* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bipolar I Disorder
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
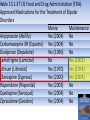
Bipolar I Disorder Treatment Therapeutic Goals • • • • Relief of immediate symptoms Improvement of patient’s well-being Elimination of stressors Combined pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy – Improved medication compliance – Better monitoring of clinical status – Decreased number and length of hospitalizations – Decreased risk of relapse – Improved social and occupational functioning Pharmacotherapy • DIVISION – Acute Phase – Maintenance Phase Treatment of Acute Mania • Lithium Carbonate – the prototypical “mood stabilizer – Therapeutic lithium levels are between 0.6 and 1.2 mEq/L • Valproate – only indicated for acute mania; has prophylactic effects – Typical dose levels of valproic acid are 750 to 2,500 mg per day, achieving blood levels between 50 and 120 µg/mL • Carbamazepine and Oxcarbazepine – Typical doses of carbamazepine to treat acute mania range between 600 and 1,800 mg per day associated with blood levels of between 4 and 12 µg/mL Treatment for Acute Mania • Clonazepam and Lorazepam – effective and are widely used for adjunctive treatment of acute manic agitation, insomnia, aggression, and dysphoria, as well as panic – Atypical and Typical Antipsychotics • Lamotrigine – Prevent recurrences of manic episodes • ECT – Effective in acute mania – Reserved for rare refractory mania or with medical complications Treatment of Acute Bipolar Depression • Combination of Antidepressants and Mood Stabilizer – Olanzepine and Fluoxetine • Electroconvulsive Therapy • Calcium Channel Blocker – Verapamil – Has acute antimanic efficacy Table 15.1-37 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)Approved Medications for the Treatment of Bipolar Disorders Mania Maintenance Aripiprazole (Abilify) Yes (2004) No Carbamazepine XR (Equetro) Yes (2004) No Divalproex (Depakote) Yes (1996) No Lamotrigine (Lamictal) No Yes (2003) Lithium (Lithobid) Yes (1970) Yes (1974) Olanzapine (Zyprexa) Yes (2000) Yes (2004) Risperidone (Risperdal) Yes (2003) No Quetiapine (Seroquel) Yes (2004) No Ziprasidone (Geodon) Yes (2004) No Maintenace Treatment of Bipolar Disorder MOOD STABILIZERS – Lamotrigine – Lithium – Olanzapine • Ameliorate affective and psychotic symptoms during acute manic episodes • Improve depression episodes during acute bipolar depressive episodes • Prevent future mood episodes with sustained treatment at therapeutic levels (prophylactic benefit) Psychotherapy • Patients taking lithium or other treatments for bipolar I disorder are usually medicated for an indefinite period of time to prevent episodes of mania or depression • Most psychotherapists insist that patients with bipolar I disorder be medicated before starting any insight-oriented therapy. Without such premedication, most patients with bipolar I disorder are unable to make the necessary therapeutic alliance. Psychotherapy • When those patients are depressed, their abulia seriously disrupts their flow of thoughts, and the sessions are nonproductive. • When they are manic, their flow of associations can be rapid, and their speech can be so pressured that the therapist may be flooded with material and may be unable to make appropriate interpretations or to assimilate the material into the patient's disrupted cognitive framework. Psychotherapy • American Psychiatric Association (APA) practice guideline for bipolar disorder – Recommends combined therapy as the best approach – It increases compliance, decreases relapse, and reduces the need for hospitalization