* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6-7 Review Game
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
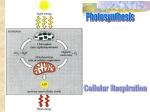
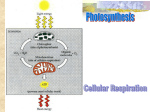
Chapter 6-7 Review Game AP Biology Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis DIRECTIONS: Organize yourselves into 6 groups Get a dry-erase board, marker and eraser for each group Put your brains together to answer these questions about cell energy For each question, simply write the letter you decide is the best answer on the dry erase board and show me when I ask!! CELLULAR RESPIRATION QUESTIONS 1. The function of cellular respiration is to: A. B. C. D. E. Reduce CO2 Extract CO2 from the atmosphere Extract usable energy from glucose Synthesize macromolecules from monomers Produce carbohydrates C. Goal of cellular respiration is to extract energy from the bonds stored in food (i.e. glucose!) 2. An electron carrier acts as an energystorage molecule when it is __ (for example, __): A. B. C. D. E. Reduced…NAD Oxidized…NAD Oxidized…NADH Reduced…NADH Oxidized…FADH2 D. NAD+ becomes NADH when it accepts an electron (Gain Electron = Reduction; LEO goes GER) 3. Which one of the following best describes the electron transport chain? A. Electrons are pumped across a membrane by active transport B. Acetyl CoA is fully oxidized to CO2 C. Hydrogens are added to CO2 to make an energy rich compound D. Electrons pass from one carrier to another, releasing a little energy at each step E. Glucose is broken down to a three-carbon compound in preparation for the Citric Acid Cycle D. Electrons move down the chain to more electronegative molecules, releasing energy in a slow fashion rather than one large burst of energy (large burst is much less usable) 4. During respiration in a eukaryotic cell, reactions of glycolysis occur __. A. B. C. D. In the cytoplasmic fluid In the mitochondria On the inner mitochondrial membrane Within the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion E. Across the inner membrane of the mitochondria A. All organisms, including prokaryotes, engage in glycolysis because it occurs outside the mitochondria. 5. When pyruvic acid is converted to acetyl CoA __. A. B. C. D. E. CO2 and ATP are formed CO2 and NADH are formed CO2 and coenzyme A are formed One turn of the Citric Acid Cycle is completed NAD is regenerated B. A carbon is lost and creates CO2 as waste; ATP formed as the phosphates are lost during the re-configuration of the molecule 6. Of the metabolic pathways listed below, the only pathway found in almost all organisms is __. A. B. C. D. E. Aerobic cellular respiration The Citric Acid Cycle The electron transport chain Glycolysis Fermentation D. A, B and C only happen in an aerobic environment; E only happens in anaerobic conditions; glycolysis occurs in all environments 7. Most of the high energy electrons released from glucose by cell respiration __. A. Are used for synthesizing lactic acid B. Are used to form ATP by the Citric Acid Cycle C. Are bound to FAD to be sent through electron transport D. Are in the carbon dioxide E. None of the above E. Are picked up by NAD+ and taken to the electron transport chain 8. Most of the NADH that delivers the high energy electrons to the electron transport chain comes from __. A. B. C. D. E. Chemiosmosis The cytoplasm Glycolysis Biosynthesis The Citric Acid Cycle E. Glycolysis and prep for Krebs give only 2 NADH each; Krebs gives 3 NADH for each glucose that enters for a total of 6 NADH 9. Why is the Citric Acid Cycle called a cycle? A. Glucose is cycled around and resynthesized B. NAD+ and FAD are recycled C. The two-carbon acetyl CoA binds to a four-carbon molecule that is restored at the end of the cycle to be used again in the Citric Acid Cycle D. Carbon dioxide is cycled back to photosynthesis E. NADH is cycled down the electron transport chain C. The starting 4-C molecule (oxaloacetate) is regenerated as citrate is reconfigured to a 5-C and then a 4-C molecule, losing electrons and phosphates along the way, picked up by NAD+/ 10. In the Citric Acid Cycle, the energy production per glucose molecule is __. A. B. C. D. E. A. 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2 38 ATP 4 ATP, 8 NADH 2 ATP, 6 NADH 1 ATP, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2 11. The energy given up by electrons as they move through the electron transport chain is used to __. A. B. C. D. E. Break down glucose Make NADH and FADH2 Pump H+ through a membrane Oxidize water Manufacture glucose C. The flow of those hydrogens through ATP synthase helps to create lots of ATP…CHACHING 12. The ATP synthase in a human cell gets energy for making ATP directly from __. A. B. C. D. Sunlight The flow of H+ through a membrane The oxidation of glucose The movement of electrons through a series of carriers E. The reduction of oxygen B. The flow of hydrogens “spins the turbine” and phosphorylates ADP; CHA-CHING 13. During respiration in a eukaryotic cell, the electron transport chain is located in or on the __. A. B. C. D. E. Cytoplasmic fluid The mitochondrion Cristae of the mitochondrion Intermembrane space of the mitochondrion None of the above C. The folds of the cristae give the mitochondria LOTS of space to have the ETC going…structure = function 14. Which part of the cellular catabolism of glucose requires molecular oxygen? A. B. C. D. E. Glycolysis The Citric Acid Cycle The electron transport chain Fermentation All of the above C. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor and forms water as a byproduct 15. The overall efficiency of respiration is approximately __. A. B. C. D. E. 0.50% 2% 40% 94% 100% C. This is good…gas in a car is only about 25% 16. How many ATPs are gained by substrate-level phosphorylation from the complete breakdown of a single molecule of glucose in the presence of oxygen? A. B. C. D. E. 2 ATP 4 ATP 6 ATP 36 ATP None of the above B. SUBSTRATE-LEVEL gives us only 4…2 net from glycolysis and 1 for Krebs (spins twice for 17. Fermentation is essentially glycolysis plus an extra step in which pyruvic acid is reduced to form lactic acid or alcohol and carbon dioxide. This last step __. A. B. C. D. E. Removes poisonous oxygen from the environment Extracts a bit more energy from glucose Enables the cell to recycle NAD+ Inactivates toxic pyruvic acid Enables the cell to make pyruvic acid into substances it can use C. The goal here is to get an electron carrier BACK, we need to get NAD+ returning to glycolysis to be able to continue producing small amounts of ATP. PHOTOSYNTHESIS QUESTIONS 1. In a rosebush, chlorophyll is located in __. A. Chloroplasts, which are in mesophyll cells in the thylakoids of a leaf B. Mesophyll cells, which are in the thylakoids in chloroplasts in a leaf C. Thylakoids, which are in mesophyll cells in the chloroplasts of a leaf D. Chloroplasts, which are in thylakoids in the mesophyll cells of a leaf E. Thylakoids, which are in chloroplasts in the mesophyll cells of a leaf E. From smallest to largest: thylakoid chloroplast mesophyll cell mesophyll layer leaf 2. The source of the oxygen produced by photosynthesis has been identified through experiments using radioactive tracers. The oxygen comes from __. A. B. C. D. E. Carbon dioxide Glucose Radioisotopes Water light D. Water – breaks down into hydrogen, 3. In photosynthesis, plants use carbon from __ to make sugar and other organic molecules. A. B. C. D. E. Water Carbon dioxide Chlorophyll The sun soil B. Carbon dioxide (during Calvin cycle) 4. The photosynthetic event known as the Calvin cycle occurs in the __. A. B. C. D. E. Thylakoid membrane Thylakoid compartment Stroma Stomata Matrix C. Stroma; the light reactions occur in the thylakoid 5. The synthesis of glucose by photosynthesis is an endergonic process. The source of the energy for the excited electrons is __. A. Chlorophyll B. Carbon dioxide C. Water D. Glucose E. Light E. Light strikes the photosystem, exciting and electron, as it flows down the ETC, a proton gradient is created (much like respiration) 6. The reaction center, antenna molecules, and primary electron acceptors that cluster in the thylakoid membrane form what structure? A. B. C. D. E. Fluorescence center Photosystem Electron transport chain Carbon-fixation unit Electromagnetic spectrum B. Photosystem II and Photosystem I are where light concentrates and excites electrons 7. The light reactions of photosynthesis generate high-energy electrons, which end up in __. The light reactions also produce __ and __. A. ATP…NADPH…oxygen B. Oxygen…sugar…ATP C. Chlorophyll…ATP…NADPH D. Water…sugar…oxygen E. NADPH…ATP…oxygen E. NADPH is associated with photosynthesis; a similar molecule (NADH) does essentially the same job in cellular respiration 8. Light reactions do all of the following except__. A. B. C. D. Convert sunlight to chemical energy Synthesize ATP and NADPH Reduce CO2 Convey excited electrons from chlorophyll to an electron acceptor E. Absorb photons C. CO2 is reduced into glucose during cellular respiration 9. Molecular oxygen is produced during __. A. B. C. D. E. Glycolysis Light reactions of photosynthesis The Calvin cycle Aerobic respiration Electron transport chain B. Oxygen is one of the results of the splitting of water; it is lost as a waste product but used as a reactant in cellular respiration 10. Both mitochondria and chloroplasts __. A. B. C. D. E. Use a H+ gradient to produce ATP Obtain electrons from water Reduce NAD+, forming NADP Release oxygen as a byproduct Are surrounded by a single membrane A. The electron transport chain is seen in both processes; it generates ATP as a result of the flow of hydrogen ions through ATP synthase 11. During photosynthesis in a eukaryotic cell, a high H+ concentration accumulates or is formed in the __. A. B. C. D. E. Thylakoid membrane Thylakoid compartment Stroma Stomata Matrix B. The hydrogen ions are concentrated INSIDE the thylakoid, as opposed to cell respiration where the hydrogen ions were concentrated on the intermembrane space of the mitochondria (outside the cristae) 12. The energy used to produce ATP in the light reactions of photosynthesis comes from the __. A. B. C. D. E. The burning of sugar molecules Splitting of water Movement of H+ through a membrane Carbon fixation Fluorescence C. Again, the flow of hydrogen causes ATP synthase to phosphorylate ADP 13. Which of the following correctly matches each of the inputs of the Calvin cycle with its role in the cycle? A. B. C. D. E. B. Carbon dioxide: high-energy electrons…ATP:energy…NADPH:high energy-electrons Carbon dioxide:carbon…ATP:energy…NADPH:highenergy electrons Carbon dioxide:high-energy electrons…ATP:carbon…NADPH:energy Carbon dioxide:energy…ATP:carbon…NADPH:highenergy electrons Carbon dioxide:hydrogen…ATP:carbon…NADPH:energy Can I have a copy of this, PLLLEAAAAAAASEEEEEEEEE? NO!!! All of these questions came from the online chapter tests…you should be doing these on your own to prepare for the tests!! 14. The reactions of the Calvin cycle are not directly dependent on light, but they usually do not occur at night. Why? A. It is often too cold at night for these reactions to take place. B. Carbon dioxide concentrations decrease at night. C. The Calvin cycle depends on the products of the light reactions. D. Plants usually open their stomata at night. E. At night, plants cannot produce the water needed for the Calvin cycle. C. Calvin cycle requires NADPH and ATP (produced in the light reactions) to proceed 15. What is the role of NADP+ in photosynthesis? A. It assists chlorophyll in capturing light. B. It acts as the primary electron acceptor for the photosystems. C. As part of the electron transport chain, it manufactors ATP. D. It assists photosystem II in the splitting of water. E. It is reduced and then carries electrons to the Calvin cycle. E. NADP+ gets reduced (GER NADPH) and transports those electrons to the Calvin cycle to help fix CO2