* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hepatitis A-E Viruses part ІІ
Viral phylodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Plant virus wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to viruses wikipedia , lookup
Oncolytic virus wikipedia , lookup
Social history of viruses wikipedia , lookup
Virus quantification wikipedia , lookup
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
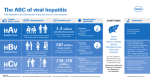
INFLAMMATON OF THE LIVER Hepatitis D-C-E Viruses part ІІ Dr. Osama AL Jiffri Hepatitis D (Delta) Virus Hepatitis D Structure Hepatitis D virus is found only in patients infected with hepatitis B Enveloped with SS RNA and forms a small particle coated with HBsAg 35-40nm Only antigen encoded is the delta antigen Hepatitis D (Delta) Virus d antigen HBsAg RNA Hepatitis D Virus Modes of Transmission • Percutanous xposures –injecting drug use • Mucosal exposures –sex contact Geographic Distribution of HDV Infection Taiwan Pacific Islands HDV Prevalence High Intermediate Low Very Low No Data Hepatitis D:Pathogenesis Pathogenesis – Immune mediated – Co-infection- infection with B at the same time (more severe) – Superinfection: acquisition of Hep D in chronically Hep B Sequelae of hepatitis D virus Hepatitis D - Clinical Features • Coinfection –severe acute disease –low risk of chronic infection • Superinfection –usually develop chronic HDV infection –high risk of severe chronic liver disease Hepatitis D: Diagnosis Serology: ELISA test (only on research ) Hepatitis D - Prevention • HBV-HDV Coinfection Pre or postexposure prophylaxis to prevent HBV infection • HBV-HDV Superinfection Education to reduce risk behaviors among persons with chronic HBV infection • Alpha interferon may help reduce hepatocellular damage Hepatitis C Non A -non B HEPATITIS Hepatitis C Structure and Classification Unclassified virus, Member of the flavivirus family (other members yellow fever and dengue) Enveloped single stranded RNA virus Humans and chimpanzees only known reservoirs (virus-specific protein in blood) 6 serotypes (genotypes) and multiple subtypes based on high variability of envelope glycoproteins Exposures Known to Be Associated With HCV Infection Injecting drug use Transfusion, transplant from infected donor Occupational exposure to blood – Mostly needle sticks Iatrogenic (unsafe injections) Birth to HCV-infected mother Sex with infected partner – Multiple sex partners Sources of Infection for Persons With Hepatitis C Injecting drug use 60% Sexual 15% Transfusion 10% (before screening) Occupational 4% Other 1%* Unknown 10% * Nosocomial; iatrogenic; perinatal Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Prenatal Transmission of HCV Transmission only from women HCVRNA positive at delivery – Average rate of infection 6% – Higher (17%) if woman co-infected with HIV – Role of viral titer unclear No association with – Delivery method – Breastfeeding HCV: Pathogenesis Blood-borne pathogen that infects hepatocytes Much like Hep A and B, liver damage and clinical illness Likely cytotoxic T cells that mediate most of the damage Like other chronic liver diseases (Hep B and chronic alcoholism), can cause hepatocellular ca (HCC) Features of Hepatitis C Virus Infection Incubation period Acute illness (jaundice) Case fatality rate Chronic infection Chronic hepatitis Agerelated Cirrhosis Mortality Average 6-7 weeks Range 2-26 weeks Mild (<20%) Low 60%-85% 10%-70% <5%-20% 1%-5% Hepatitis C: Clinical Features Acute infection asymptomatic in over 80% of patients, when present, acute illness usually mild – Acute symptoms include jaundice, nausea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, dark urine Chronic Hepatitis C Factors Promoting Progression or Severity Increased alcohol intake Age > 40 years at time of infection HIV co-infection Other – Male gender – Chronic HBV co-infection Hepatitis C: Diagnosis Dose not grow in cell culture ELISA-a serological test which is usually positive within 2-5 months after infection – 3rd generation assays now 99% specific and sensitive Confirmatory testing – PCR (positive 1-2 weeks post infection) both quantitative and qualitative (I.e. ye/no) available – RIBA (recombinant immunoblot assay)- looks for 2 or more antibodies to HCV viral antigens Genotype testing done when treatment anticipated HCV Infection Testing Algorithm for Diagnosis of Asymptomatic Persons Screening Test for AntiHCV Negative STOP Positive OR RIBA for Anti-HCV Negative STOP Negative Indeterminate Additional Laboratory Evaluation (e.g. PCR, ALT) Negative PCR, Normal ALT Positive PCR, Abnormal ALT Source: MMWR 1998;47 (No. RR 19) NAT for HCV RNA Positive Medical Evaluation Positive Hepatitis C Therapy Systemic effects (fatigue, myalgias, depression, anemia) Standard of care is pegylated interferon alpha and ribavirin Overall response rate to treatment is 4050% (higher for non 1 genotypes) Hepatitis E Virus Hepatitis E Non-enveloped single stranded RNA virus Resembles calicivirus or Norwalk agent Similar illness to Hep A except high mortality in pregnant women Geographic Distribution of Hepatitis E Hepatitis E - Epidemiology • Most outbreaks associated with fecally contaminated drinking water • Minimal person-to-person transmission • U.S. cases usually have history of travel to HEV-endemic areas Hepatitis E - Clinical Features • Incubation period: • Case-fatality rate: Average 40 days Range 15-60 days Overall, 1%-3% Pregnant women, 15%-25% • Illness severity: Increased with age • Chronic sequelae: None identified Hepatitis E Virus Infection Symptoms ALT IgG anti-HEV Titer IgM anti-HEV Virus in stool 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Weeks after Exposure 8 9 1 0 1 1 1 2 1 3 Prevention and Control Measures for Travelers to HEV-Endemic Regions • Avoid drinking water (and beverages with ice) of unknown purity, uncooked shellfish, and uncooked fruit/vegetables not peeled or prepared by traveler • IG prepared from donors in Western countries does not prevent infection • Vaccine? Heptitis viruses A B C D E Virus genome SSRNA DSDNA SSRNA SSRNA Unknown Transmission faecal- Sex,blood, Blood,other oral,food congenital ,water As for HBV water-borne, epidemic www.kau.edu.sa/ojiffri الملفات سيرة ذاتية FID 6370 6373 13534 13537 أخرى العنوان ● نماذج الوصف منشورات تاريخ اإلضافة Papilloma فيروسات viruses محاضرة رقم and ()1 Poxviruses Viral 11/7/200 Agents فيروسات محاضرة رقم 8 5:53:55 Causingتحميل الملف PM Gastroent ()2 eritis 12/26/20 BIOSAFE BIOSAFE 08 5:15:12تحميل الملف TY-01 TY-01 PM 12/26/20 BIOSAFE BIOSAFE 08 5:39:23تحميل الملف TY-02 TY-02 PM 11/7/200 8 5:43:56تحميل الملف PM