* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Q:A Patient requiring some antibiotic for his recent infection is
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
Zoopharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Intravenous therapy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cephalosporins wikipedia , lookup
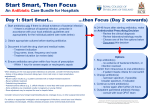
General PrincipleAntimicrobial Chemotherapy C C-Competency based questions Which Competencies? –refer syllabus 1. Questions 1-3: For each of the following questions, select the most appropriate principle which describes the statement. Answers may be used more than once. (A) Selective Toxicity (B) Antibiotic Activity (C) Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (D) Post Antibiotic Effect (E) Transferrable Resistance 1. Microbial death which occurs in the absence of detectable antibiotic. D 2. Products of Penicillium spp. molds which are able to kill Staphylococci. B 3. Due to microbial conjugation. E 2. Questions 4-6: For each of the following questions, select the most appropriate chemotherapeutic agent which describes the statement. Answers may be used more than once. (A) Vancomycin (B) Ketoconazole (C) Penicillin V (D) Amphotericin B (E) Tetracycline 4. A fungicidal compound D 5. Prevents aminoacyl tRNA from binding the 30S ribosomal subunit. E 6. Useful for treating resistant Staphylococcal infection. A 3. The following is considered a typical mechanism by which resistance emerges in bacteria (A) Aggregation of enterococcal bacteria (B) Induction of membrane-bound efflux transporters (C) Alteration of membrane phospholipid content (D) Transfer of chromosomal DNA (E) Dessication of anaerobic bacteria 4. The following is a situation in which the use of antimicrobial combination therapy is LEAST justified C (A) Polyinfection (B) Emergence of resistance (C) Empiric therapy for a lifethreatening infection (D) Mycobacterium spp. infection (E) Prophylaxis prior to dental surgery 5. The following combination of antimicrobial agents is inappropriate (A) An aminoglycoside and a penicillin (B) Amphotericin B and Flucytosine (C) Isoniazid and Rifampin (D) Chloramphenicol and a cephalosporin (E) Neomycin and Polymyxin B 6. Selection of an appropriate antimicrobial agent should NOT be based on the following factor (A) Antimicrobial activity (B) Pharmacokinetics (C) Adverse effects (D) Cost (E) Drug accumulation Q:A Patient requiring some antibiotic for his recent infection is diabetic and immunocompromised. Strategically Which type of drug will you give him emperically? [Clue:Remember pt doesn’t have significant contribution of immunity to fight against the invading organism] C Relevant Slide No-37(Chapter1) • Following the treatment of an oral abscess with clindamycin, a patient develops a greenish, foulsmelling watery diarrhea with left lower quadrant pain. Other signs and symptoms include fever, leukocytosis, and lethargy. If the toxin produced by Clostridium difficile is detected in the stool, the patient would most appropriately be treated with [Clue:what is that syndrome known as and which kind of drug cause this? What is the back up drug for this?] A. cisapride B. gentamicin C. loperamide D. metronidazole E. sulfasalazine C Relevant Slide No-48 (Chapter1) • A patient treated for months with large doses of oral broad spectrum antibiotics would be most likely to develop which of the following? • [Clue:Think, has broad spectrum antibiotic has anything to do with intestinal flora which causes decreased absorption of one vitamin which is responsible for synthesis of some clotting factors?] A. Bleeding in joints B. Bony abnormalities C. Decreased night vision D. Neurologic deficits E. Scurvy C