* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review ch 11 Patterns of Inheritance
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Sexual dimorphism wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
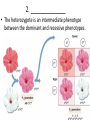
Review ch 11 Complex Patterns of Inheritance Biology Types of Inheritance you should know • • • • • • • • • Incomplete Dominance Co-dominance Multiple Alleles Epistasis Sex Determination Dosage Compensation Sex-Linked Traits Polygenic Traits Environmental Influences What type of Inheritance is shown in the following slides? • On a blank sheet of paper, write your name, class hour, and number it from #1-12. • Work with your table partner to determine the types of inheritance patterns from the following examples………-> 1. ______________ • The image shows a heterozygote both the dominant normal red blood cell and the recessive sickle cell present at the same time. • Heterozygous individuals are able to live relatively normal lives 2. ______________ • The heterozygote is an intermediate phenotype between the dominant and recessive phenotypes. 3. _________________ • Some traits exhibit many phenotypes and vary across a broad range. – – – – – Height of a person Hand and foot size Hair color Skin color Eye color • Many genes on different chromosomes give unlimited phenotype possibilities • A red shorthorn bull may 4. ______________ • Both alleles are expressed in the heterozygous condition be all red, all white, or a combination of red and white hair in the heterozygous (roan cattle) 5. ______________ • This inheritance can also show a hierarchy of dominance from just 4 alleles Two answers needed: 6. ____and______ • Blood groups in Humans have three alleles, two are dominant and one is recessive. • Both dominant alleles show as individual phenotypes when combined in heterozygotes 7. ______________ • A person’s gender is determined by just one set of chromosomes. If the y chromosome is present, the offspring will be a male. 8. ______________ • This inheritance pattern event occurs in females of all mammals as they have XX while males have Xy. This is also called X-inactivation. Example: Calico cats can only be female 9. ______________ • This inheritance pattern results when one allele hides the effect of another allele. • Dominant E allele will determine if the coat will have any dark pigment • Dominant B allele determines how dark the pigment will be 10. ______________ • This inheritance pattern is more likely to be present in males than in females. Traits are found on the X chromosome which men only have Xy 11. _____&_____ • This inheritance is more likely to be present in males than females, and females could be a “carrier” without showing any symptoms. • Can males be a carrier of a recessive hemophilia allele? _______ 12. What has to happen for a girl to be colorblind? • _________________ 13. What can we learn from a Karyotype? Give two answers:_______ and _______ Answers: • • • • • • 1. codominance 2. incomplete dominance 3. polygenic inheritance 4. codominance 5. multiple alleles 6. multiple alleles and codominance • 7. sex determination • 8. dosage compensation • 9. epistasis • 10. x-linked • 11. x-linked, no • 12. A girl who is colorblind must get a colorblind gene from her mom and her dad must be colorblind (XbXb) • 13. number of chromosomes, sex of offspring, if any nondisjunctions have occured