* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
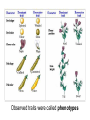
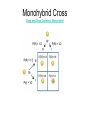
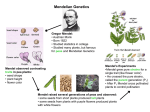
Genetics http://www.youtube.com/watch?fe ature=endscreen&NR=1&v=YxKF dQo10rE Gregor Johann Mendel • Austrian monk • How do mothers and fathers pass down traits to their children? • Mendel tested his idea of heredity on pea plants • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v =EvR_Sdm1orU • Pea plants is normally selfpollinating • Easy to control the parental crosses • Easily grown and matured quickly, producing many seeds • Allowed him to study many generations over a relatively short period of time • Showed several pairs of obvious, contrasting traits Observed traits were called phenotypes • After several years of self-pollinating the pea plants, Mendel established purebred plants • When self-pollinated, these plants always create plants that look like themselves • Mendel also cross bred the purebred plants that were different for only one contrasting pair of traits – The purebred parent plants were called the P generation – The offspring were called hybrids – First generation of hybrids – F1 generation – Second generation of hybrids – F2 generation Results? • The F1 generation hybrids had the same trait • The traits of tallness dominated the traits of dwarf-ness • Mendel called them the dominant traits • Trait that was not expressed = recessive trait • Mendel crossed his F1 generation plants to determine whether they were identical to the P generation plants • If they were, then F1 cross would produce only tall plants • F2 generation yielded 3 tall plants and 1 dwarf plant • Phenotypic ratio of F2 was 3:1 – Proportion of individuals in a generation that express a certain trait • The F1 hybrid were different from the purebred tall plants • The gene for plant height has two different forms (alleles): tall and dwarf – Tall = dominant – Dwarf = recessive • He suggested that each plant’s phenotype was determined by a PAIR of alleles that could be identical or different • The only way a plant to develop as a dwarf is if both its alleles are recessive Mendel’s Law of Segregation • Members of a pair of alleles for a given trait are segregated (separated) when gametes are formed • Once Mendel came up with the Law of Segregation, he was able to describe the gene makeup, or genotype • He used letters of the alphabet to represent the genes • The allele for dominant trait was represented by T • The allele for recessive trait was represented by t • Purebred tall plant = TT • Purebred dwarf plant = tt • Hybrid tall plant = Tt Homozygous Heterozygous Monohybrid Cross Drag-and-Drop Genetics: Monohybrid MONOHYBRID PROBLEMS • Problems dealing with one trait only ie. height or colour 1.Write the cross 2.Produce the gametes 3.Draw the Punnett square 4.List the phenotype and genotype ratios • 1. In dinosaurs, the gene for sharp teeth (S) is dominant over the gene for dull teeth (s). Cross a heterozygous sharp toothed dinosaur with a dulltoothed dinosaur to produce the F1 (first generation) offspring. • 2. Cross a homozygous sharp toothed dinosaur with a homozygous dull-toothed dinosaur to produce the F1 offspring. • 3. Now cross two of the F1 generation offspring from question #2 to produce the F2 offspring.