* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Notes for Chapter 4 and 5
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
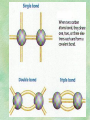
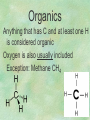
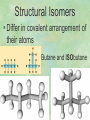
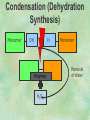
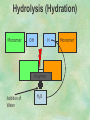
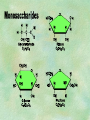
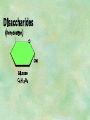
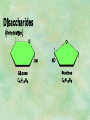
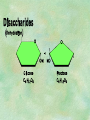
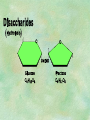
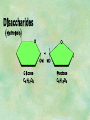
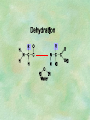
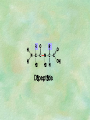
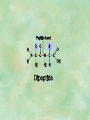
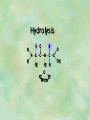
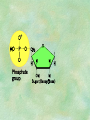
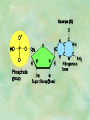
Organic Chemistry Chapters 4 and 5 Chemical Compounds in Living Things In varying combinations, the elements C, H, O, and N make up practically all the chemical compounds in living things C easily forms covalent bonds that are strong and stable. How many bonds can it make? 4 Organics Anything that has C and at least one H is considered organic Oxygen is also usually included Exception: Methane CH4 Hydrocarbons A molecule that just has a basic C skeleton with H filling all of the covalent binding sites is a hydrocarbon They store E Ex: gasoline Nonpolar Organic Variations Organics can vary by their shape Molecules made of the same number and type of atoms, but arranged in different ways, are called isomers (same-part) Three basic types Structural Geometric Enantiomers (Optical) Structural Isomers Differ in covalent arrangement of their atoms Butane and ISObutane Geometric Isomers Have identical covalent bonds, but differ in the order in which the atoms are arranged in space; usually around a double bond Enantiomers Mirror images of each other Because of their three-dimensional structure, they cannot be superimposed no matter how they are rotated Organic Variations Organics can vary by the “danglies” off of the C skeleton A change in placement or type of functional group can change the effect of the overall molecule Estradiol vs. Testosterone in vertebrates Functional groups Hydroxyl Carbonyl Carboxyl Amino Sulfhydryl Phosphate Hydroxyl Groups –OH Polar because electronegative oxygen attracts covalent e-s Makes the O-molecule water soluble Found in alcohols and sugars Can give the molecule an –ol ending Ethanol, Propanol Just because it has an –OH doesn’t mean that it’s an alcohol –OH covalent bonds usually to C OH ionic bonds usually to a metal Carbonyl Groups C double bonded to O Water soluble due to electronegative O An aldehyde if at end of a C chain A ketone if attached to an “interior” C Carboxyl Groups COOH C double bonded to O; single bonded to OH Highly polar; therefore water soluble Acts as a weak acid (releases H+) Found in amino acids and fatty acids Amino Groups N bonded to two H Weakly basic (accepts H+) Water soluble (polar molecule) Found in amino acids Sulfhydryl Groups –SH Also called thiols Similar to hydroxyls (water soluble); notice where S is on the periodic table Help form 2O and 3O protein structure (stabilizes internal protein structure at “disulfide bridges”) Found in amino acid cysteine Perms create disulfide bridges – makes hair curly and stinky Phosphate Groups –PO42 Weakly acidic; one or two H+ ions can be released Water soluble Found in ATP, other nucleotides, DNA, RNA, many proteins, and phospholipids Fig. 4.10 Page 64-65 Polymerization Large compounds are formed from strings of smaller compounds The small compounds are called MONOMERS When joined together, they are call POLYMERS We only have 26 letters in the alphabet, but we join those letters in long and short ways to make an infinite number of words Condensation (Dehydration Synthesis) Monomer OH H Polymer H 20 OH Monomer Removal of Water Hydrolysis (Hydration) Monomer OH H Polymer Addition of Water H 20 OH Monomer Carbohydrates Functions E storage (starch, glycogen) Structure/support (chitin, cellulose) Membrane receptors (glycoproteins) Monomers = monosaccharides Adding monomers creates di- and polysaccharides Lipids Functions E storage (fats, oils) Membranes (phospholipids) Triglycerides: glycerol and 3 fatty acids Saturated: all single bonds Unsaturated: some double bonds Glycerol + 3 Fatty acids Triglyceride + 3 Water Lipids Sterols 4 interconnecting C rings Vitamin D, cortisone, testosterone, estrogen, and cholesterol Cholesterol produced by liver during breakdown of saturated fats Excess cholesterol can accumulate in inner lining of blood vessels Avoid too much saturated fat Lipids Waxes Fatty acids combined with either alcohols or other hydrocarbons Usually hard Water-repellent, which helps to waterproof fur, feathers, and leaves Proteins Functions Transport (hemoglobin) Muscle action (myosin, actin) Blood clotting (thrombin, fibrin) Support (collagen, elastin) Immunity (antibodies) Rxn catalysis (enzymes) Monomers = amino acids Proteins Conformation: 3-D structure O 1 : sequence of amino acids O 2 : H-bonds between nonadjacent carboxyl and amino groups • Alpha helix • Beta-pleated sheets O 3 : disulfide and ionic bonds between R groups O 4 :H- and ionic bonds between separate polypeptides Nucleic Acids Functions Transfer of genetic information Monomers = nucleotides Nucleotides: Nitrogenous base 5-C sugar Phosphate group