* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Announcements Pre‐lab Lecture Module 2: Design Overview Primer design for mutagenesis
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
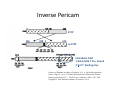
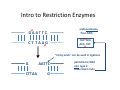
Announcements Pre‐lab Lecture Module 2: Design Overview Primer design for mutagenesis Intro to Restriction Enzymes Today in Lab: M2D1 Announcements • iGEM competition • Introducing… Xiaosai, your TA for Module 2 Inverse Pericam EYFP 145 238 1 144 cp EYFP calmodulin CaM Æbinds M13 if Ca2+ bound Æ4 Ca2+ binding sites Courtesy of National Academy of Sciences, U. S. A. Used with permission. Source: Nagai, T., et al. “Circularly Permuted Green Fluorescent Proteins Engineered to Sense Ca2+.” PNAS 98, no. 6 (March 6, 2001): 3197-3202. Copyright © 2001 National Academy of Sciences, U.S.A. Goal: Affect Binding Properties Designing Mutagenic Primers 5’ TCGAT / CTA AG T A TC / GAT Intro to Restriction Enzymes G A A T T C endonucleases Æcut DNA C T T A A G TGC GCA ACA CGT “sticky ends” can be used in ligations G AATTC CTTAA G palindromic DNA also type 2 leave blunt ends Today in Lab • Study inverse pericam at multiple levels • Design primers silent mutation – Amino acid change – Silent change make new, unique restriction site • For next time: begin reading two papers – Focus on Nagai; other one is for some history/context – Time in class on D2 to finish MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 20.109 Laboratory Fundamentals in Biological Engineering Spring 2010 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.