* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MUTATIONS
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
E. coli long-term evolution experiment wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
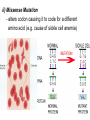
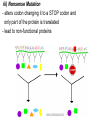
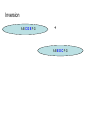
Mutations MUTATIONS Cells have evolved mechanisms to avoid errors during DNA replication. Strands are “proofread” to ensure accuracy and correct any mistakes. Still, changes in the genetic message (nucleotide sequence of DNA) can occur. Mutations can arise spontaneously or as a result of exposure to mutagens. Types of Mutations 2 Categories : point mutations and chromosomal POINT MUTATIONS – mutations at a specific base pair. Include: i) Silent Mutation - has no effect due to occurring in introns of DNA or redundant nature of genetic code (e.g. GAA and GAG both code for glutamic acid) DNA: CCCATTCTT mRNA: GGGUAAGAA if CCCATTCTC GGGUAAGAG ii) Missense Mutation - alters codon causing it to code for a different amino acid (e.g. cause of sickle cell anemia) iii) Nonsense Mutation - alters codon changing it to a STOP codon and only part of the protein is translated - lead to non-functional proteins iv) Base-pair Insertion/Deletions - when one or more nucleotide pairs are either inserted or deleted from a gene - have a greater effect on proteins than substitutions - can cause frameshift mutations: occurs when number of nucleotides inserted/deleted is not 3 or a multiple of 3 - causes nucleotides to be improperly grouped into codons producing non-functional proteins (unless at end of gene) HEY MAN HOW ARE YOU BRO Compare to: HEY MAN HWA REY OUB RO_ HEY MAN HOQ WAR EYO UBR O__ Chromosomal Mutations: - involve large segments of DNA Duplication Translocation Inversion ABCDEFG ABEDCFG •