* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzyme Notes Activation Energy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
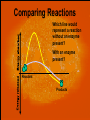
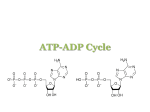
ENZYMES and Activation Energy What is Energy? • Energy is the ability to cause matter to move or change. • All life processes are driven by energy • Where does all energy come from? Chemical Reactions • Occurs when bonds are broken and reformed to make different substances. EX: Reactants Products CO2+H20 H2CO3 What is Metabolism? • Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in your body - Metabolism is basically two components 1. 2. Breaking down foods for energy Building new compounds to make you • Literally, you are what you eat! What is needed to start a reaction? reactant Products What is a Catalyst? • A catalyst is anything that lowers activation energy There are basically two kinds: 1. Organic 2. Inorganic • Organic catalysts are called Enzymes Why is the activation energy lower? reactant Products Comparing Reactions Which line would represent a reaction without an enzyme present? With an enzyme present? Reactant Products How Do Enzymes Work? • Enzymes work like a lock and key. • Specific enzymes work with specific substrates. enzyme substrate How Do Enzymes Work? • Each substrate fits into the enzyme’s active site. • Then the enzyme controls chemical reaction. Enzymes can be affected by: • Temperature: Battery Acid • pH: 0 Blood (7.5) 3 5 7 Neutral • Concentration: 9 Bleach 11 13 All Cells Need Energy •Cells need energy to do a variety of work: Making new molecules. Building membranes and organelles. Moving molecules in and out of the cell. Movement. Where Does A Cell Get Energy? • Food is broken down to a form the cell can use. • Extra energy is stored in an ATP molecule, a nucleotide. What Is ATP? • ATP – adenosine triphosphate is a molecule made up of an adenine, ribose, and 3 phosphate groups. Adenine Ribose How Does ATP Work? • Energy is stored in the bond between the second and third phosphate group. • When the bond is broken, energy is released and ADP is formed. Adenine Ribose ATP – Energy Currency • Within a cell, formation of ATP from ADP and phosphate occurs over and over, storing energy each time. • As the cell uses energy, ATP breaks down repeatedly to release energy and form ADP and phosphate. ATP stores Energy • ATP is the special carrier molecule that stores energy available for cell use. energy P ATP ADP energy P • ATP is the energy currency of the cell; the energy source for all cell functions. Making Energy • Cells make energy in two ways: –Photosynthesis – takes place in the chloroplasts. –Respiration – takes place in the mitochondria.