* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document 8260505
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct Xa inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Dydrogesterone wikipedia , lookup
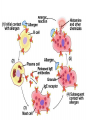
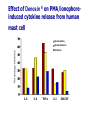
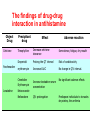
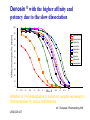
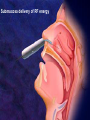
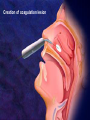
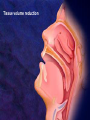
過敏性鼻炎治療的新趨勢 高雄榮總耳鼻喉部 紀昭全 醫師 May, 2007 鼻炎的分類 Allergic rhinitis (過敏性鼻炎) Nonallergic rhinitis (非過敏性鼻炎) infectious rhinitis (感染性鼻炎) 其他: Hormonal rhinitis: hypothyroidism,pregnancy,oral contraceptives, menstrual cycle Occupatiohal rhinitis Drug-induced rhinitis (藥物性鼻炎) Atrophic rhinitis (萎縮性鼻炎) vasomotor rhinitis (血管運動性): idiopathic rhinitis , (Postnasal drip? Chronic rhinitis?) Allergic rhinitis (過敏性鼻炎) Seasonal allergic rhinitis: pollens,molds (outdoor allergens) Perennial allergic rhinitis: dust mites, molds, and animal dander (indoor allergens) Often co-exist In collaboration with the World Health Organization ARIA program First phase: Development of evidence-based guidelines during a workshop held at WHO in December 1999 (J Allergy Clin Immunol, suppl, Nov 2001). Document has been endorsed by several allergy, respiratory, ENT and paediatric associations. ARIA program Second phase: To produce materials to help improve delivery of care to those with rhinitis. In particular a pocket guide To implement ARIA guidelines To update the workshop report ARIA The classification "seasonal" and "perennial" allergic rhinitis has been changed to "intermittent" and "persistent" allergic rhinitis ARIA Classification Duration of symptom Presentation with severity ARIA Classification Intermittent . < 4 days per week . or < 4 weeks Persistent . ≥ 4 days per week . and ≥ 4 weeks Moderate-severe Mild normal sleep & no impairment of daily activities, sport, leisure & normal work and school & no troublesome symptoms one or more items . abnormal sleep . impairment of daily activities, sport, leisure . abnormal work and school . troublesome symptoms PATHOPHYSIOLOGY (1) Basophils and mast cells release histamine during the early-phase reaction, whereas basophils alone are considered the predominant source of histamine in the late-phase response. Histamine is the major mediator released after immunological challenge by mast cells and basophils. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY (2) Other important components of the earlyphase and late-phase allergic response are cytokines, interleukin (IL) 3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, and IL-8, and the cellular adhesion molecules such as intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and E selectin, leukotrienes, and prostaglandins. Pharmacotherapy Antihistamine Corticosteroid: intra-nasal , oral Decongestant: topical , oral Mast cell destablizer first-generation H1antihistamines diphenhydramine and chlorpheniramine, are available as over-the-counter preparations, whereas others, such as hydroxyzine, are available by prescription. poor receptor selectivity for the H1-receptor and block muscarinic receptors, causing substantial anticholinergic effects dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention, and tachycardia, and conferring an overall unfavorable risk-benefit ratio. second-generation, H1antihistamines Since 1980, produced more specific H1-receptor selectivity faster onset of action, longer duration of action, greater potency, or fewer adverse events. Can not cross BBB (blood-brain barrier) Available US SecondGeneration Antihistamines Desloratadine Loratadine Cetirizine Fexofenadine 5(mg/d) 10(mg/d) 10(mg/d) 180(mg/d) ANTIALLERGIC AND ANTIINFLAMMATORY EFFECTS newer-generation oral antihistamines have been shown to have a range of additional antiinflammatory properties; however, the mechanism of action for these effects remains unclear. Effect of Denosin ® on PMA/ionophoreinduced cytokine release from human mast cell 70 Desloratadine Dexamethasone Percentage Inhibition 60 Cetirizine 50 40 30 20 10 0 IL-6 IL-8 TNF-α IL-3 GM-CSF UNDESIRABLE PHARMACOLOGICAL EFFECTS Drug Interactions Central Nervous System Effects Cardiotoxicity What is a drug interaction? Definition : Refers to an event with a negative patients’ consequence that is associated with the specific combination of two or more drugs. Wider ranging definition may include any or all of the following : Drug-drug interaction Drug-disease state interaction Drug-food interaction Drug interaction-a big problem Drug interaction are responsible for 3% to 10% of admissions of older patients to the hospital in USA. When two for four different drugs are taken, the potential for interaction is 6%, but the risk increases to 50% with five drugs and to almost 100% with eight drugs. The Fatal Drug-Drug Interaction Product Brand Name Launch Withdrawal from USA Terfenadine Teldane 1985 1997 Astemizole Hismanal 1988 1999 Ketoconazole, erythromycin, marcolides --- Torsades de points The findings of drug-food Interaction in antihistamine Object drug Food Effect Astemizole Food Reduce absorption by 60% fexofenadine Grapefruit/ Apple/Orange juice Reduce bioavailability by 60~80% The findings of drug-drug interaction in antihistamine Object Drug Cetirizine Fexofenadine Loratadine Precipitant drug Effect Adverse reaction Theophylline Decrease cetirizine clearance Somnolence, fatigue, dry mouth Droperidol Prolong the QT interval Risk of cardiotoxicity erythromycin Increased AUC No change in QTc interval. Cimetidine Erythromycin Ketoconazole Increase loratadine serum concentration Nefazodone QTc prolongation No significant adverse effects Predispose individuals to torsades de pointes, the arrthmia Denosin ® pharmacokinetics Denosin ® with multiple pathways in Allergic Rhinitis Anti-allergic effect Anti-inflammatory effect Decongestion effect Immune-modulating effect Denosin ® with the higher affinity and potency due to the slow dissociation %Maximum specific binding 100 90 Norastemizole Desloratadine 80 Cabastine 70 Loratadine Terfenadine 60 Cetirizine Ebastine 50 Astemizole 40 Fexofenadine 30 20 10 0 -11 -10.5 -10 -9.5 -9 -8.5 -8 -7.5 -7 Inhibitor, M -6.5 -6 -5.5 -5 Inhibition of [3H ]desloratadine to human H1 receptor expressed on CHO membranes by various antihistamine ref : European J.Pharmacology 449 (2002)229~237 The Rank Order of Potency Among Antihistamines Norastemizole > Desloratadine > Carebastine > Cetirizine > Terfenadine > Astemizole > Ebastine > Loratadine > Fexofenadine ref : European J.Pharmacology 449 (2002)229~237 Denosin ® Desloratadine is the only antihistamine with least drug-drug interaction due to without CYP450 metabolism, which contributed to safety of complicated therapy in allergic diseases. Lack of Interaction Between Denosin ® and Erythromycin 10 1 Desloratadine+placebo Desloratadine +erythromycin 3-OH desloratadine + placebo 3-OH desloratadine +erythromycin 0.1 0 4 8 12 16 20 24 Mean plasma desloratadine and 3-hydroxy (3-OH) desloratadine comcentrations on day 10 following oral administration of 7.5mg desloratadine with erythromycin or with placebo to healthy adult volunteers(n=24) ref : Clin Pharmacokinetics 2002;41 Suppl.29-35 Lack of Interaction Between Denosin ® and Ketoconazole Mean(± SEM) plasma desloratadine concentration-time profile Day 10 following oral administration of 7.5mg desloratdine with ketoconazole or with placebo to healthy adult volunteers(n=24) ref : Clin Pharmacokinet 2002;41 Suppl1:37~44 Comparison with other Antihistamines Difference of Pharmacokinetics in Denosin ® v.s Loratadine Desloratadine Loratadine Potency ++++ ++ Decongestion effect ++++ _ Drug interaction with CYP3A4 inhibitors (Macrolide, antifungals) with CYP2D6 inhibitors(H2-blocker,) No No First-pass Metabolism No Metabolite T1/2 3-OH desloratadine ↑ Plasma Concentration ↓ Plasma Concentration Yes >13 metabolites 27 hr 7.8 hr Onset 1 hr 2 hr Sedation 2.1% 8% NHI price 12.2/ tab 12/ tab Comparison with other antihistamines Desloratadine Levocetirizine Potency ++++ Decongestion effect ++++ ++ + No No No available No available Potentially Potentially Drug interaction with CYP3A4 inhibitors (Macrolide, antifungals) with CYP2D6 inhibitors (H2-blocker) ++ Fexofenadine No + First-pass Metabolism No T1/2 27 hr 7 hr 14.4 hr Onset 1 hr 0.8 hr 1-2 hr Sedation 2.1% NHI price $ 12.2/ tab No available 14%? $ 11.8/ tab No 1.8% $16.2/ 180mg tab $6/60mg tab Denosin ® meets ARIA / EAACI criteria ARIA/EAACI criteria for antihistamine Potent and selective H1 receptor blockade Additive anti-allergic activities No clinically relevant pharmacokinetic interference by foods, medications or intestinal transport proteins No known interaction with Cytochrome P450 (CYP3A) No known interaction with disease to avoid toxic reactions Efficacy for all nasal symptoms including nasal obstruction Improvement of eye symptoms Improvement of asthma symptoms(short term studies) Reduction of asthma exacerbations(long term studies) An improvement of pulmonary function tests, FEV1 and peak flow rates are usually not altered. ARIA/EAACI criteria for antihistamine No sedation or cognitive or psychomotor impairment No anti-cholinergic effects, no weight gain No cardiac side effects Possible use in pregnancy and breast feeding Rapid onset of action, long duration, at least persistence 24-h dosing period, so the drug can be administration once a day No likelihood of development of tolerance(tachyphylaxis) Indication Allergic rhinitis Chronic idiopathic urticaria Dosage and Usage Over 12 years old. In patients with liver or renal impairment, a starting dose of one 5mg tablet every other day. Pregnancy Pregnancy Category C Contraindications Denosin®(desloratadine) is contraindicated in patients are hypersensitive to this medication or any its ingredients, or to loratadine. Second generation antihistamine 2o Antihistamine (oral) Cetirizine (Metabolite of hydroxyzine) Desloratadine (Metabolite of loratadine) Fexofenadine (Metabolite of off-market terfenadine) Protein binding 93% 82-89% 60-70% Half-life Elimination t ½(hours) t ½(hours) 7-10 17.23-24 16-23 8.3 27 14.4 Pregnancy category B C C Cardiac K+ channel blocking No Metabolism Renal or hepatic impaired Limited 1st pass, 70%/10% unchanged in urine/feces Decrease dose by 50% No Extensive 87% No adjustment Possible Limited 1st pass,Unchange d 80%,/1% feces/urine Decrease dose by 50% and dose qd High CYP 3A4,lower CYP 2D6, 40%/,40% urine/feces Decrease interval to Loratadine 97% 7.8-11 8.4 to 28 for B No every metabolite day Source:Drug and Comparisons Facts accessed 05/24/04, Renwick et al,1999, Marttila et al,1999, Horak etother al, 1999. Treatment conclusion 1st line Basic Antihistamine Intranasal corticosteroids Additive Decongestants Leukotriene-receptor antagonist Nasal irrigation Intranasal anticholinergic 2nd line Immunotherapy Subcutaneous Sublingual Oral/depot corticosteroid +antihistamine J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006;118:985-998. Treatment of allergic rhinitis (ARIA) Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma moderate severe intermittent mild persistent moderate severe persistent mild intermittent intra-nasal steroid local chromone oral or local non-sedative H1-blocker intra-nasal decongestant (<10 days) or oral decongestant allergen and irritant avoidance immunotherapy 外科手術在鼻過敏的角色 冷凍治療 Submucosa turbinectomy CO2 laser KTP laser radiofrequency Submucosa delivery of RF energy Creation of coagulation lesion Tissue volume reduction Thanks!