* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Metabolism of the whole organism
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
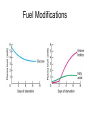
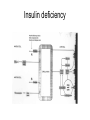
Metabolism of the whole organism • • • • • • • Metabolic profiles of organs Metabolic conditions Blood glucose levels: 90 mg/dL Fuel reserves glucose triacylglycerols proteins Metabolic homeostasis Metabolic profiles Brain • Nervous system: maintain membrane potentials • uses glucose (120g/day) • 60% of all glucose • blood levels of 84.7 = 1mM in brain • starvation use ketone bodies • Heart : uses fatty acids or ketone bodies Muscle • contraction • store glycogen • resting use fatty acid oxidation • active use glucose • starvation muscle broken down to alanine for gluconeogenesis Adipose Tissue • uses fatty acids for energy • exports fatty acids • glycerol exported out to the liver Liver & Kidney • Liver: provides fuel to other organs • gluconeogenesis, maintain blood glucose • store glycogen • export ketone bodies • uses keto acids for fuel • Kidney: needs energy for active transport • uses FA, KB, glucose, amino acids, • gluneogenic tissue Metabolic conditions • Controlled by hormones • insulin • glucagon • epinephrine • Normal regulation of blood glucose Insulin secretion Hormonal control Hormones Exercise • fuels during different levels of exercise • ATP production Starvation/Fasting • • • • Fuel mobilization after 3 day changes long term shifts hormonal changes Starvation profiles Fuel Modifications Liver modifications Diabetes • types of diabetes • changes in fuels • problems Insulin deficiency