* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Cigarette smoking for weight loss wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Calorie restriction wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Waist–hip ratio wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Fat acceptance movement wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Adipose tissue wikipedia , lookup
Childhood obesity in Australia wikipedia , lookup
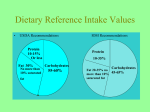
THE RELATIVE COMPARISON OF BODY FAT TO LEAN BODY MASS (MUSCLE, BONE, ORGANS). OR FAT WEIGHT COMPARED TO FAT FREE WEIGHT BODY WEIGHT = 200 LBS. %BODY FAT = 20% FAT WEIGHT = 40 LBS FAT FREE WEIGHT = 160 LBS • NORMAL PHYSIOLOGICAL FUNCTIONING • PROTECTION OF ORGANS FROM BODILY HARM • INSULATION AND BODY TEMPERATURE REGULATION • ENERGY STORAGE •EVALUATE YOUR HEALTH •BETTER PLAN A PROGRAM OF WEIGHT CONTROL •EVALUATE YOUR PROGRESS ON EXERCISE AND NUTRITION PROGRAM Fat and Muscle are two distinctly different things and one can not turn into another. MUSCLE FAT Properties: Fibrous Lipids, adipose contractible and tissue connective tissue Weight / Density: Heavier, more Lighter, less dense dense Function: Moves skeleton Protection, (body) insulation Change in Increases with Decrease with response to exercise, exercise exercise: METHODS OF ESTIMATING BODY COMPOSITION: FAT TISSUE MEASURED WITH A CALIPER AT VARIOUS LANDMARKS ON THE BODY. BODY VOLUME DETERMINED BY WATER DISPLACED. BODY DENSITY DETERMINED BY BODY WEIGHT IN WATER. INSTRUMENT THAT MEASURES THE SPEED OF ELECTRICAL IMPULSES THROUGH THE BODY MUSCLE IS A BETTER CONDUCTOR THAN FAT OLD METHOD BASED ON AVERAGES FOR FRAME SIZE NO CONSIDERATION FOR PERCENT BODY FAT WHAT IS RECOMMENDED % BODY FAT? 2 TYPES OF BODY FAT FAT THAT IS STORED IN THE ORGANS AND TISSUES OF THE BODY. ESSENTIAL FAT IS THE BARE MINIMUM FAT THAT IS REQUIRRED FOR NORMAL BODY FUNCTIONING. 2%-4% 10%-12% (CHILD BEARING) ADIPOSE TISSUE FOR INSULATION, PROTECTION, AND TEMPERATURE REGULATION 8% - 12% FOR MALES AND FEMALES EXCESS STORAGE FAT CONTRIBUTES TO A HIGHER RISK FOR HEART DISEASE AND OTHER HEALTH RELATED PROBLEMS •FAT CELLS ARE FORMED DURING THE LAST MONTH OF FETAL DEVELOPMENT AND CONTINUE TO FORM UNTIL THE EARLY 20’S. •FAT CELL FORMATION IS ESPECIALLY RAPID DURING THE FIRST FEW YEARS OF LIFE •AFTER YOUR 20’S, THE NUMBER OF FAT CELLS ARE SET, BUT THEY CAN INCREASE IN SIZE. •OVERFEEDING CHILDREN CAN LEAD TO A LIFETIME OF OBESITY. How much body fat? Males Females Essential 2%-4% 10%-12% Athletes 5%-13% 13%-17% Normal Range 14%-17% 18%-24% Over Fat = Acceptable? 18%-25% 25%-31% Obese 26%+ 32%+ The amount of energy it takes to raise the temperature of one kilogram of water one degree centigrade; aka. UNIT OF ENERGY DERIVED FROM FOOD HOW MANY CALORIES DOES IT TAKE TO BURN ONE POUND OF BODY FAT? CALORIES IN - CALORIES OUT = NET CALORIC BALANCE IN OTHER WORDS . . . TAKE IN MORE CALORIES THAN YOU BURN … YOU GAIN WEIGHT. BURN MORE CALORIES THAN YOU TAKE IN … YOU LOSS WEIGHT CALORIES IN PURPOSE OF CALORIES IN (EATING AND DRINKING): •TO MEET METABOLIC NEEDS OF BODY •TO SUPPLY FUEL FOR PHYSICAL ACTIVITY - CALORIES OUT HOW DO YOU BURN CALORIES? •METABOLISM •PHYSICAL ACTIVITY =NET CALORIC BALANCE LOSS WEIGHT, STAY THE SAME, OR GAIN WEIGHT HOW MANY CALORIES CAN YOU BURN IN ONE MINUTE BY EXERCISING IN YOUR TRAINING HEART RATE ZONE? 8-15 CALORIES PER MINUTE Somatotype = Body Type • Endomorph – large, soft bulging body and pear-shaped appearance *most dangerous body type • Ectomorph – slender, slight build • Mesomorph – solid, muscular, and largeboned physique IF WEIGHT LOSS IS DESIRED, WHAT IS THE RECOMMENDATION FOR SAFE, PROPER, AND LONG-TERM WEIGHT LOSS? (AMERICAN MEDICAL ASSOCIATION) TO INSURE QUALITY NUTRIENTS TO MEET THE BODY’S NEEDS TO INCREASE YOUR METABOLISM Nutrient Carbohydrate Fats Protein Food Source Grains, breads, veggies, fruits, pastas Function in the Body Primary source of fuel Meats, poultry, whole milk dairy products, vegetable oils Meats, poultry, fish, dairy products, eggs Essential to proper functioning of the human body. Converts to body fat Amino acids to build muscle, organs, hormones, and enzymes Cals/g Recommended/Actual % of calories in diet 4 60-70 45-55 9 20-30 40-50 4 12-15 15-20 Food source: Grains, breads, veggies, fruits, pastas function in the body: Calories per gram: Recommended % of calories in diet: Actual % of calories in an average U.S. diet: Primary source of fuel Food source: MEATS, POULTRY, WHOLE MILK PRODUCTS, VEGETABLE OILS function in the body: INCREASES LIPIDS IN THE BLOOD THAT LEADS TO DEPOSITS IN THE ARTERIES Calories per gram: Recommended % of calories in diet: Actual % of calories in an average U.S. diet: Food source: MEATS, FISH, POULTRY, DAIRY PRODUCTS, EGGS function in the body: AMINO ACIDS TO BUILD MUSCLE, ORGANS, HORMONES, AND ENZYMES Calories per gram: Recommended % of calories in diet: Actual % of calories in an average U.S. diet: EXCESS CALORIES OF CARBOHYDRATES, FATS, AND PROTEINS ARE ALL CONVERTED TO ... FAT INTAKE SHOULD BE BASED UPON: •YOUR BODY WEIGHT •YOUR PERSONAL AND FAMILY HISTORY OF HEART DISEASE •YOUR BLOOD CHOLESTEROL LEVEL YOUR PHYSICAL ACTIVITY LEVEL Only 20 to 30 percent of your total calories should be from dietary fat. What food source does your body utilize most during exercise?