* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bioprecursor Prodrugs
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
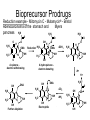
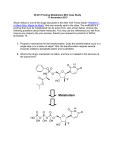
Bioprecursor Prodrugs Reduction example - Mitomycin C - Mutamycin® - Bristol Adenocarcinoma of the stomach and Myers pancreas H2N H2N O O H2 N OH OMe NH N H3 C O O H H2N Reduction H2N O O H OMe -OCH3 NH N H3 C O H2 N NH N + H3 C OH A hydroquinone electron donating A quinone electron withdrawing O H -H+ H+ OH H2 N H2 N H3 C N NH OH Further alkylation H2N DNA OH DNA O -CO2 H3 C OH N + Electrophile NH -NH3 O OH H2 N N H3 C OH NH Bioprecursor Prodrugs Phosphorylation example – H N O HO O H N I Viral Thymidine O Kinase O O O P O O O OH Iodoxuridine - Herplex® Allergan - lipid soluble! Opthalmic product for Herpes simplex keratitis Higher affininty for viral kinases than mammalian kinases but some toxicity O I Not lipid soluble OH ATP H N O O O O -O P O P O P O O O O O O I OH TWO mechanisms of action: 1. Inhibits DNA polymerase 2. Incorporated into DNA affording incorrect base pairing and template activity Chemical Delivery Systems • We have already seen 2 examples of this: – Sulfasalazine – an azo compound – Methenamine – An urinary antibacterial agent • Requirements – Prodrug reach the site of action in high concentrations – Knowledge of high metabolism at site – Other factors • Extent of organ or site perfusion • Information on the rate of prodrug conversion to the active form at both target and non-target sites • Rate of input/output of prodrug from the target site • Limit side effects and increase effectiveness Chemical Delivery Systems Types of carriers that have been used Proteins– Polysaccharides– Liposomes– Emulsions– Cellular carriers (erythrocytes and leukocytes)– Magnetic control targeting– Implanted mechanical pumps– What is the Basic Goal? Protect a non-specific biological environment from a drug– Protect a drug from a non-specific biological environment– Especially evaluated for drugs with a narrow therapeutic window especially anti-cancer agents – Chemical Delivery Systems • The ideal situation: – – – – Prodrug readily transported to the site of action Prodrug is rapidly absorbed at the site Selective and rapid conversion to the active drug Kidney and Liver are easy targets due to high perfusion and high metabolic rates • Other tissue sites can be problematic for the same reasons – Drug migrate slowly (site of action to a site of excretion) – Ideal situation is VERY complex to achieve • Example: Methenamine – the lower the pH, the faster the rate of formaldehyde formed – blood pH 7.4 therefore, little formaldehyde formed Chemical Delivery Systems Example: Cancer Chemotherapy Tumor cells have a much higher growth fraction– This translates into higher enzymatic activity that can be exploited– Target a prodrug to these sites and exploit higher enzyme activity– Example: L-Dopa or Levodopa – Anti-Parkinsonism agent Larodopa® – Roche and Dopar® - Procter & Gamble– HO HO HO CO2H Decarboxylase NH2 HO NH2 Dopamine Brain has a specific transport system for L-amino acids– Dopamine does not cross the blood brain barrier efficiently, is rapidly – metabolized by oxidative deamination, and can cause peripheral side effects