* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diuretic - e
Discovery and development of direct thrombin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotease inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
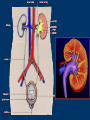
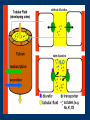
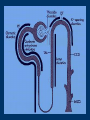
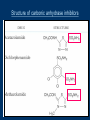
Vilasinee Hirunpanich B.Pharm(Hon), M.Sc In Pharm (Pharmacology) Outline of diuretic drugs Basic knowledge in anatomy and physiology Classification of diuretics Classification of Diuretics Loop Diuretics Thiazides Diuretics K+-sparing diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 1. Loop diuretics (high ceiling diuretics) block Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransport in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle high efficacy: 25% of filtrated solute is reabsorbed Structure of loop diuretics Mechanism of action of Loop of Henle pharmacokinetic Rapidly absorbed Eliminate by renal secretion Torsemide (1h) is more rapidly than furosemide (Lasix) (2-3 h) Duration 2-3 h (furosemide), 3-4 h(torsemide) Adverse effects 1. Fluid and electrolytes imbalance Hyponatremia, Hypokalemia and hypomagnesia 2. H+ loss metabolic alkalosis 3. Ototoxicity ethacrynic most often Adverse effects (cont) 4. Hyperuricemia 5. Hyperglycemia 6. Hypersensitivity to sulfonamide skin rash 7. Others: dehydration Drug interaction Ototoxic drugs; aminoglycoside digitalis glycoside NSAIDs probenecid Litium anticoagulant Clinical indications 1. Hypertension and CHF 2. Acute pulmonary edema 3. Other edematous conditions 3. Mild hyperkalemia (simultaneous NaCl and water) 4. I-, Br- intoxication 2.Thiazide Diuretics Thiazide diuretics Sulfonamide and benzothiadiazide (thiazide) derivatives – Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), indapamide, chlorthalidone, metolazone Mechanism of action of thiazide diuretics Mechanism of actions Increase Na+, Cl-, K+, Mg2+ in urine….water retention Some drug has vasodilator effect such as indapamide (Natrilix ) Pharmacokinetic Chlorothiazide is less lipid soluble and must given in large dose Indapamide is excreted primarily by the billiary system Adverse effects 1.Fluid and electrolytes imbalance Hypokalemia Hyponatremia Hypercalcemia 2. hyperglycemia due to impaired pancreatic release of insulin 3.hyperlipidemia 4.allergic reaction 5. Other: weakness, fatigability Drug interaction Decrease the effect of Increase the effect of anticoagulant digitalis glycoside uricosuric agent lithium sulfonylurea insulin Decrease the effect of thiazide NSAIDs bile acid sequestering probencid Clinical indications Hypertension, CHF hepatic cirrhosis nephrolithiasis due to idiopathic hypercalcinuria nephrogenic diabetes insipidus Br- intoxicity + K -sparing 3. diuretics + K sparing diuretics 1. Aldosterone antagonists 2. Inhibitor of renal epithelium Na+ channel Aldosterone antagonist Structure similar to aldosterone hormone Ex. spironolactone (synthesis steriod), eplerenone (spironolactone analog) spironolactone specific antagonist prevent protein synthesis that required for Na+ and K+ transport increase Na+ excretion and preserve of K+ Potentcy is low and depend on aldosterone level pharmacokinetic Spironolactone Onset and duration of action are determined by the kinetic of aldosterone response in target tissue. Slow onset (48 hr) Canrenone is the active metabolized which has very long t12.than parent drug. Adverse effects hyperkalemia…..life threatening Endocrine effects -gynecomastia -hirsutism -deepening voice - decrease libido contraindication Pts using salicylate because inhibiting canrenone K+ administration Clinical use coadministration with thiazide or loop diuretic for edema (additive effect) hyperaldosteronism 2. Inhibitor of renal epithelium Na+ channel Triamterene amiloride Mechanism of action of K+-sparing diuretic late distal tubules and collecting ducts block Na+ channel in the luminal membrane increase NaCl excretion and decrease K+ excretion Adverse effect anemia: triamterene, folic antagonist kidney stone (triamterene is poorly soluble) ARF (acute renal failure) (combination of triamterene and indomethacin has been reported ) hyperkalemia life-threatening: contraindication Renal failure other K+ sparing diuretic ACEI K+ supplement NSIADs Clinical Use Co administration with other diuretic (additive effect) + prevent depletion of intracellular K store Osmotic diuretics Properties 1. Freely filtered at the glomerulus 2. No reabsorption at the renal tubule 3. No pharmacological effects Glycerine, Isosorbide, Mannitol, Urea site of action: Proximal tubule and descending limb of Henle’s loop Structure of osmotic diuretics Mechanism of action Limit water reabsorption act as increase urine volume. increase renal blood flow Pharmacokinetic Poorly absorbed so they must be given parenterally Mannitol is excreted by glomerular filtration within 30-60 min Adverse effects 1. Extracellular volume expansion Rapidly distributed in the extracellular compartment and extract water from the intracellular compartment 2. Dehydration 3. Nausea, vomiting, headache Clinical Indications 1. To increase urine volume 2. Reduction of intracranial and intraocular pressure extract water from the eye and brain Glycerine: control intraocular pressure, pre/post operative ocular surgery Mannitol, urea: reduce cerebral edema before/after neurosurgery 5. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors Inhibit carbonic anhydrase enzyme at proximal tubule SO2NH2 (sulfonamide) group is essential for activity. Acetazolamide (Diamox), dichlorophenamide, ethoxalamide, methazolamide Structure of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors Mechanism of action of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 1. increase the excretion of HCO3(Urine alkalinization, pH 8) Increase Na+, K+, secretion 2. Metabolic acidosis 3. eye; decrease formation of aqueous humor 4. Paresthesia, Drowsiness, Somnolence Pharmacokinetic Well absorbed after oral administration The effect of increased of HCO3- is apparent within 30 min. Maximal effect within 2 h Persist for 12 h after single dose Excrete by tubular secretion Adverse effects 1. Hypersensitivity sulfonamide derivative (fever, rashes, bone marrow suppression) 2. Renal stone Ca2+ salt are relatively insoluble at alkaline pH. 3. Metabolic acidosis and urine alkalinization 4. Renal potassium wasting 5. Others: drowsiness, paresthesia Clinical indications 1. Glaucoma (decrease intraocular pressure) Dorzolamide, brinzolamide (topically use) 2. Urinary alkalinization increase the secretion of uric acid, weak acid drugs(aspirin) 3. Metabolic acidosis 4. Acute mountain sickness (24 h before ascent) Diuretic combination Loop diuretic& thiazide (different position) K+sparing diuretic& loop diuretic or thiazide (decrease ADR) Moduretic (amiloride + HCTZ) Dyazide (triamterene+HCTZ)