51 MORPHOLOGY AND GENERAL PROPERTIES OF FUNGI
... the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from plants, animals, protists and bacteria. One major difference is that fungal cells have cell walls that contain chitin, unlike the cell walls of plants and some protists, which contain cellulose, a ...
... the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from plants, animals, protists and bacteria. One major difference is that fungal cells have cell walls that contain chitin, unlike the cell walls of plants and some protists, which contain cellulose, a ...
Protists and Fungi
... which means “false foot,” is a temporary extension of cytoplasm and plasma membrane that helps protozoa move and feed. To form a pseudopod, the cell cytoplasm flows outward, forming a bulge. This bulge spreads, anchors itself to the surface it is on, and pulls the rest of the cell toward it. Pseudop ...
... which means “false foot,” is a temporary extension of cytoplasm and plasma membrane that helps protozoa move and feed. To form a pseudopod, the cell cytoplasm flows outward, forming a bulge. This bulge spreads, anchors itself to the surface it is on, and pulls the rest of the cell toward it. Pseudop ...
exam 2 review pdf - Iowa State University
... d. None of the above 9. Which phylum of fungi is responsible for many species of frogs going extinct? a. Phylum Chytridomycota b. Phylum Zygomycota c. Phylum Glomeromyta d. None of the above 10. Which phylum of fungi does not have much diversity due to only reproducing asexually? a. Phylum Basidomyc ...
... d. None of the above 9. Which phylum of fungi is responsible for many species of frogs going extinct? a. Phylum Chytridomycota b. Phylum Zygomycota c. Phylum Glomeromyta d. None of the above 10. Which phylum of fungi does not have much diversity due to only reproducing asexually? a. Phylum Basidomyc ...
24 | fungi - Net Texts
... the hyphae, where they process nutrients in the environment. Then, the smaller molecules produced by this external digestion are absorbed through the large surface area of the mycelium. As with animal cells, the polysaccharide of storage is glycogen, rather than starch, as found in plants. Fungi are ...
... the hyphae, where they process nutrients in the environment. Then, the smaller molecules produced by this external digestion are absorbed through the large surface area of the mycelium. As with animal cells, the polysaccharide of storage is glycogen, rather than starch, as found in plants. Fungi are ...
Fungi Diversity
... of living organisms collectively referred to as Eumycota, or true fungi. While scientists have identi ed about 100,000 species of fungi, this is only a fraction of the over 1 million species likely present on Earth. Edible mushrooms, yeasts, black mold, and Penicillium notatum (the producer of the a ...
... of living organisms collectively referred to as Eumycota, or true fungi. While scientists have identi ed about 100,000 species of fungi, this is only a fraction of the over 1 million species likely present on Earth. Edible mushrooms, yeasts, black mold, and Penicillium notatum (the producer of the a ...
Teacher`s Guide
... w h i ch are not identified ye t . U n l i ke bacteri a , whose cells are without nu cl e i , fungus cells have at least one nu cleus.The tubular-shaped cells of fungi join together to form long, h o l l ow strands called hy p h a e , w h i ch make up most of the body, or mycelium, of each fungus.Th ...
... w h i ch are not identified ye t . U n l i ke bacteri a , whose cells are without nu cl e i , fungus cells have at least one nu cleus.The tubular-shaped cells of fungi join together to form long, h o l l ow strands called hy p h a e , w h i ch make up most of the body, or mycelium, of each fungus.Th ...
fungi - Stjosephcs.org
... – Some parasitic fungi are actually human pathogens causing athlete's foot and ringworm – Some parasitic fungi are plant pathogens that destroy crops ...
... – Some parasitic fungi are actually human pathogens causing athlete's foot and ringworm – Some parasitic fungi are plant pathogens that destroy crops ...
FUNGI
... – Some parasitic fungi are actually human pathogens causing athlete's foot and ringworm – Some parasitic fungi are plant pathogens that destroy crops ...
... – Some parasitic fungi are actually human pathogens causing athlete's foot and ringworm – Some parasitic fungi are plant pathogens that destroy crops ...
Kingdom Fungi
... 2. Parasitic fungi: absorb nutrients from living cells. 3. Mutualistic fungi: live in a close relationship with another species (such as a plant or algae) ...
... 2. Parasitic fungi: absorb nutrients from living cells. 3. Mutualistic fungi: live in a close relationship with another species (such as a plant or algae) ...
Mammalian Characteristics
... Until recently, systematists thought that fungi lost flagella only once in their history, after chytrids had diverged from other lineages. However, molecular data now indicates that some flagellated fungi are more closely related to another fungal group, the zygomycetes. If this is true, flagella we ...
... Until recently, systematists thought that fungi lost flagella only once in their history, after chytrids had diverged from other lineages. However, molecular data now indicates that some flagellated fungi are more closely related to another fungal group, the zygomycetes. If this is true, flagella we ...
CHAPTER 31
... Fusion of two different mating types is followed by plasmogamy, resulting in the formation of dikaryotic cells, each with two haploid nuclei representing the two parents. The cells at the tips of these dikaryotic hyphae develop into many asci. Within each ascus, karyogamy combines the two parental g ...
... Fusion of two different mating types is followed by plasmogamy, resulting in the formation of dikaryotic cells, each with two haploid nuclei representing the two parents. The cells at the tips of these dikaryotic hyphae develop into many asci. Within each ascus, karyogamy combines the two parental g ...
Lab 1
... Plant Mitosis Models skip Onion Root Tip Slide 1. Identify a cell in anaphase on a slide under a microscope and put the pointer on it. Call me over to check it and ask for my initials here: ________ Summary of Mitosis: Read about Cytokinesis on the next page (p. 70), before filling in the chart. sig ...
... Plant Mitosis Models skip Onion Root Tip Slide 1. Identify a cell in anaphase on a slide under a microscope and put the pointer on it. Call me over to check it and ask for my initials here: ________ Summary of Mitosis: Read about Cytokinesis on the next page (p. 70), before filling in the chart. sig ...
FUNGI “Plants without chlorphyll”
... Reproduction of Fungi • Fungi reproduce by releasing large numbers of microscopic spores. • Spores are haploid single cells with thick cell walls that function as the dispersal stage in the reproduction of fungi. • These tough reproductive cells are spread by the wind and can withstand unfavor ...
... Reproduction of Fungi • Fungi reproduce by releasing large numbers of microscopic spores. • Spores are haploid single cells with thick cell walls that function as the dispersal stage in the reproduction of fungi. • These tough reproductive cells are spread by the wind and can withstand unfavor ...
Kingdom Fungi
... • Many Ascomycetes produce asexual spores called conidia. • Some reproduce sexually by forming specialized structures that contain male and female nuclei. • Yeasts are the only unicellular Ascomycete. They do NOT have hyphae or fruiting bodies. They reproduce asexually by budding. ...
... • Many Ascomycetes produce asexual spores called conidia. • Some reproduce sexually by forming specialized structures that contain male and female nuclei. • Yeasts are the only unicellular Ascomycete. They do NOT have hyphae or fruiting bodies. They reproduce asexually by budding. ...
The Kingdom Fungi
... many hyphae tangled together into a thick mass called a mycelium. The mycelium is well suited to absorb food. The fruiting body is a reproductive structure that develops from a mycelium that grows below the surface of the ground. ...
... many hyphae tangled together into a thick mass called a mycelium. The mycelium is well suited to absorb food. The fruiting body is a reproductive structure that develops from a mycelium that grows below the surface of the ground. ...
Chapter 12: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa, and Parasites
... Reproduction: Conidiospores not enclosed in a sac. Become airborne easily. Form chains (broom(broom-like ...
... Reproduction: Conidiospores not enclosed in a sac. Become airborne easily. Form chains (broom(broom-like ...
fungi - Mr. Wells` wikispace
... – Reproduce asexually AND sexually • Sexually if an opposite mating type makes contact… ...
... – Reproduce asexually AND sexually • Sexually if an opposite mating type makes contact… ...
The Kingdom Fungi
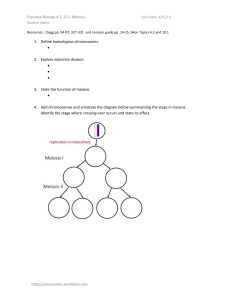
... Details of sexual reproduction vary in different groups of fungi but fusion of haploid nuclei and meiosis are common to all. When fungi reproduce sexually, hyphae of two genetically different but compatible mating types come together, their cytoplasm fuse followed by nuclear fusion. In two of the th ...
... Details of sexual reproduction vary in different groups of fungi but fusion of haploid nuclei and meiosis are common to all. When fungi reproduce sexually, hyphae of two genetically different but compatible mating types come together, their cytoplasm fuse followed by nuclear fusion. In two of the th ...
Lecture 13: The Fungus Among Us I. What are they? A. Fungi are
... A. Fungi are a diverse and vital group of organisms, crucial to life on earth. B. The next time you eat a mushroom pizza, give a little thanks to the guys on top. And remember, mycology is better than yours! ...
... A. Fungi are a diverse and vital group of organisms, crucial to life on earth. B. The next time you eat a mushroom pizza, give a little thanks to the guys on top. And remember, mycology is better than yours! ...
Blog resource: http://tinyurl
... 14. A diploid cell carries genes A and B. There are dominant and recessive alleles for these genes. The cell is heterozygous for both genes. a. What combination of gametes could be produced if there was no crossing over? AB or ____ ...
... 14. A diploid cell carries genes A and B. There are dominant and recessive alleles for these genes. The cell is heterozygous for both genes. a. What combination of gametes could be produced if there was no crossing over? AB or ____ ...
PPT PowerPoint Presentation – I. Introduction to class
... Dimorphism in nonpathogenic fungi may depend on other factors: Carbon dioxide concentration. ...
... Dimorphism in nonpathogenic fungi may depend on other factors: Carbon dioxide concentration. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - I. Introduction to class
... Dimorphism in nonpathogenic fungi may depend on other factors: Carbon dioxide concentration. ...
... Dimorphism in nonpathogenic fungi may depend on other factors: Carbon dioxide concentration. ...
Mating in fungi

Mating in fungi is a complex process governed by mating types. Research on fungal mating has focused on several model species with different behaviour. Not all fungi reproduce sexually and many that do are isogamous; the terms ""male"" and ""female"" do not apply to many members of the fungal kingdom. Homothallic species are able to mate with themselves, while in heterothallic species only isolates of opposite mating types can mate.Mating between isogamous fungi may consist only of a transfer of nuclei from one cell to another. Vegetative incompatibility within species often prevent a fungal isolate from mating with another isolate. Isolates of the same incompatibility group do not mate or mating does not lead to successful offspring. High variation has been reported including same chemotype mating, sporophyte to gametophyte mating and biparental transfer of mitochondria.