive) – XhXh • Male Dominant – XHY • Male Recessive – XhY Give it a try… Parent Father (Carrier) Gametes Children Mother (Heterozygous Normal) Recessive vs. Dominant • X-linked recessive disorders: – Common red-green color-blindness. – Hemophilia. – Duchenne muscular dystrophy. • More males than females display the disease. • X-linked dominant are very rare in humans (ie. hypophosphatemia) and affected males pass the condition only to their daughters who may pass this on to both sons and daughters. • • • • • • Examples of Sex-linked Traits: Red-green colorblindness Male Pattern Baldness Hemophilia Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Hairy Ears – Y Chromosome Hemophilia • Hemophilia is an X-linked recessive disorder – Inability to properly form blood clots. • Until recently, hemophilia was untreatable, and only a few hemophiliacs survived to reproductive age because any small cut or internal hemorrhaging after even a minor bruise were fatal. • Hemophilia is treated with blood transfusions and Factor 7. Hemophilia continued… • Hemophilia affects – males much more frequently (1 in 10,000). – females (1 in 100,000,000). • Since males only carry one X chromosome, if that is defective, hemophilia will immediately show up. • Females, carry two X chromosomes. – If only one is defective, the other normal X chromosome can compensate. The woman will have normal blood clotting; she will simply be a carrier of the recessive defective gene. Sample Sex-linked Trait Problem • In humans, red-green colorblindness is a recessive sex-linked trait. • It is found on the X chromosome, not the Y. • Because, males only have one X chromosome, they have a much greater chance of having red-green colorblindness. – Females would have to be homozygous recessive in order to have red-green colorblindness. Color Blindness Parent’s Phenotypes: • Normal Vision Father x Normal Vision Mother (Carrier) Phenotypes of Offspring: Females Normal Vision Males Normal Vision Males w/ Colorblindness Color Blindness Parent’s Phenotypes: • Normal Vision Father x Colorblind Mother Phenotypes of Offspring: Females Normal Vision Males Normal Vision Males w/ Colorblindness First, let’s take a look at Queen Victoria’s son Leopold’s family. His daughter, Alice of Athlone, had one hemophilic son (Rupert) and two other children—a boy and a girl—whose status is unknown. a) What is the probability that her other son was hemophilic? b) What is the probability that her daughter was a carrier? Hemophilic? c) What is the probability that both children were normal?