* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Toxicology Drugs
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Urban legends about drugs wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
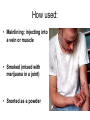
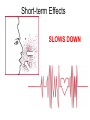
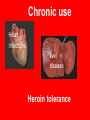
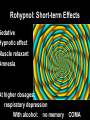
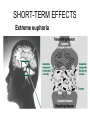
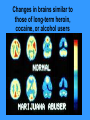
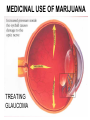
TOXICOLOGY DRUGS DRUGS • NATURAL OR SYNTHETIC SUBSTANCES • USED TO PRODUCE PSYCHOLOGICAL OR PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS Psychological dependence Psychological Dependence Drug is used to fulfill EMOTIONAL needs - Cope with life - To feel more comfortable in social settings CRACK is the most PSYCHOLOGICALLY addictive Physical Dependence Physical Dependence • Physical dependence means the body gets used to the drug, it needs more and more of it to accomplish the same effect. • Finally, the drug is merely used to counteract the withdrawal symptoms that appear when no drugs are being taken. Perspiring, feeling cold, goose flesh/pimples (cold turkey), running nose, stomach cramps, aching muscles, diarrhea. DRUGS • NECESSARY TO SUSTAIN AND PROLONG LIFE EXAMPLES: • INSULIN • AIDS DRUGS DRUGS • • AS AN ESCAPE DRUGS AS A WAY TO END LIFE LEGAL EUTHANASIA: IN US OREGON NETHERLANDS, BELGIUM SWITZERLAND Narcotics Substances that reduce or relieve pain and induce sleep Heroin Derived from morphine which is obtained from the opium poppy Street Names: “dope” “smack” “China white” “Cheese” “Black Tar” How used: • Mainlining: injecting into a vein or muscle • Smoked (mixed with marijuana in a joint) • Snorted as a powder Short-term Effects » SLOWS DOWN Euphoria Clouds Mental Function Long-Term Effects Most physically Addictive drug Chronic use Heart Infections liver disease Heroin tolerance CODEINE • Prepared synthetically from MORPHINE • 1/6 as strong as morphine Methadone synthetic opiate Used to treat heroin addiction Propoxyphene (Darvon) Pain Reliever 1 of top 10 drugs found in bodies at autopsy Oxycontin – – acetaminophen (tylenol) and oxycodone – used to treat severe pain – – – tablets crushed & ingested or dissolved in water and injected SHORT-TERM EFFECTS OF OXYCONTIN • “RUSH” SIMILAR TO HEROIN • RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION • CONSTIPATION, NAUSEA, VOMITING • CARDIAC ARREST • SEVERE WITHDRAWAL (“FLU x 1000”- 2 WKS) Depressants Barbiturates Relax and produce sleep “Barbs” “Yellow Jackets” “Blue Devils” “Reds” Fast-acting barbiturates are the most commonly abused : Secobarbital, Pentobarbital, Amobarbital 1/3 of all Drug-related deaths Short-term Effects • Relaxes • Impairment of higher thinking • Induces sleep Long-term Effects of Barbiturates Withdrawal: • • • • • Insomnia Muscle spasms Delirium Convulsions Can lead to death Methaqualone • Quaaludes “Ludes” • Non-barbiturate depressant • Powerful sedative & muscle relaxant Tranquilizers • Depressants that relax • Proper dosage does not impair Ketamine – • Veterinarian anesthesia “Special K” “Vitamin K” new ecstasy Ketamine Hallucinogenatory effects: -Euphoria -Delirium -Amnesia -High blood pressure Higher doses can stop breathing-DEATH Mixed in drinks As a powder–snorted “K-HOLE” • NO PAIN • HALLUCINOGEN • COMA GHB “Liquid X” “G” “Liquid E” GHB IS MADE OF: A CNS DEPRESSANT GHB: DATE-RAPE DRUG • COLORLESS • ODORLESS • SLIGHT, BITTER TASTE • DISSOLVES IN WATER GHB: Short-term Effects • • • • • • • Drowsiness Vomiting Delusions Depression Amnesia Coma Death Increasing dosages GHB: Long-term Effects • Physically addictive • unknown “Roofies” Tasteless Odorless Dissolves in water Used crushed Also Legal in 60 countries ….not in U.S. Rohypnol: Short-term Effects Sedative Hypnotic effect Muscle relaxant Amnesia At higher dosages: respiratory depression With alcohol: no memory COMA HUFFING: INHALANT ABUSE • RAG IS SOAKED IN INHALANT AND PLACED IN MOUTH. THE INHALANT VAPORIZES AND GOES TO THE LUNGS,THEN TO THE BRAIN • COMMON HOUSEHOLD PRODUCTS • ONLY TYPE OF DRUG ABUSE MORE COMMON IN YOUNGER CHILDREN THAN IN TEENS GLUE-SNIFFING USUALLY TOLUENE SHORT-TERM EFFECTS: Exhilaration, euphoria,slurred Speech, impaired judgement, Double vision LONG-TERM EFFECTS: Liver, heart, brain damage DEATH LEGAL STIMULANTS SPEEDS UP CNS AMPHETAMINES • SYNTHETIC STIMULANTS • “UPPERS” • “SPEED” THE NAZIS USED AMPHETAMINES SO TROOPS WOULD NOT NEED SLEEP WORLD WAR II SOLDIERS USED AMPHETAMINES TO STAY AWAKE METHAMPHETAMINES “ICE” “CRANK” “METH” “SPEED” METHAMPHETAMINES • Powerful stimulant • Taken orally, injected, snorted, or smoked • Use is on rise because it is mixed with Ecstacy Meth: Short-term Effects Increased energy Decrease in appetite Euphoria Irritability Aggression Then EXHAUSTION and DEPRESSION Decrease in Heart and Breathing Rates Violent, destructive behavior Hallucinations Acute psychosis Delusions “Meth Mites” Your Brain on Meth.. • Healthy Brain SPECTscan – shows blood flow to brain Meth Brain Effects Similar to Stroke or Alzheimers Meth: Long-term Effects • Can overdose on Meth COCAINE/CRACK (“WHITE COLLAR”) (“BLUE COLLAR”) “SNOW” “COKE” FROM COCA PLANT COCAINE: Snorted or dissolved in water And then injected CRACK: smoked or snorted SHORT-TERM EFFECTS Extreme euphoria COCAINE: SHORT-TERM EFFECTS • • • • • • Increased Body Temperature Increased Heart Rate Increased Blood Pressure Imsomnia Loss of appetite CARDIAC ARREST/RESPIRATORY FAILURE LONG-TERM EFFECTS • PARANOIA • AGGRESSION • STRONGEST PSYCHOLOGICALLY -ADDICTIVE DRUG STIMULANTS: RITALIN • Abused by crushing &snorting OR • Injected like heroin • euphoria RITALIN: SHORT-TERM EFFECTS SIMILAR TO COCAINE • • • • • • Increased Body Temperature Increased Heart Rate Increased Blood Pressure Imsomnia Loss of appetite CARDIAC ARREST/RESPIRATORY FAILURE LONG-TERM EFFECTS Irregular heartbeat & breathing Anxiety Paranoia Hallucinations Delusions HALLUCINOGENS AFFECTS MOODS ATTITUDES PERCEPTION MARIJUANA ACTIVE INGREDIENT: TetraHydroCannabinol - THC Short-term Effects: Distorted perception Problems with memory and learning MARIJUANA: LONG-TERM EFFECTS • HIGHER CONCENTRATION THAN TOBACCO OF CANCERCAUSING COMPOUNDS • STRONG PSYCHOLOGICAL DEPENDENCY Changes in brains similar to those of long-term heroin, cocaine, or alcohol users Is Marijuana a GATEWAY DRUG? • Koob, M.D., of the Scripps Research Institute says that studies of long-term exposure to cannabinoids, the active ingredient in marijuana, suggest that addiction to one drug could make a person vulnerable to abuse and addiction to other drugs. Cannabis abuse, he says, appears to activate corticotropin-releasing factor, a brain chemical that increases during periods of stress. Consequently, Koob says, this could "lead to a subtle disruption of brain processes that are then 'primed' for further and easier disruption by other drugs of abuse." George • Critics of the idea note that even if people who use cocaine started with marijuana, it is not clear that the marijuana use caused or encouraged the cocaine use: The person may simply have encountered marijuana first, and/or is the sort of person more inclined than others to experiment with a variety of illegal drugs. Fewer than one percent of marijuana users go on to become cocaine addicts. MEDICINAL USE OF MARIJUANA TREATING GLAUCOMA TREATING NAUSEA FROM CHEMOTHERAPY LSD “ACID” -Produced from ergot – a fungus -First synthesized in 1938 by Dr. Albert Hoffman LSD: Short-term Effects • Hallucinations • Alters mood • Distorts reality • Increases Heart Rate LSD: Long-Term Effects FLASHBACKS PSYCHOTIC REACTIONS (LOSS OF CONTACT WITH REALITY) PCP: PHENCYLIDINE • INTRAVENOUS ANASTETIC • “ANGEL DUST” “KILLER WEED” • SNORTED, SMOKED, OR INGESTED • Often used as an additive to marijuana, LSD, or methamphetamine PCP: Short-Term Effects • Increased breathing rate, blood pressure, and pulse rate • High doses: vomiting, nausea • Aggressive behavior • violence • inability to feel pain PCP: Long-term Effects • • • • Memory loss Speech difficulties Depression Mixing PCP with alcohol or other depressants can lead to coma or death ECSTASY • • • • MDMA A synthetic drug Tablet form “Adam” “Bean” “E” “XTC” Ecstacy: Short-Term Effects • • • • • Increase in REM EXCESSIVE energy FIRST EFFECTS Euphoria Serotonin high Pschological effects: confusion, depression, anxiety, paranoia • Physical Effects: nausea, blurred vision, HIGH BODY TEMPERATURES (104-1150F), DEHYDRATION, INCREASED HEART RATE, HYDRATION ECSTASY: Long-Term Effects • Permanent damage to neurons that release serotonin • Memory impairment • Kidney damage • Permanent brain damage • May develop addiction to HEROIN because it is often laced into Ecstacy ANABOLIC STEROIDS SYNTHETIC–RELATED TO TEST0STERONE INGESTED OR TOPICAL TESTOSTERONE: • ACCELERATED MUSCLE GROWTH SHORT-TERM • SECONDARY MALE EFFECTS CHARACTERISTICS • MASCULIZING EFFECTS ON FEMALES • DIMINISHED SEX DRIVE IN MALES • UNPROVOKED ANGER AND DESTRUCTIVE BEHAVIOR ANABOLIC STEROIDS: LONG-TERM EFFECTS • LIVER DISEASES • LIVER CANCER • FEMINIZATION OF MALES XENADRINE RFA-1: A DIETARY SUPPLEMENT • COMPOSED OF CAFFEINE AND EPHEDRA • TABLETS ARE INGESTED • SHORT-TERM EFFECTS: Increases blood pressure and heart rate, insomnia, increases METABOLISM LONG-TERM EFFECTS DRUG CONTROL LAWS THE CONTROLLED SUBSTANCE ACT OF 1970: DRUGS CLASSIFIED BY: 1. POTENTIAL FOR ABUSE 2. PHYSIOLOGICAL OR PSYCHOLOGICAL DEPENDENCE 3. MEDICAL VALUE SCHEDULE 1 DRUGS: • High potential for abuse • High potential for physiological and/or psychological dependence • No medical value SCHEDULE 1 DRUGS: HEROIN, MARIJUANA, LSD, METHQUOLENE SCHEDULE 2 DRUGS: • High potential for abuse • Potential for physiological and/or psychological dependence • ACCEPTED medical value • SCHEDULE 2 DRUGS: AMPETAMINES,COCAINE,METHODONE, PCP, and most BARBITURATES (amobarbital, secobarbital, pentobarbital) and DRONABINOL(A SYNTHETIC EQUIVALENT OF THC – TREATING GLAUCOMA AND EFFECTS OF CHEMOTHERAPY) SCHEDULE 3 DRUGS: • LESS potential for abuse • LOW TO MODERATE potential for physiological • HIGH psychological dependence • Medical use in US SCHEDULE 3 DRUGS: ALL BARBITURATES(EXCEPT PHENOBARBITOL) NOT COVERED IN SCHEDULE 2 , CODEINE, AND ANABOLIC STEROIDS SCHEDULE 4 DRUGS: • LOW potential for abuse • LIMITED potential for physiological and or psychological dependence • Medical use in US SCHEDULE 4 DRUGS: PHENOBARBITOL, DARVON, VALIUM SCHEDULE 5 DRUGS: • LOW potential for abuse • LOW potential for physiological and or psychological dependence • Medical use in US SCHEDULE 5 DRUGS: NON-NARCOTIC MEDICINES