* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Compounds
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
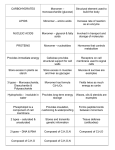
Organic Compounds Organic molecules are a class of molecules which contain CARBON. Organic molecules are composed of C, H, O, N, P, and S. They are large molecules known as MACROMOLECULES. The macromolecules are composed of submits called MONOMERS. A POLYMER is composed of many monomers. Each macromolecule has a carbon skeleton . This hydrocarbon chain may be : 1. Straight chain 2. Branched 3. Ringed The carbon skeleton has functional groups in the structure. These are clusters of atoms that behave in a particular manner regardless of how the rest of the molecule looks. Examples: COOH is a carboxyl PO4 a phosphate OH is an alcohol NH2 is an amino C=O is a sugar 4 CLASSES OF IMPORTANT BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES • CARBOHYDRATE • LIPIDS • PROTEINS • NUCLEIC ACIDS CARBOHYDRATES • Monomer is monosaccharide • Function is for energy storage or structural • Monosaccharides are the simplest sugars • They contain C, H and O in a 1:2:1 ratio and may be represented by the general formula CH2O • They usually have 5 or 6 carbons Monomer is monosaccharide Monomer is monosaccharide Formation of complex CARBOHYDRATES • POLYSACCHARIDES form by condensation reaction • GLYCOGEN(animals) and STARCH(plants) are energy storing • Cellulose is in plant cells • Chitin is the major component in the exoskeleton of arthropods LIPIDS • Monomer is the fatty acid • Class includes fats, oils, and waxes • DO NOT DISSOLVE IN WATER • Composed of a glycerol and 3 fatty acids • Energy storing molecule (9 calories/gram) Types of fats • Saturated fats have only carbon-carbon single bonds with the maximum number of hydrogen atoms • Unsaturated fats have at least one carbon-carbon double bond and do not have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms. 4 TYPES OF LIPIDS • FATTY ACID - Long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group on the end • FATS AND OILS - lipids used to store energy ( Formed from the combining of 3 fatty acids + a glycerol) • Phospholipids- composes the cell membrane differ from other lipids in structure but are classified as a lipid because they are insoluble in water • Steroids- – examples : cholesterol progesterone PROTEINS • Important structural functions • Proteins compose hair, muscles, nails,etc. • Collagen is the most abundant protein in your body • ENZYMES are special proteins which assist in chemical reactions COMPOSITION OF A PROTEIN • • • • Monomer is amino acid Each has an amino group (NH2) 20 different amino acids A polypeptide is a long chain of amino acids ( usually 100 - 300) • A protein is composed of one or more polypeptides • Insulin is the smallest protein (51) STRUCTURES OF PROTEIN 1 . Primary - amino acid sequence 2 . Secondary- alpha or beta 3 . Tertiary-three dimensional shape 4 . Quaternary- arrangement of the polypeptides chains NUCLEIC ACIDS • Monomer is Nucleotide – which is composed of a ribose sugar, a base and a phosphate group Adenine guanine cytosine PO4 thymine • DNA - Deoxyribonucleic Acid – Carries the genetic code • RNA - Ribonucleic Acid