* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CVS 5
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
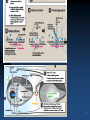
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct Xa inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct thrombin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
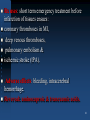
DRUGS AFFECTING THE BLOOD 1 Drugs Affecting Blood Treatment of Anemia Thrombosis Bleeding 2 Drugs used to treat thrombotic disorders Anticoagulants Thrombolytics 3 Drugs for treatment of anemia Vitamin B12 Erythropoietin Folic acid Iron 4 Drugs for treatment of bleeding Aminocaproic acid Enoxaparin Heparin Warfarin Lepirudin 5 Platelet Response To Vascular Injury Platelet adhesion to site of vascular injury Activation of platelets by factors that include TxA2, ADP, serotonin, collagen & thrombin Increase expression of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors Aggregation of platelets by a cross-linking reaction due to fibrinogen binding to glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors Formation of the thrombus by fibrin monomer cross link. 6 7 8 Platelet aggregation inhibitors These agents are beneficial in the prevention and treatment of occlusive cardiovascular diseases 9 Antiplatelet drugs Aspirin Ticlopidine and clopidogreal Abciximab Tirofiban and eptifibatide Dipyridamole 10 Platelet Inhibitors Aspirin Blocks cyclooxygenase 1, inhibiting the formation of thromboxane A2 Arachidonic Acid Cyclooxygenase Prostaglandins, Thromboxane 11 ASPIRIN Used as prophylactic in treatment of TIA & atrial fibrillation. Low dose: prevent incidence of MI and recurrence SE; GI disturbance, Bleeding Time prolonged. 12 Ticlopidine Inhibits the binding of ADP to its receptor on platelet resulting in a ↓ in platelet aggregation and thrombus formation Very effective (adverse effect: neutropenia) Clopidogrel – NEWER DRUG (same mechanism- no neutropenia) 13 Abciximab, Eptifibatide & Tirofiban Tirofiban & Eptifibatide: antagonists of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors – decrease aggregation by preventing cross- linking reaction. Abxicimab: is a monoclonal antibody that binds to GPIIb/IIIa preventing platelet aggregation 14 Anticoagulants Are drugs used to treat and prevent clotting via inhibition of various steps in the coagulation pathway which involves two interrelated pathways called the intrinsic and extrinsic pathway 15 16 Heparin Binds to antithrombin III in blood causing rapid inactivation of factors IIa & Xa (mainly). Heparin is a large polysaccharides given IV/SC. No placental access. 17 18 Heparin Effective in acute treatment of Venous thrombosis prevention - post surgical Deep venous thromboembolism Acute myocardial infarction Prevention of clotting in medical devices (catheters, hemodialysis, heart lung machines) 19 HEPARIN SE: HEMORRHAGE HYPERSENSITIVITY THROMBOSIS THROMBOCYTOPENIA Monitor the activated partial thromboplastin time CI – hypersensitive pts, OR BLEEDING DISORDERS, ALCHOLICS.. Excessive Bleeding caused by heparin use can be reversed with protamine sulfate 20 Low molecular weight Heparin LMWH e.g., enoxaparin Binds to antithrombin III also causing rapid inactivation of factor Xa Longer half-life Can be used in hospital as well as out-patient setting. Given subcutaneously Uses: same as heparin Adverse effect: same as heparin but less likely to cause HIT 21 ARGATROBAN Is a direct thrombin inhibitor It does not require ATIII Does not interact with heparin-induced antibodies Can be used to treat HIT 22 Lepirudin (hirudin) Closely related to hirudin –a thrombin inhibitor from leech Lepirudin is produced in yeast cells by recombinant DNA tech Thrombin inhibition Property of preventing coagulation of the blood. 23 Lepirudin is approved for use in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia/thrombosis syndromes. 24 DANAPAROID Anti-factor IIa and Xa but more an anti-Xa Given SC USES: prophylaxis of DVT in hip replacement surgery Used for HIT Adverse effect: bleeding 25 Warfarin (Coumarin) Is an antagonist of vitamin K that prevents gamma carboxylation reactions in hepatic synthesis of coagulation factors II, VII, IX , X, protein C & S by inhibing the enzyme vit Kepoxide reductase No effect on factors already made by the liver – slow onset – 24 – 48 hrs. Reversal (antagonist): vitamin K – Increase cofactor synthesis, but slow onset; fresh frozen plasma – rapid. 26 27 Warfarin – Vitamin K-Antagonist ORAL Met: by liver via P450 Effective in: longer-term anticoagulation for thromboses, emboli, post MI, heart valve damage & artificial heart valves caused thromboembolism Monitor prothrombin time 28 Warfarin Crosses placenta Teratogenic Contraindicated in pregnant women Anticoagulation in pregnancy heparin 29 Adverse effects: hemorrhage, skin necrosis, “purple toe” syndrome, teratogenic (bone dysmorphogenesis). 30 Drug interaction ↑es warfarin level and activity: Aspirin, sulfonamides, cimetidine, acute alcohol, metronidazole e.t.c., ↓es warfarin level and activity: Chronic alcohol ingestion, barbiturates, rifampin, griseofulvin etc., 31 THROMBOLYTIC AGENTS ALTEPLASE (t PA) STREPTOKINASE 32 Thrombolytics tPA (Tissue Plasminogen Activator Activates plasminogen bound to fibrin Streptokinase Activates free plasminogen into active plasmin Plasminogen tPA, Streptokinase Plasmin Fibrin Fibrin Degradation Products 33 34 Alteplase (tPA): natural activator, so no allergy problems; clot(fibrin)specific, acting on fibrin-bound plasminogen. Streptokinase: acts on bound & free plasminogen Decrease fibrinogen and factors V & VIII; Bacterial protein - hypersensitivity. 35 Rx uses: short term emergency treatment before infarction of tissues ensues: coronary thromboses in MI, deep venous thromboses, pulmonary embolism & ischemic stroke (tPA). Adverse effects: bleeding, intracerebral hemorrhage. Reversal: aminocaproic & tranexamic acids. 36 37 CAUSES OF BLEEDING Genetic diseases such as hemophilia Use of thrombolytics Use of anticoagulants 38 DRUGS USED TO TREAT BLEEDING Infusion of factors VIII and IX made by recombinant DNA technology or from human blood serum to treat hemophilia Aminocaproic acid and tranexamic acid: to reverse bleeding caused by use of thrombolytics. Act by inhibiting plasminogen activation Protamine sulfate: reverse bleeding caused by heparin. Acts by binding ionically to heparin forming an ion complex Vitamin K: reverse bleeding caused by warfarin use. Though fresh-frozen plasma is used if immediate hemostasis is required. Blood transfusion 39 ANEMIA Is defined as a ↓ in Hb concentration resulting from a ↓ in number of circulating RBCs. 40 CAUSES OF ANEMIA Chronic blood loss Bone marrow abnormalities Increased hemolysis Malignancies Renal disease Drugs: anticancer agents Nutritional deficiency: in iron, folic acid and vitamin B12. 41 AGENTS USED TO TREAT ANEMIA Iron Folic acid Vitamin B12 Erythropoietin: made by recombinant DNA technology used in those pts with renal failure 42 AGENT USED TO TREAT SICKLE CELL DISEASE Hydroxyurea: an anticancer drug MOA: ↑ fetal Hb levels ↑ nitric oxide level in blood → in vasodilation → ↓ in sickling 43