* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch3 - Cycles in Nature
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
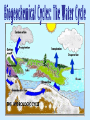
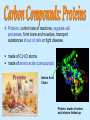
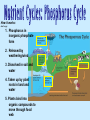
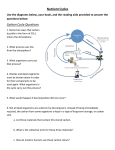
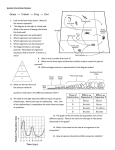
(Nutrients) Ecosystems need nutrients and energy Nutrients are Organisms transform nutrients Energy flows “Circle of Life” Organisms Matter (Nutrients) Environment How do we know energy is flowing? Why is this cycle important? If something removed? Water molecules enter atmosphere as water vapor (gas) by: Evaporation-water changes to water vapor Transpiration-evaporation from the leaves of plants Don’t copy How it works: 1. Sun heats up the atmosphere, water rises up and cools 2. Water vapor condense to form droplets then clouds 3. Water droplets get bigger and return to Earth as precipitation (rain, snow, sleet or hail) 4. Precipitation runs on land to river or stream that carries the runoff back to ocean or lake Nutrient Cycles Nutrients- organisms building blocks or chemical needed to help grow/carry out essential life functions 3 nutrient cycles: Carbon Nitrogen Phosphorus Carbon Cycle: Carbon is the key ingredient in all living organisms Don’t copy Carbon found: In atmosphere: CO2 gas In oceans: dissolved CO2 On Land: in organisms, rocks, soil Underground: coal, petroleum, Calcium Carbonate Don’t copy next slides, review 4 groups of organic compounds found in living things: 1. Carbohydrates: Living things use carbs as main source of energy. Sugar and starch molecules made of H and O animals- use in liver and muscles plants-for food and cellulose 2. Lipids: can be used to store energy. Makes biological membranes of cells and waterproof coverings. fats, oils, waxes made of C and H atoms Cell Membrane 3. Nucleic Acids: store and transmit hereditary information 2 kinds (RNA, DNA) made of H,O,N,C,P atoms RNA strand 4. Proteins: control rate of reactions, regulate cell processes, form bone and muscles, transport substances in/out of cells or fight disease. made of C,H,O atoms made of amino acids (compounds) Amino Acid Chain Protein: made of amino acid chains folded up CO2 released into the atmosphere by: volcanic activity respiration- when consumers exhale burning of fossil fuels decomposition of organic matter don’t copy Terrestrial plants-remove CO2 from the atmosphere Aquatic plants- remove CO2 from the water Producers-convert CO2 into Carbs (Glucose) “food” Consumers-carry out cellular respiration breaking down glucose into CO2 Nitrogen Cycle: Organisms need nitrogen to make amino acids and build proteins Nitrogen Gas (N2) is 78% of the Earth’s atmosphere Can’t be absorbed directly Cacteria convert N2 into compounds for use: Nitrogen Fixation- bacteria living in soil, water or roots of plants (legumes/bean plants) convert N2 into ammonia Nitrification- 2-step process NH3 -> NO2 -> NO3 Don’t copy 1.NH3 Ammonia in soil is converted by bacteria to Nitrite ions (NO2) but is toxic to plants 2. Then it is converted to Nitrate ions (NO3) which is taken up by plants 3. Plants eaten by consumers and reuse N to make proteins 4. Decomposers break down dead and return ammonia (NH3) to the soil copy Denitrification- other bacteria convert nitrates into N2 (gas) to be released into the atmosphere again Phosphorus Cycle: Phosphorus is nutrient for plants and animals which forms DNA and RNA Does not enter atmosphere like C,N,O Found in land, rock, soil and ocean sediments How it works: don’t copy 1. Phosphorus in inorganic phosphate form 2. Released by weathering/wind 3. Dissolved in soil and water 4. Taken up by plant roots in land and water 5. Plants bind into organic compounds to move through food web *Limiting factor for plants Limiting nutrient- when an ecosystem is limited by a single nutrient that is scarce of cycles slowly Consumers get phosphorus by eating producers/animals Animal wastes and decay of dead organisms return phosphorus to soil and water Guano- manure of fish eating birds