* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download w/o Narration - Fulton County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
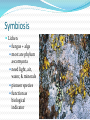
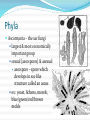
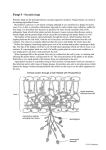
Unit 6 Lecture 4 Kingdom Fungi aka Kingdom Mycetae eukaryotes [domain Eukarya] unicellular or multicellular heterotrophic saphrophytic mutualistic parasitic Kingdom Fungi immobile sexual and asexual reproduction diverse in color, location, and shape/size Amillaria mushroom in Mi most similar in appearance to plants, but similar in DNA to animals Fungus Structure hypha(e) – thread-like strings of nuclei come from spores can be tiny to acres large feeding system [like plant roots] secrete enzymes to digest materials hyphae Fungus Structure hypha(e) – thread-like strings of nuclei can be partitioned with septa(e) septate / coenocytic mycelium – group of hyphae hyphae Fungus Structure hypha(e) – thread-like strings of nuclei haustorium – tip of parasitic fungi; penetrates host tissue to feed hyphae Fungus Structure chitin – makes up cell walls of fungi gives strength and flexibility hyphae Discuss What is the difference between the composition of plant cell walls vs that of fungal cell walls? What two functions can hyphae serve for a fungus? Fungus Structure pileus scales fruiting body – grows above the soil; produces spores in some types, this is the mushroom pileus – cap scales – make up cap hyphae pileus Fungus Structure lamellae fruiting body – grows above annulus the soil; produces spores lamella(e) – gill(s) stape annulus – ring stape - stem volva – cup volva hyphae scales Economic Importance medical applications food applications antibiotics bread enzymes wine other medicines cheese mushrooms yogurt Harm Though fungi can be extraordinarily beneficial to us and to the ecosystem [decomposers], they can also be harmful plant damage – “rusts” toxins in food diseases Discuss Name two beneficial uses for fungi. Name one harmful fungus for a human. Name the most economically important fungus. Symbiosis Lichen fungus + alga most are phylum ascomycota need light, air, water, & minerals pioneer species function as biological indicator Symbiosis Mycorrhizae fungus + plant most are phylum zygomycota hyphae grow through plant roots absorb minerals for plant, plant gives fungus organic sugars and amino acids may help with water retention Symbiosis wood-boring beetles other plants – orchids cannot germinate w/o fungus Discuss What is the symbiotic partner of a lichen? mycorrhiza? What does it mean that lichens function as “biological indicators”? What other organisms can also be “indicators”? Phyla phyla are grouped by the type of spores they create: zygomycota ascomycota basidiomycota deuteromycota Phyla Zygomycota sexual [zygospores] & asexual zygospore – thick-walled hearty spores which form sexually and last through harsh conditions coenocytic hyphae [no septa] most are decomposers [bread mold] Phyla Ascomycota – the sac fungi largest & most economically important group sexual [ascospores] & asexual ascospore – spore which develops in sac-like structure called an ascus ex: yeast, lichens, morels, blue/green/red/brown molds Phyla Basidiomycota – the club fungi most are saprobes/saphrophytes sexual [basidiospores] & asexual basidiospore – develop on gills of mushroom in club-shaped structures called basidia ex: mushrooms, puffballs, shelf-fungi [on trees], bird’s nest fungi, plant rusts Phyla Deuteromycota – the imperfect fungi asexual reproduction only useful in making food cheese, jams, anything “fruit-flavored” for citric acid ex: Penicillium spp., ringworm, blue stuff in bleu cheese Discuss How are fungal phyla separated? Which phylum reproduces… using zygospores? only asexually? using spores in sacs? using spores in club-shaped structures? Homework BDOL 20.1 and BDOL 20.2 worksheet