* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL BIOLOGY TECHNIQUES
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
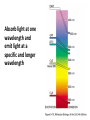
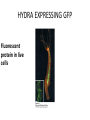
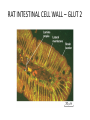
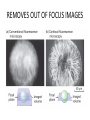
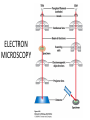
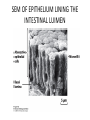
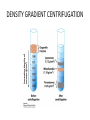
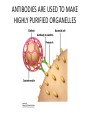
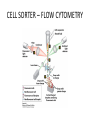
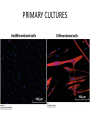
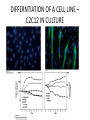
CELL BIOLOGY TECHNIQUES Visualize cells - Microscopy Organelles – Fractionation of subcellular components Culturing cells Light Microscopy Light Microscopy • Resolution of 0.2µm • Magnification – objective and projection lens • Resolution – D = 0.61λ/N sin α Resolution is improved by using shorter wavelengths or increasing either N or α. BRIGHT FIELD PATH MICROSCOPY Visualize unstained living cells • Phase Contrast microscopy – Thin layers of cells but not thick tissues • Differential Interference contrast – Suited for extremely small details and thick objects – Thin optical section through the object Microscopy of Live cells Fluorescence Microscopy • Major Function: Localization of specific cellular molecules – example proteins • Major Advantages: – Sensitivity:“glow” against dark background – Specificity: immunofluorescence – Cells may be fixed or living • Fluorescent dyes or proteins (Flurochromes) – flurochromes may be indirectly or directly associated with the cellular molecule – Multiple flurochromes may be used simultaneously Absorb light at one wavelength and emit light at a specific and longer wavelength HYDRA EXPRESSING GFP Fluorescent protein in live cells FIX EMBED SECTION STAIN Immunofluorescence Microscopy and Specific Proteins • Fluorescently tagged primary anti body • Fluorescently tagged secondary antibody • Fluorescently labelled antibody to tagged proteins such as myc or FLAG RAT INTESTINAL CELL WALL – GLUT 2 CONFOCAL AND DECONVOLUTION MICROSCOPY • This overcomes the limitations of Fluorescence microscopy – Blurrred images – Thick specimens REMOVES OUT OF FOCUS IMAGES EXAMPLE OF IMAGE RECONSTRUCTED AFTER DECONVOLUTION MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY • Transmission EM – theoretically 0.005 nm; practically 0.1 nm –1 nm (2000x better than LM) – High – velocity electron beam passes through the sample – 50-100 nm thick sections – 2-D sectional image – surface details are revelaed – Subcellular organelles • Scanning EM – Resolution about 10 nm – Secondary electrons released from the metal coated unsectioned specimen – 3-D surface image GOLD PARTICLES COATED WITH PROTEIN A ARE USED TO DETECT ANTIBODY BOUND TO PROTEIN TEM IMAGE CRYOELECTRON MICROSCOPY • HYDRATED, UNFIXED AND UNSTAINED SAMPLES • SAMPLES ARE OBSERVED IN ITS NATIVE HYDRATED STATE • METHOD - AN AQUEOUS SUSPENSION OF SAMPLE IS APLLIED ON A GRID AND HELP B Y A SPECIAL MOUNT • 5 nm RESOLUTION SURFACE DETAILS BY METAL SHADOWING SEM OF EPITHELIUM LINING THE INTESTINAL LUIMEN PURIFICATION OF CELL ORGANELLES • CELL DISRUPTION • SEPARATION OF DIFFERENT ORGANELLES USING CENTRIFUGATION • PREPARATION OF PURIFIED ORGANELLES USING SPECIFIC ANTIBODIES BREAKING OPEN PLASMA MEMBRANES IN CELLS • • • • CELLS ARE SUSPENDED IN ISOTONIC SUCROSE SONICATION HOMOGENIZATION CELLS IN HYPOTONIC SOLUTION – RUPTURE OF CELL MEMBRANES SEPERATING ORGANELLES • DIFFERENTIAL CENTRIFUGATION • DENSITY GRADIENT CENTRIFUGATION DENSITY GRADIENT CENTRIFUGATION ANTIBODIES ARE USED TO MAKE HIGHLY PURIFIED ORGANELLES CELL SORTER – FLOW CYTOMETRY CELL CULTURE REQUIREMENTS • SOLID MEDIA – Specially coated plastic dishes or flasks (CAMs’) – Agar as the medium GROWTH MEDIA Rich in nutrients- amino acids, vitamins, salts fatty acids, glucose, serum provides the different growth factors, TYPES OF CULTURED CELLS • PRIMARY CELL CULTURES – DIFFERENTIATE IN CELL CULTURE • CELL STRAIN – ALSO HAVE A FINITE LIFE SPAN (FROM A PRIMARY CULTURE) • CELL LINE - INDEFINITE LIFE SPAN PRIMARY CULTURES STAGES IN CELL CULTURE DIFFERNTIATION OF A CELL LINE – C2C12 IN CULTURE HOMEWORK-1 • CHAPTER 9 – REVIEW CONCEPTS QUESTIONS -2,5,7,9 – ANALYZE THE DATA DUE NEXT WEEK IN THE WORKSHOPS