* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendel Discovers “Genes” 9-1
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
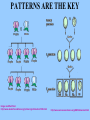
The Work of Gregor Mendel 11-1 http://sps.k12.ar.us/massengale/genetics%20tutorial.htm http://www.jic.bbsrc.ac.uk/germplas/pisum/zgs4f.htm Objectives: • -Describe how Mendel studied inheritance in peas • Summarize Mendel’s conclusion about inheritance • Explain the principle of dominance • Describe what happens during segregation Transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring _______________________is called ___________________. heredity how those SCIENCE that studies _____ The _________ characteristics are _________ passed on from one generation to the next is called Genetics ___________________ http://www.jic.bbsrc.ac.uk/germplas/pisum/zgs4f.htm The __________________ Father of Genetics is _________________, Gregor Mendel study a monk whose _________ of genetic traits was the beginning of our _________________ about understanding _____________________. how genes work http://hus.yksd.com/distanceedcourses/YKSDbiology/lessons/FourthQuarter/Chapter11/11-1/images/MendelExperiment.gif Mendel designed experiments using ____________ Pea plants in the __________ monastery garden _______ MALE part of flower makes Pollen ___________ (sperm) FEMALE __________ part of flower makes _______ egg cells http://www.cedarville.edu/academics/education/resource/schools/chca/2scideb/debwebpv.htm In pea plants, the pollen normally joins with an egg from the _______ same plant (=_______________ Self pollinating ) so seeds have “_________________” ONE parent http://hus.yksd.com/distanceedcourses/YKSDbiology/lessons/FourthQuarter/Chapter11/11-1/images/MendelExperiment.gif MENDEL’S PEA EXPERIMENTS Mendel started his experiments with peas that were _________________ true breeding = if allowed to _________________ self pollinate they would produce ____________________ offspring identical to themselves. http://hus.yksd.com/distanceedcourses/YKSDbiology/lessons/FourthQuarter/Chapter11/11-1/images/MendelExperiment.gif MENDEL’S PEA EXPERIMENTS removed pollen Mendel ____________________ making parts and ____________ added pollen from _______ another plant. This allowed him to _____________ cross-breed plants with ______________ different characteristics and study the results ________ http://hus.yksd.com/distanceedcourses/YKSDbiology/lessons/FourthQuarter/Chapter11/11-1/images/MendelExperiment.gif specific characteristic is A _____________________ trait called a ____________ Mendel ______________ studied 7 traits in peas. Pearson Education Inc,; Publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall MENDEL’S EXPERIMENTS P1 generation ____ (_________) parental F1 generation ____ filial (______= offspring) F2 generation ___ Principles of Dominance Section 11-1 P Generation Tall Go to Section: Short F1 Generation Tall Tall F2 Generation Tall Tall Tall Short Principles of Dominance Section 11-1 P Generation Tall Go to Section: Short F1 Generation Tall Tall F2 Generation Tall Tall Tall Short Principles of Dominance Section 11-1 P Generation Tall Go to Section: Short F1 Generation Tall Tall F2 Generation Tall Tall Tall Short crossed PURE PLANTS When Mendel ______________ with 2 ______________ traits: contrasting (EX: Tall crossed with short) He always found same pattern: 1. ONLY ______ ONE trait ____________ showed F1 in the ____ generation BUT . . . Missing trait ____________ returned in 2. ___________ F2 generation the ____ in a _________ 3:1 ratio PATTERNS ARE THE KEY Image modified from: http://www.laskerfoundation.org/rprimers/gnn/timeline/1866.html http://www.accessexcellence.org/AB/GG/mendel.html Mendel decided that there must be a __________________ that pair of FACTORS control ________each trait and that __________ one factor must be able to _______ HIDE the other. We now know that Mendel’s factors are genes carried on ________________ the pair of________________ homologous _________________ chromosomes http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/Crossover.gif ________ DIFFERENT gene CHOICES for a _______ trait are called ___________. ALLELES http://sps.k12.ar.us/massengale/genetics%20tutorial.htm DOMINANT __________________ = An allele HIDES the presence of that ________ another allele RECESSIVE __________________ = An allele that __________________ the is hidden by presence of another allele Why did the recessive trait disappear in the F1 generation and reappear in the F2? The pattern corresponds movement of to the ____________ chromosomes during ______________ MEIOSIS ____________________ Image modified from: http://www.laskerfoundation.org/rprimers/gnn/timeline/1866.html WHAT DOES MEIOSIS HAVE TO DO WITH IT? REMEMBER _____________ HOMOLOGOUS chromosomes SEPARATE ________________ during ANAPHASE I = _________________ SEGREGATION Image modified from: http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/Crossover.gif ____ F1 offspring __________ received an allele for tallness from their _______ TALL parent and an allele for shortness from their ________ SHORT parent. The F1 plants ALL ___________ LOOK TALL carryingan but are ___________ allele for _____________ shortness Images from: BIOLOGY by Miller & Levine; Prentice Hall Publishing ©2006 EXPLAINING the F1 CROSS SEGREGATION LAW OF ___________________ alleles are separated when the F1 plants ______________ made gametes When these gametes recombined to make the recessive F2 generation, the _____________ trait _______________ reappears in ¼ of the offspring Image from: BIOLOGY by Miller & Levine; Prentice Hall Publishing ©2006 Core High School Life Science Performance Descriptors High school students performing at the ADVANCED level: predict the function of a given structure; predict the outcome of changes in the cell cycle; INTRODUCTION TO BE ABLE TO DO LATER High school students performing at the PROFICIENT level: describe the relationship between structure and function compare and contrast the cell cycles in somatic and germ cells; INTRODUCTION TO BE ABLE TO DO LATER predict how traits are transmitted from parents to offspring explain how traits are transmitted from parents to offspring; High school students performing at the BASIC level recognize that different structures perform different functions describe the life cycle of somatic cells; INTRODUCTION TO BE ABLE TO DO LATER identify that genetic traits can be transmitted from parents to offspring;