* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download food and flora
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
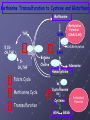
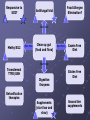
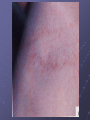
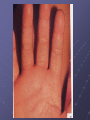
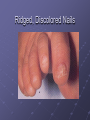
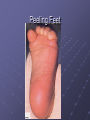
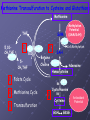
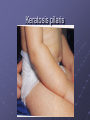
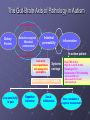
BIOMEDICAL INTERVENTIONS FROM A TO ZINC Thursday, May 21, 2009 Chicago, IL Nancy O’Hara, M.D., M.P.H. 150 Danbury Road Wilton, CT 06897 www.drohara.com Follow those who seek the truth but flee from those who have found it. Yaclav Havel Where To Begin One Child Patterns PATTERNS Genetic Predisposition Family History-autoimmune, gastrointestinal (Valicenti-McDermott et al, 2006) Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Increased Susceptibility (Herbert, 2005) Neurologic Problems Altered Sensitivity Abnormal Processing Immune System Dysregulation Altered Sensitivity (decreased IgA, NK cells, increased TNF) (Jyonuchi et al, 2005) Abnormal Processing (autoantibodies, TH1 & TH2 skewing) (Ashwood et al, 2006) PATTERNS Digestive Abnormalities Maldigestion (altered enzyme function) (Horvath et al, 1999) Dysbiosis (change in bowel flora) Increased Permeability (antigens, peptides, toxins) (Vojdani et al, 2004) Inflammation (enterocolitis, LNH, pro-inflammatory cytokines) (Torrente et al, 2002) Biochemical Peculiarities Impaired detoxification Oxidative Stress (James et al, 2004) Mitochondrial defects (Filipek et al, 2003 SOME GUIDING PRINCIPLES WHAT DOES EACH CHILD NEED TO: GET GET RID OF WHAT CAN I AS A PARENT DO? Methionine Transsulfuration to Cysteine and Glutathione Methionine THF 5,10CH2THF MTHFR 1 SAM MS B12 2 BHMT 5CH3THF Betaine Choline 2 Methionine Cycle 3 Transsulfuration MTase Cell Methylation SAH SAHH Homocysteine 1 Folate Cycle B6 3 Methylation Potential (SAM/SAH) Adenosine CBS Cystathionine B6 Cysteine GSH GSSG Antioxidant Potential WHAT DO WE NEED TO GIVE TO OR GET OUT OF OUR CHILDREN? Exercise/Activity Basic Nutritional Changes Fresh, unprocessed, unrefined, organic, whole foods Varied and rotational Non allergenic (crave that which most sensitive to) Protein (every 4-5 hours) Avoid excitotoxins (caffeine, MSG, dyes); phenolics (grapes, strawberries) Juicing; raw foods; fermented foods (kefir); good fats WHAT DO WE NEED TO GIVE TO OR GET OUT OF OUR CHILDREN? 3 R’S Remove: Sugars, junk food, germs, toxins GF/CF/SF/YF/SCD/LOD/BED/GAPS/LP Replenish: Probiotics, enzymes, EFAs, antiglutamates Repair/Restore: Detoxification Anti-inflammatories (LDN, Actos, Spironolactone, IG, HBOT) Responsive to SCD? Food Allergen Elimination? Antifungal trial I Start Here Methyl B12 Start Here Clean up gut (food and flora) Start Here Casein Free Diet Start Here Transdermal TTFD/GSH Digestive Enzymes Detoxification therapies Supplements (start low and slow) e Gluten Free Diet Second tier supplements REMOVE Foods Casein (sticky protein in dairy) 100% elimination for 3 weeks Gluten (protein in wheat, barley, rye, hidden sources) Tests can be inaccurate 100% elimination for 3 months Healthy alternative not just GFCF Food sensitivities (IgG reactive) Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) Restricts all disaccharides (2 sugars) and polysaccharides (starches) Not able to digest carbs due to mucosal damage→germ overgrowth feeds on unabsorbed sugars→enzyme destruction→further inhibition metabolism and microvilli damage Watch nut and nut flours REMOVE FOODS Gut and Psychology Syndrome (GAPS) Low Phenol (Feingold: faulty sulfation) Apples, grapes, bananas, salicylates, artificial ingredients Low Oxalate Diet (LOD) Leaky gut→oxalates not metabolized and absorbed→inflammation, pain Decrease leaves of plants; nuts; soy; berries Body Ecology Diet (BED) Proper food combining, low acid formation, easily digested foods Principles of anti-yeast diets including no sugars, fermented foods GERMS Bacteria (history of positive response to antibiotics) Strep (tics, OCD, tantrums, PANDAS) Daniel- 8 years old Sudden change in behavior Uncontrolled agitation OCD behavior Hyperactivity Recurrent sore throats Yeast? Taurine? Drugs? Strep (PANDAS) ASO Ab- 452 (nl < 200) DNase Ab – 960 (nl < 120) Swedo et al, 1998 TREATMENT-STREP Probiotics Xylitol Saccharomyces Boulardii/Alkalinization/Charcoal Antibiotics (Snider et al, 2004) IM Bicillin (1.2 million units-perhaps monthly) Penicillin, Omnicef, Zithromax Antimicrobial herbs Immune Modulators (March et al, 2004) Oral immunoglobulins Transfer factor/colostrum Mushroom extracts/plant sterols LDN, Actos, Spironolactone, HBOT IVIG REMOVE GERMS Bacteria (history of positive response to antibiotics) Strep (tics, OCD, tantrums, PANDAS) Clostridia (aggression, agitation, foul mucousy stools, diarrhea) TREATMENT FOR BACTERIA Probiotic/Prebiotic/Saccharomyces Antibiotics (Vancomycin, Metronidazole, Alinia) Homeopathic/Herbals/HBOT REMOVE GERMS Bacteria (history of positive response to antibiotics) Strep (tics, OCD, tantrums, PANDAS) Clostridia (aggression, agitation, foul mucousy stools, diarrhea) Parasites (have to treat; bizarre behavior, insatiable appetite, picking/biting/itching/grinding/smearing) Blastocystis hominis (treat with Bactrim and Humatin) Probiotics Antiparasitics (Metronidazole, Paromomycin, Mebendazole) Natural remedies (artemesia, pumpkin seeds, coconut) TSO therapy REMOVE Germs Bacteria Parasites Fungus (spacey, moody, crave sugar, frequent urination, inappropriate laughter) Diet-limit carbs, sugar Probiotics Herbals Medications Biofilm Yeast Free Diet Refined carbs (sugar) feed yeast (soda has 38 gm, grape juice has 57 gm of sugar) Condiments Leftovers or aging foods (aging cheeses) Juice (all commercial juices have started to age and ferment) Dried fruits or fruits too small to peel Specific Carbohydrate Diet Body Ecology Diet Herbal Remedies Garlic (1-2 fresh cloves or pills/day) Caprylic acid (500-1000 mg with meals) Oregano oil (0.2 ml 2x/day) Grapefruit or citrus seed extract (1/3 adult dose) Saccharomyces boulardii (3-6 capsules/day) Saccharomyces Boulardii Yeast against yeast Like swallowing the pharmaceutical company Promotes good flora Potential for very severe die-off Theoretically increases secretory IgA Is indistinguishable in lab from S.cerevisae Czerucka et al, 2002 The Antifungal Parade Non-absorbable S.boulardii: 3 months (at least 3-6/day) Nystatin: 1,000,000 units 4X day Amphotericin B (oral) Systemic Sporanox (Itraconazole) Diflucan (Fluconazole) Lamisil (Terbinafine) Nizoral (Ketaconazole) Die-off Occurs when yeast dies, releasing toxins. Antidote: activated charcoal up to 6X per day. Also treats the acidosis accompanying stress/illness: Alka Seltzer Gold, one tablet in water several times daily. GEORGE 3 year old with ASD Constipation/Hard stools Craved sweets Red cheeks/ears No interaction with peers 9 courses of antibiotics for chronic OM Mood swings/sensitivities Breath smelled of bread Rashes/toe peeling/nail ridges Ridged, Discolored Nails Peeling Feet GEORGE TREATMENT Elevated yeast metabolites on urine organic acid test Fluconazole, Terbinafine, Ketaconazole Better communication, engagement, social interaction Specific Carbohydrate Diet – “normal” Saccharomyces, probiotic, trisalts, CLO “Misdiagnosed” according to neurologist REMOVE Germs Bacteria Parasites Fungus Virus (regression after live viral vaccines, viral infection, fatigue, cold sores, warts, visual issues) Antiviral agents (vitamin A, olive leaf extract, monolaurin) Antiviral medications (valacyclovir, acyclovir, famvir) Immune modulators/support Toxins Detoxification (glutathione, ammonia) Chelation (DMSA, DMPS, EDTA) Homeopathy REPLENISH GLUTATHIONE! (oral, inhaled, transdermal, IV) Enzymes (speeds disassembly of foods; -ase) Mixed (helps kids with poor digestion) Plant based (papaya and pineapple) Peptidase specific (helps specific peptide digestion) Probiotics (between meals with room temperature water) Reflorestation is tough Essential when treating dysbiosis Miraglia del Giudice et al, 2004 Symptomatic (yeast die off) Activated charcoal (mop up toxins) Alka Seltzer Gold (alkaline) REPLENISH Enzymes Probiotics Symptomatic AntiGlutamates Pycnogenol (Trebaticka et al, 2006) Chamomile Taurine, GABA Treat High Ammonia Charcoal Fiber/Pectin Yucca Nutrients (MVI) (Carlton et al, 2000) Methionine Transsulfuration to Cysteine and Glutathione Methionine THF 5,10CH2THF MTHFR 1 SAM MS B12 2 BHMT 5CH3THF Betaine Choline 2 Methionine Cycle 3 Transsulfuration MTase Cell Methylation SAH SAHH Homocysteine 1 Folate Cycle B6 3 Methylation Potential (SAM/SAH) Adenosine CBS Cystathionine B6 Cysteine GSH GSSG Antioxidant Potential NUTRIENTS Zinc (Sturniolo et al, 2001) > 200 enzymatic functions; in energy metabolism, protein, immunity, detox Acne, mouth sores, spots/lines on nails, pica, loss of smell, taste Deficiency causes language, attention and immune issues Best given alone, at night (piccolinate, acetate) Ratio with copper; taste test Magnesium (Martineau et al, 1985) > 300 enzymatic functions; neuromuscular, neurotransmitters, BP Deficiency causes hyperactivity, anxiety, twitches, insomnia Sighing/salt craving/constipation Calcium Bone/tooth/muscle/nerve function; cell membrane permeability Deficiency causes rigidity, poor sleep, anxiety, teeth grinding Secondary deficiency Absorption vs taste Nutrients Continued Molybdenum With deficiency – poor detoxification, chemical sensitivity With excess – high uric acid, low copper, anemia Selenium Important for redox reactions, antioxidant With deficiency – immune dysfunction, cell fragility With excess – fatigue, brittle hair/nails, parasthesias Chromium Important for glucose control, insulin/liver function With deficiency – insulin resistance, Syndrome X, neuropathy Iron Important for oxygen transport, cell differentiation With deficiency – anemia, malabsorption, fatigue With excess – liver and free radical damage Nutrients - Vitamins Vitamin A (retinol) Immunity, vision, cell differentiation, anti-CA With deficiency – vision, immune dysfunction Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) Antioxidant, healing, neurotransmitter function With deficiency – bruising, poor immune function, anxiety, depression (diarrhea with excess) Vitamin D Ca absorption, thyroid function, anti-inflammatory With deficiency – scaling, muscle pain, restlessness, sweating Vitamin E Antioxidant, prevents lipid peroxidation With deficiency – jaundice, xs clotting, impaired reflexes Folic acid (folinic, 5- THF) Methioneine/aa metabolism, growth/brain development With deficiency – fatigue, weakness, immune/cognitive dysfunction NUTRIENTS - B VITAMINS B12 (cobalamin – cyano, methyl, adenosyl) Deficiency - decreased communication, anemia, memory loss, poor balance Methyl B12- SQ, IN, TD, oral; need adequate folate B1 (thiamine- deficiency can cause ataxia, enuresis, sensory loss) B2 (riboflavin- deficiency can cause mouth fissures, photophobia) B3 (niacin- deficiency can cause dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia) B5 (pantothenic acid- deficiency can cause toe walking, grinding, restlessness, insomnia) B6 (P5P- deficiency can cause immune dysfunction, anemia, sensory issues, tantrums) B15 (DMG/TMG) Deficiency leads to poor communication Give with folate to decrease hyperactivity Keratosis pilaris NUTRIENTS - OTHER EFAs (Richardson et al, 2006) Deficiency can cause keratosis pilaris, dry, coarse hair Cell communication Protection in bone, liver, lung, immune function Amino Acids Taurine GABA AKG Phosphatidylcholine-counteracts oxidative stress, replenish glutathione Carnitine/CoQ10/Biotin Spironolactone/Aldactone-anti-inflammatory, ↓ testosterone Oxytocin ↓ anxiety/aggression; acts at amygdala Melatonin (Reichenberg et al, 2001) Regulates serotonin balance The Gut-Brain Axis of Pathology in Autism Opioid peptides excess Defective enzyme/ Microbial environment Dietary Protein Intestinal permeability In autism patient Opioid peptides excess Low active tissue peptidases with antagonism endorphins Systemic carriage Opioid receptors in brain Low sensitivity to pain Repetitive behaviour Inflammation Social deficiencies • High TNF-α titre • High IL-1 and IL-6 titre • Skewing to Th2 • Depression of Th1 immunity - Decreased NK cell - Decreased Th1 CD cell - Decreased Ig A Some retardation in Cognitive development Putting It All Together Diet Baseline Nutrients MVI Probiotics EFAs Enzymes Look At Your Child Treat underlying dysbiosis Treat underlying oxidative stress Treat inflammation Detoxification What Is It That My Child Needs: To Get To Get Rid Of Keep an open mind Not a label Find clues and clusters Keep Your Faith in All Beautiful Things: In the sun when it is hidden, in the spring when it is gone.