* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download X h - Cloudfront.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
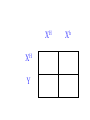
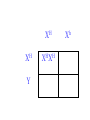
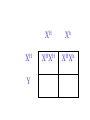
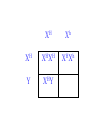
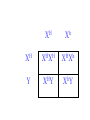
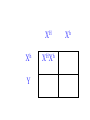
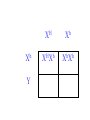
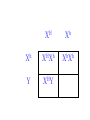
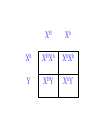
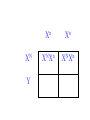
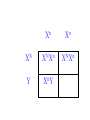
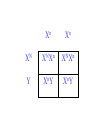
SEX-LINKED TRAITS Karyotype: a picture of chromosomes. … Autosomes: the first 22 homologous pairs of chromosomes. • Autosomes are the same for both males and females. Sex chromosomes: determines the sex of the individual. • The sex chromosomes are the 23rd pair of chromosomes. XX = female XY = male Which parent determines the sex of an offspring? DAD Why? • All moms have the genotype XX. When egg cells are made, they will all carry a single X chromosome. • All dads have the genotype XY. When sperm cells are made, 50% will have an X chromosome and 50% will have a Y chromosome. • Therefore, males and females are born in roughly a 50:50 ratio. SEX-LINKED TRAITS: those traits that are controlled by genes on the X or Y chromosomes. • NOTE: The Y chromosome is much smaller than the X chromosome and only contains a few genes. Most sex-linked traits are on the X chromosome. In humans, hemophilia is a sex-linked trait. Having hemophilia is recessive (Xh) to being normal (XH). The heterozygous female is called a carrier. Cross a carrier female with a normal male. XHXh X _____ In humans, hemophilia is a sex-linked trait. Having hemophilia is recessive (Xh) to being normal (XH). The heterozygous female is called a carrier. Cross a carrier female with a normal male. XH Xh X XH Y H X H X Y h X H X H X Y H H X X h X H X Y H X h X H H X X H h X X H X h X H X H H X X H h X X Y H X Y H X h X H X H H X X H h X X Y H X Y h XY Genotypic ratio: 1 XHXH :1XHXh :1XHY :1XhY Phenotypic ratio: 2 normal females: 1normal male: 1 male with hemophilia Cross a carrier female with a male with hemophilia. XHXh X _____ Cross a carrier female with a male with hemophilia. XHXh X XhY H X h X Y h X H X h X Y H h X X h X h X Y H X h X H h X X h h XX H X h X h X H h X X h h XX Y H X Y H X h X h X H h X X h h XX Y H X Y h XY Genotypic ratio: 1 XHXh :1XhXh :1XHY :1XhY Phenotypic ratio: 1 normal female: 1 female with hemophilia:1 normal male: 1 male with hemophilia In humans, red-green colorblindness is a sexlinked trait. People with red-green colorblindness can not tell the difference between red and green. Colorblindness is the result of a recessive allele. Cross a female with colorblindness with a male with normal vision. XnXn X _____ In humans, red-green colorblindness is a sexlinked trait. People with red-green colorblindness can not tell the difference between red and green. Colorblindness is the result of a recessive allele. Cross a female with colorblindness with a male with normal vision. X nX n X X N Y n X N X Y n X n X N X Y N n X X n X N X Y n X n X N n X X N n X X n X n X N X N n X X N n X X Y n XY n X n X N X N n X X N n X X Y n XY n XY Genotypic ratio: 2 XNXn : 2 XnY Phenotypic ratio: 2 normal females: 2 males with colorblindness Why are sex-linked traits more common in males than in females? • Because a male only has to inherit ONE recessive allele in order to get a sex-linked trait and a female has to inherit TWO recessive alleles in order to acquire the sex-linked trait. It is easier to inherit one recessive allele than two. If the female only inherits one recessive allele, then they are a carrier but have the normal phenotype.