* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slayt 1 - SCIS Teachers
Survey
Document related concepts
Sexually dimorphic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
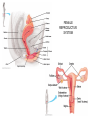
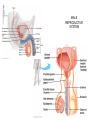
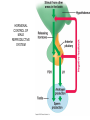
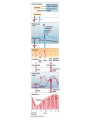
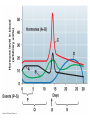
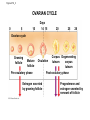
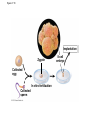
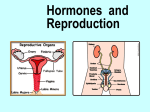
HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SL TOPIC 6.6 6.6 Reproduction • Draw and label diagrams of the adult male and female reproductive systems. • Outline the role of hormones in the menstrual cycle, including FSH (follicle stimulating hormone), LH (luteinizing hormone), estrogen and progesterone. • Annotate a graph showing hormone levels in the menstrual cycle, illustrating the relationship between changes in hormone levels and ovulation, menstruation and thickening of the endometrium. • List three roles of testosterone in males. • Outline the process of in vitro fertilization (IVF). • Discuss the ethical issues associated with IVF. FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM What are the organs of female reproductive system? Ovaries: produce egg cells and estrogen and progesterone Oviduct: transfer egg cell from ovaries to the uterus. Fertilization takes place in oviduct. Uterus: Embryo develops in the uterus. Cervix: entrance of uterus. It holds the fetus in the uterus during pregnancy. Vagina: entrance for sperm and exit for the fetus. MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM What are the organs of male reproductive system? • • • • Testes: to produce sperm and testosterone. Epididimis: sperms structures are completed here. Sperm duct: storage of sperms Glands (bulbourethral, prostate, seminal): to secrete nutritional fluid and anti acid fluid. • Penis: to deliver sperms to the females body. It has eractile spongy tissue which blood fills during erection. • Urethra: carries semen during ejaculation and urine during urination. HORMONAL CONTROL OF MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ROLES OF HORMONES • FSH: stimulates testes to produce sperm • LH: stimulates testes to produce testosterone • Testosterone: a. stimulates testes cells (leydig cells) for sperm production (meiosis) b. provides secondary sexual characteristics c. stimulates hypothalamus for the regulation of FSH and LH secretion and for reproductive behaviors (libido). d. initiates prenatal development of male genitelia MENSTRUAL CYCLE Monthly cycle of ovulation and menstruation in female. (28 days) It includes hormonal changes and structural changes in the uterus and ovaries. There are two cycles in the menstrual cycle. 1- Ovarian cycle: 2- Uterus cycle. Figure 27.6_3 OVARIAN CYCLE 0 10 5 Days 14 15 20 25 28 Ovarian cycle Growing follicle Mature follicle Ovulation Pre-ovulatory phase Estrogen secreted by growing follicle Corpus Degenerating corpus luteum luteum Post-ovulatory phase Progesterone and estrogen secreted by remnant of follicle Figure 27.6_4 0 5 10 Days 14 15 20 25 28 Peak causes LH surge Ovarian hormones in blood Estrogen Progesterone Low levels of estrogen trigger menstruation Progesterone and estrogen promote thickening of endometrium Figure 27.6_5 UTERUS CYCLE Menstrual cycle Endometrium 0 5 Menstruation 10 14 15 Days 20 25 28 FOLLICLE PHASE (10-12 DAYS) New cycle starts with a menstrual period. 1- FSH is secreted by the pituitary gland and stimulates development of a follicle (immature egg cell( in the ovary. 2- Developing follicle secretes estrogen which stimulates; a. uterus to increase thickness of the endometrium. b. pituitary gland ( reduces secretion of FSH, negative feedback control) 3- Estrogen level increases and leads to LH secretion. OVULATION PHASE • LH stimulates mature follicle and egg cell is released into oviduct. • LH also convert follicle to corpus luteum (yellow body) which secretes progesterone. CORPUS LUTEUM PHASE 1- Follicle cells secrete progesterone. 2- Progesterone; -stimulates endometrium to increase thickness (prepares it self for the implantation of embryo) -stimulate pituitary gland to inhibit secretion of FSH, and LH. 3- Low level of FSH and LH degenerate corpus luteum, so progesterone level decreases. 4- New cycle starts with menstrual period which endometrium tissue breaks down and is lost through the vagina. 3. IN VITRO FERTILIZATION • In vitro fertilization (IVF) is the most common assisted reproductive technology. Fertilization occurs in a culture dish and an early embryo is implanted in the uterus. Figure 27.18 Implantation Zygote Collected egg In vitro fertilization Collected sperm 8-cell embryo Figure 27.18_1 Sexual activity can transmit disease • Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) caused by bacteria can often be cured. • Chlamydia – is the most common bacterial STD, – often produces no symptoms, and – can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Sexual activity can transmit disease • Viral diseases – such as genital herpes and HIV, – can only be controlled. • The best way to avoid the spread of STDs is abstinence. • Latex condoms provide the best protection against disease transmission for “safer sex.” © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Table 27.7