* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (Igf2) receptor (Igf2r)
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
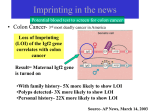
Final noon Thursday May 5 I will post answers for any remaining questions emailed to me by noon on Tuesday May 3 Imprinting results from pre-programmed differences in DNA methylation of selected genes in the sperm and egg Imprinted genes affect fetal growth Insulin growth factor 2 (Igf2) growth Insulin growth factor 2 receptor (Igf2r) growth What happens if dad’s copy of Igf2 is deleted? Insulin growth factor 2 (Igf2) growth Insulin growth factor 2 receptor (Igf2r) growth What happens if mom’s copy of Igf2 isn’t imprinted? Beckwith-Weidemann syndrome Insulin growth factor 2 (Igf2) Insulin growth factor 2 receptor (Igf2r) overgrowth growth What if mom’s copy of Igf2r is deleted? Insulin growth factor 2 (Igf2) overgrowth Insulin growth factor 2 receptor (Igf2r) growth T F A mouse that inherits a mutant maternal copy of Igf2 exhibits fetal undergrowth. T F A mouse that inherits a mutant Igf2r gene from its mother is born 40% smaller than normal. T F Maternal imprinting of the human Igf2r gene prevents fetal overgrowth. T F Maternal imprinting of the human Igf2 gene prevents fetal overgrowth. T F Mutations in the paternal copy of the mouse Igf2 gene cause mice to be born 40% smaller than normal. Experiment #2 Chromatin transferred from myoblasts can transform untreated fat cells. Transformation frequency suggests only one or few of the genes have this ability C3H/10T cells = fibroblast cells (make connective tissue, synthesize the extracellular matrix and collagen) If treated with azacytadine, C3H/10T cells can be induced to form muscle, fat and cartilage cells. Ultimately a single gene was identifiedmyoD -whose expression could convert any other cell type into muscle cells Getting the terminology down: C. elegans Vulva Early larval stage Anchor cell (AC) Figure 6.27 Gonad VPCs AC Basement membrane Gonad P3.p-P8.p are the Vulva Precursor Cells (VPCs) Later larval stage P5.p,P6.p and P7.p lineages make the vulva P3.p,P4.p and P8.p lineages non-vulval 3° 3° 2° 1° 2° P3.p P4.p P5.p P6.p P7.p 3° P8.p The Ras pathway is abnormally activated in many human tumors eg: pancreatic cancer, colorectal cancer, lung adenocarcinoma, gall bladder cancer, bile duct cancer and thyroid cancer Another representation of the RAS pathway (VPC cells) LIN-3 signal Inductive and lateral signals induce the vulva gonad Anchor cell VPCs VPCs after induction P8 3° 3° 2° 1° 2° 3° The primary and secondary cells form the vulva A signal from P6.p actives notch (lin-12) in P5.p and P7.p Figure 6.27 The transmembrane receptor is the Lin-12 protein, a receptor protein related to Notch “ Primary cell” “ Secondary cells” Both membrane and receptor are membrane bound! Generation of Different Cell Types From Equivalent Cells in C. elegans: Initial specification of the Anchor Cell also requires Notch The signal: lag-2 (delta) Figure 6.28 The receptor: lin-12 (notch) If anchor cell signaling is disrupted, all VPCs cells adopt a non-vulva fate anchor cell gonad 3° cell 3° cell 3° cell 3° cell no vulva 3° cell 3° cell