* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Development of analogs of thalidomide wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
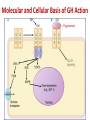
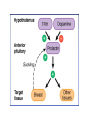
Hypothalamic & Pituitary Hormones Kaukab Azim, MBBS, PhD Uses of Hypothalamic & Pituitary Hormones • Short stature due to hypopituitarism (Pituitary dwarfism) • Acromegaly and gigantism • Carcinoid syndrome, VIPoma, and ruptured esophageal varices • Hyperprolactinemia • Induction of labor • Diabetes insipidus • SIADH 2 Concepts in Endocrinology • Primary, secondary and tertiary endocrine disorders • Feedback regulation • Endocrine disorders: – Deficiency, or – Excess • Mechanisms of action • Uses of hormones /analogs: – Diagnostic use – Therapeutic use 3 Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) • GHRH analog: Sermorelin • Used rarely as a diagnostic test for GH responsiveness 4 Growth Hormone • Secretion of GH is stimulated by GHRH and inhibited by GIH (somatostatin) • GH preparations for therapeutic use: – Somatropin: Recombinant human GH IGF-1 as Peripheral effector – Somatrem: Recombinant human GH 5 Growth hormone (Somatotropin) • Most of the actions of GH are mediated by IGF-1 ( insulinlike growth factor 1) “somatomedins” - the peptides produced in the liver and cartilage. • The somatomedins stimulate skeletal growth, amino acid transport, protein synthesis, nucleic acid synthesis and cell proliferation. 6 Therapeutic uses of GH • Short stature due to Congenital/acquired GH deficiency (Pituitary Dwarfism) • GH deficiency in adults • Turner’s syndrome • AIDS related muscle wasting 7 GH preparations: Adverse effects In children • Increased Intracranial tension • Headache • Papilledema • Scoliosis • Diabetes mellitus In adults • • • • • • Peripheral edema Arthritis Arthralgia Myalgia Carpal tunnel syndrome Diabetes mellitus 8 Growth hormone inhibiting hormone (Somatostatin) Somatostatin analogs: • Octreotide – S/C, daily • Sandostatin-LAR - (Slow release preparation of octreotide) once every 4 weeks • Administration of somatostatin analogs result in decrease in GH and IGF-1 levels 9 Somatostatin analogs: Therapeutic uses • Acromegaly • To prevent gigantism • Carcinoid syndrome • VIPoma, gastrinoma • Ruptured esophageal varices 10 Somatostatin analogs: Adverse drug reactions • GIT problems: – Abdominal cramps, diarrhea, malabsorption, steatorrhea – Gall stones – Vitamin B12 deficiency • Cardiovascular problems: – Sinus bradycardia, conduction disturbances 11 GH antagonist Pegvisomant • Decreases IGF-1; GH remains high • Effective in those who do not/stop responding to octreotide 12 Molecular and Cellular Basis of GH Action 13 Prolactin Secretion of prolactin is under the control of DOPAMINE (prolactin inhibiting hormone) secreted by hypothalamus 14 Hyperprolactinemia • Prolactin secreting pituitary adenoma • Drug induced hyperprolactinemia – Antipsychotics – Metochlopramide Drugs to manage hyperprolactinemia: • Bromocriptine • Cabergoline (ka-BER-goe-leen) 16 Oxytocin Actions meditated through IP3/DAG ↑ Ca+2 Therapeutic uses • To induce and augment labor after cervix has ripened • To control post-partum hemorrhage • To improve milk ejection – nasal oxytocin 17 Oxytocin : Adverse reactions • Cardiac arrhythmia, CNS stimulation, excessive uterine contractions, and hyponatremia. Contraindications: • • • • Fetal distress Abnormal fetal presentation Prematurity CPD (cephalo-pelvic disproportion) 18 Vasopressin (arginine-vasopressin) Vasopressin has: – Antidiuretic activity – Vasopressor activity (Vasoconstriction) • Decreased secretion/response to ADH causes Diabetes insipidus • Excessive secretion of ADH causes: SIADH 19 Vasopressin receptors 1. V1 receptors: – On vascular smooth muscles – Pressor effect: meditated through IP3/DAG ↑Ca+2 2. V2 receptors – Renal: On distal and collecting duct cells of nephron • Antidiuretic effect: mediated through ↑cAMP – Extrarenal: • Release of coagulation factors VIIIc and Von willebrand factor 20 Therapeutic uses of vasopressin/analogs • Vasopressin (Pitressin) Therapeutic uses • Advanced Cardiac life support • Bleeding esophageal varices • Desmopressin Long-acting synthetic analog of vasopressin Antidiuretic : vasopressor activity = 3000:1 Therapeutic uses: • Neurogenic diabetes insipidus • Von Willebrand disease and hemophillia • Enuresis 21 SIADH • Due to excessive secretion of ADH Drug induced SIADH: – Carbamazepine, vinca alkaloids, Chlorpropamide Drugs to manage SIADH – Demeclocycline – Conivaptan (vasopressin antagonist) 22 Questions… 23