* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
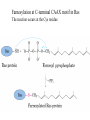
Study Guidelines for Chemistry in Chapters 1 and 2 • Look at the slides that follow containing the list of reactions on which to focus. • Re-read the indicated pages where each reaction is described in Creighton. Look at related power point slides and examples discussed in class. • Put together a summary sheet with each reaction in as much detail as presented in Creighton or in class and explain how it is used. Reactions in Chapter 1 1) Coupling of carboxyl groups to amines catalyzed by carbodiimides Pg 8 A critical step in peptide synthesis is the activation of the carboxyl group for nucleophilic attack by an amine and consequent formation of a peptide bond. This activation can be achieved in a variety of ways - see examples on pg 44. In the example of peptide synthesis presented in class the carboxyl group was activated by reaction with a carbodiimide. Another example is given on pg 46 Creighton. Summarize this reaction in the context of one full round of peptide synthesis. 2) Reaction of Cys with iodoacetate pg 17 3) Irreversible oxydation of Cys with performic acid pg 18 4) Disulfide bond formation between Cys residues and reaction with reducing agents. pg 19 and 98 5) Reaction of amino acids with reagents to produce strongly absorbing or fluorescent compounds: a) ninhydrin b) fluorescine c) o-phthalaldehyde pg 21 and 22 6) Determination of amino terminal residue. pg 31 and power point slide Reaction with: a) fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene b) dansyl chloride 7) The Edman degradation reaction pg 33 and class notes 8) Cleavage of peptides after Met by reaction with CNBr pg 39 Reactions in Chapter 2 N and C-terminal modifications: 9) Acylation of the N-terminus pg 87 10) Myristoylation of the N-terminus pg 88 11) Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor at C-terminus pg 89 12) Farnesylation of C-terminus pg 90 and following slide Farnesylation at C-terminal CAAX motif in Ras The reaction occurs at the Cys residue 13) Amidation of C-terminus in hormones containing C-terminal Gly residue pg90 Sidechain modifications: 14) Glycosylation – pgs 91-93 N-glycosylation of Asn – pg 91 O-glycosylation of Ser, Thr and Hyl – pg 93 15) Lipid attachment pg 94 example of palmytoylation of Cys residues reactions at terminals, 11 and 13 above, are also lipid attachments 16) Phosphorylation pg 96-97 S, T, Y H, K, D 17) ADP-ribosylation pg 98 H, R, N, K, E 18) Disulfide bond formation pg 98-99