* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Drug Inter. - Dr.
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
List of comic book drugs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
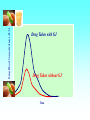
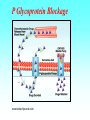
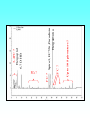
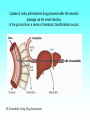
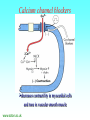
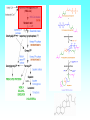
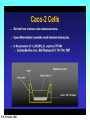
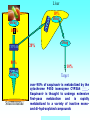
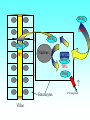
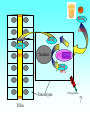
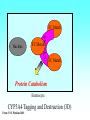
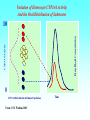
Grapefruit Juice-Drug Interaction Paul F. Cancalon Florida Department of Citrus http://www.wlap.org/wl-repository/umich/cacr/grand-rounds/20031202-annarbor-01-watkins/real/sld011.htm P. B. Watkins 2003 Drug Blood Concentration (AUC) Drug Taken with GJ Drug Taken without GJ Time P. B. Watkins 2003 Cytochrome P450 Cytochrome P450 Definition Cytochrome P450 enzymes are a superfamily of more than 160 known members that play a major role in the metabolism a wide array of xenobiotics including drugs, chemical carcinogens, insecticides, petroleum products, and other environmental pollutants. Although the liver is the primary organ for drug metabolism, extrahepatic tissues such as lung, kidney and intestine, also play an important role for detoxification or biotransformation of xenobiotics. Each tissue has a unique P450 isozyme distribution and regulatory mechanism for cytochrome P450 gene (CYP) expression. Cytochrome P450 Naming classification: CYP 3 A 4 *15 A-B family isoenzyme allele >40% sequencesub-family homology >55% sequencehomology J R Oesterheld : Drug-Drug Interactions Model of rat P450 2B1, showing mode of membrane attachment home.ccr.cancer.gov Lock/Key or Enzyme/Substrate Reaction Irreversible Inhibition P-Glycoprotein Cell Membrane P Glycoprotein Blockage www.biotechjournal.com Furanocoumarins P450 Interactions Furanocoumarins as potent chemical defenses Furanocoumarins are toxic compounds found primarily in species of the Apiaceae and Rutacea. They come in a variety of flavors and have adverse affects on wide variety of organisms, ranging from bacteria to mammals. Some of the furanocoumarins are photoactive--their toxicity is enhanced in the presence of ultraviolet radiation.. The furanocoumarins found in wild parsnip play a dominant role in resistance of this plant to its principal enemy the parsnip webworm May R. Berenbaum Two potential outcomes of a coevolutionary interaction are an escalating arms race Diversification of cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (P450s) is thought to result from antagonistic interactions between plants and their herbivorous enemies Grapefruit Furanocoumarins O O O OH O OH The immediate precursors for furanocoumarin synthesis are umbelliferone and isoprene. Two categories of furanocoumarins are produced; the linear furanocoumarins have the furan ring in line with the benz-2-pyrone nucleus, while the angular furanocoumarins have the furan ring oriented at an angle to the nucleus. O O O O O O O O O O OH Bergapten Bergaptol O O O O Bergamottin O O O OH O O O OH 6,7-DHB 6,7-Epoxybergamottin O O O O Paradisin C O O Paradisin A O O O OH OH P. B. Watkins 2003 Spiro3,FC726,Paradisin Bergamotin 3-4FC ? Bergaptol 6,7 DHB Up to 10 Spiroesters ? FC ? FC ? FCs ? 040610Bergaptol_Bergamottin_Std_MSMS #356-364 RT: 5.02-5.12 AV: 5 NL: 1.00E5 T: + c ESI Full ms2 [email protected] [ 55.00-210.00] 159.1 100 95 90 85 80 O 75 O 70 O 65 OH 60 147.1 55 Bergaptol 50 45 40 175.0 35 131.1 30 203.2 25 20 160.1 15 10 148.3 132.1 5 103.2 158.6 142.1 118.9 161.5 176.1 174.1 204.2 183.8 186.8 0 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 m/z 140 150 160 170 180 190 202.2 200 210 040610Bergaptol_Bergamottin_Std_MSMS #2638-2644 RT: 34.95-35.02 AV: 4 NL: 2.50E7 T: + c ESI Full ms2 [email protected] [ 90.00-400.00] 203.2 100 O 95 O 90 O 85 OH 80 75 70 Bergaptol 65 60 55 O O O 50 45 O 40 35 30 Bergamottin Geranyl side chain 25 20 15 10 243.3 137.1 5 0 229.0 109.1 135.5 137.8 100 150 271.1 202.6 200 250 m/z 283.1 297.1 300 321.1 339.1 359.9 350 379.2 400 0402Dihydroxybergamottin #20 RT: 0.42 AV: 1 NL: 1.82E5 T: + c ESI Full ms2 [email protected] [ 100.00-400.00] 354.8 100 95 90 85 80 75 O 70 O O O O 65 O 60 OH OH 55 O 50 203.2 OH 45 OH Bergaptol 40 6,7-DHB OH 35 30 25 20 15 153.0 10 337.0 135.0 5 0 100 170.9 243.4 203.8 120 140 160 180 200 220 240 259.8 260 m/z 335.5 280 300 320 352.6 350.7 355.6 340 360 372.0 373.1 380 395.3 400 0303PSL_Ruby_Juice_02 #1792 RT: 37.64 AV: 1 NL: 8.67E6 T: + c ESI Full ms [ 90.00-1500.00] 749.2 100 95 90 85 Spiroester3 80 75 O 70 O O 65 60 O 55 Spiro3 50 Bergaptol 45 750.2 O 40 O O 35 30 O 355.0 203.3 25 OH O 372.8 20 726.9 OH 15 OH 792.0 OH 10 5 153.0 219.2 337.1 697.8 557.0 613.4 391.1 457.0 548.3 656.1 873.2 910.0 983.7 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 1473.6 793.1 800 m/z 900 1000 1095.1 1142.3 1185.2 1100 1200 1337.4 1389.0 1300 1400 1500 The order of inhibitory potency of these compou nds was FC726>6,7DHBG>bergamottin> bergapten> bergaptol Ohnishi A et al. : Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Jul;130(6):1369-77. O > O O > O OH O O O > O O O O O OH bergapten 6,7 DHB Paradisin A (Spiro 3) bergamottin > O O O OH bergaptol Drug Bioavailability Uptake of orally administered drug proceeds after the stomach passage via the small intestine. In the gut and liver, a series of metabolic transformation occurs. J R Oesterheld : Drug-Drug Interactions www.siumed.edu/~dking2/ erg/images arbl.cvmbs.colostate.edu/.../ smallgut/villus Site of Action of Some Drugs Affected by Grapefruit Juice Calcium channel blockers Target Blocked - calcium channel blockers in actionwww.thediabetesvillage.com Blocked - calcium channel blockers in actionwww.thediabetesvillage.com Calcium channel blockers decreases contractility in myocardial cells and tone in vascular smooth muscle www.soton.ac.uk Drug- Grapefruit Juice Interaction P. B. Watkins 2003 P. B. Watkins 2003 Time-course of recovery of CYP3A function after single doses of grapefruit juice. Greenblatt DJ, von Moltke LL, Harmatz JS, Chen G, Weemhoff JL, Jen C, Kelley CJ, LeDuc BW and Zinny MA. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2003;74:121-12 Liver microsome method microsome Artefactual spherical particle, not present in the living cell, derived from pieces of the endoplasmic reticulum present in homogenates of tissues or cells: microsomes sediment from such homogenates when centrifuged at 10 6 g and higher: the microsomal fraction obtained in this way is often used as a source of mono-oxygenase enzymes micro.magnet.fsu.edu Paradisin C: a new CYP3A4 inhibitor from grapefruit juice Tetrahedron 58 (2002) 6631-6635Tetrahedron 58 (2002) 6631-6635 CYP3A4 inhibition assay CYPP3A4 activity is based on nifedipine oxidation. 100 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) containing 50 uM nifedipine 5 mM glucose-6-phosphate, 0.5 mM 3-NADP+, glucose-6phosphate dehydrogenase. CYP3A4 is preincubated in 7 uL of the buffer at 37EC for 5 min and added to the sample solution The solution is incubated at 37EC for 1 h. The residue is analyzed by reverse phase HPLC for the nifedipine metabolite (nifedipine pyridine), and for nifedipine. The value of IC50, the concentration required for 50% inhibition of CYP3A4 activity. Liver 10% Drug Drug 100% CYP3A4 80% Drug Small Intestine 20% Drug 10% Target over 90% of saquinavir is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4 {01} . Saquinavir is thought to undergo extensive first-pass metabolism and is rapidly metabolized to a variety of inactive monoand di-hydroxylated compounds Drug 100% Drug Drug 30% Nucleus CYP3A4 Drug 70% Drug ? Enterocytes Villus P Glycoprotein FC Drug 100% Drug Drug 70% Nucleus FCCYP3A4 Drug 30% X Enterocytes Villus P Glycoprotein ? CYP3A4 Nucleus FC FC Competitive Enzyme/Substrate Binding Enterocyte From: P. B. Watkins 2003 Nucleus CYP3A4 FC Metab FC Metab FC Metab Enzymatic Metabolism of FC (1h) Enterocyte From: P. B. Watkins 2003 Nucleus CYP3A4 FC Metab FC Metab FC Metab Protein Catabolism Enterocyte CYP3A4 Tagging and Destruction (3D) From: P. B. Watkins 2003 P. B. Watkins 2003 Variation of Enterocyte CYP3A4 Activity And the Oral Distribution of Substrates CYP3A4 Activity Drug Blood Concentration 10 0 CYP3A4 Distribution in Human Population From: P. B. Watkins 2003 Time P. B. Watkins 2003 Conclusions What are the active compounds DHB or its metabolites? Are P-glycoproteins involved in GJ/Drug Interactions ? Is the liver involved in GJ/Drug Inter and do CYP3A4 and Pgly act similarly in the intestine & the liver ? Are most GJ/Drug Interactions problems factored in during drug testing ? Information Gathering Potential Drug Interactions With Grapefruit Lead author: William A. Kehoe, Pharm.D., MA, Drug(s) Findings Implications Amiodarone (Cordarone) Increases blood levels of the drug. Watch for irregular heart rhythm. Alprazolam (Xanax) Diazepam (Valium) Midazolam (Versed) Triazolam (Halcion) Increases blood concentrations by inhibiting the intestinal metabolism. Watch for possible increased sedation. Clinical significance on cognitive function is not known. One reference indicates alprazolam may have a small or negligible effect. Buspirone (BuSpar) Increases absorption and blood concentrations. Despite significant effects, the action of the drug does not appear to be affected significantly. Caffeine Decreases caffeine metabolism. Watch for possible increase in side effects, such as nervousness or insomnia. Amlodipine (Norvasc) Diltiazem (Cardizem) Felodipine (Plendil) Nicardipine (Cardene) Nifedipine (Procardia, Adalat) Nimodipine (Nimotop) Nisoldipine (Sular) Verapamil (Calan, Verelan) Increases blood concentrations, most likely the result of grapefruit inhibiting the intestinal metabolism. Look for signs of toxicity, such as flushing, headache, fast heart rate, and low blood pressure. Some references dispute the clinical relevance of the interactions with amlodipine, diltiazem, and verapamil. However, there is considerable interindividual variability in the effect of grapefruit on drug metabolism. Carbamazepine (Tegretol) Increases blood concentrations. Look for signs of toxicity, such as dizziness, poor balance and coordination, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, tremor, and agitation. Drug(s) Findings Implications Carvedilol (Coreg) Increases blood levels. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known. Cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune) Increases blood concentrations. Look for signs of toxicity, such as kidney and liver damage, and immune suppression. Estrogens Increases absorption and blood concentrations. Effects are unknown at this time. Fexofenadine (Allegra) Might decrease oral absorption and blood levels. The clinical significance of this interaction is unknown. Tell patients it’s best to take fexofenadine with a plain glass of water. Atorvastatin (Lipitor) Lovastatin (Mevacor) Simvastatin (Zocor) Increases absorption and blood concentrations. Grapefruit interaction unlikely with pravastatin (Pravachol) or fluvastatin (Lescol). Look for increased toxicity, such as headache, GI complaints, and muscle pain. Itraconazole (Sporanox) Impairs absorption. Losartan (Cozaar) Might reduce the blood levels of the drug. Methylprednisolone (cortisone) Increases plasma concentration ofl methylprednisolone. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known. Theoretically it could decrease efficacy of itraconazole. Might reduce the effectiveness of losartan, but further studies are needed to determine significance. Consumption of large amounts of grapefruit might increase the risk of adverse effects. Quinidine Decreases drug elimination. The clinical significance of this interaction is unknown. Sertraline (Zoloft) Increases serum concentrations. The clinical significance of this interaction is unknown P450 DRUG-INTERACTIONS TABLE Substrates 1A2 2B6 2C19 2C9 2D6 2E1 3A4,5,7 amitriptyline caffeine clomipramine clozapine cyclobenzaprine estradiol fluvoxamine haloperidol imipramine N-DeMe mexiletine naproxen ondansetron phenacetin=> acetaminophen=>NAP QI propranolol riluzole ropivacaine tacrine theophylline verapamil (R)warfarin zileuton zolmitriptan bupropion cyclophosphamid e efavirenz ifosfamide methadone Proton Pump Inhibitors: lansoprazole omeprazole pantoprazole E-3810 NSAIDs: diclofenac ibuprofen meloxicam Snaproxen=>N or piroxicam suprofen Beta Blockers: carvedilol S-metoprolol propafenone timolol Anesthetics: enflurane halothane isoflurane methoxyfluran e sevoflurane Macrolide antibiotics: clarithromycin erythromycin (not 3A5) NOT azithromycin acetaminophe n =>NAPQI aniline benzene chlorzoxazon e ethanol N,N-dimethyl formamide theophylline =>8-OH Anti-arrhythmics: quinidine=>3-OH (not 3A5) Anti-epileptics: diazepam=>Nor phenytoin(O) S-mephenytoin phenobarbitone amitriptyline carisoprodol citalopram clomipramine cyclophosphamid e hexobarbital imipramine NDeME indomethacin R-mephobarbital moclobemide nelfinavir nilutamide primidone progesterone proguanil propranolol teniposide R-warfarin=>8OH Oral Hypoglycemic Agents: tolbutamide glipizide Angiotensin II Blockers: losartan irbesartan amitriptyline celecoxib fluoxetine fluvastatin glyburide phenytoin=>4OH rosiglitazone tamoxifen torsemide S-warfarin Antidepressants: amitriptyline clomipramine desipramine imipramine paroxetine Antipsychotics: haloperidol perphenazine risperidone=>9OH thioridazine alprenolol amphetamine bufuralol chlorpheniramine chlorpromazine codeine (=>OdesMe) debrisoquine dexfenfluramine dextromethorphan encainide flecainide fluoxetine fluvoxamine lidocaine metoclopramide methoxyamphetamin e mexiletine nortriptyline minaprine ondansetron perhexiline phenacetin phenformin propranolol quanoxan sparteine tamoxifen tramadol venlafaxine Benzodiazepines : alprazolam diazepam=>3OH midazolam triazolam Immune Modulators: cyclosporine tacrolimus (FK506) HIV Antivirals: indinavir nelfinavir ritonavir saquinavir Prokinetic: cisapride Antihistamines: astemizole chlorpheniramine terfenidine Calcium Channel Blockers: amlodipine diltiazem felodipine lercanidipine nifedipine nisoldipine nitrendipine verapamil HMG CoA Reductase Inhibitors: atorvastatin cerivastatin lovastatin NOT pravastatin simvastatin Steroid 6betaOH: estradiol hydrocortisone progesterone testosterone Miscellaneous: alfentanyl buspirone cafergot caffeine=>TMU cocaine dapsone codeine- Ndemethylation dextromethorpha n eplerenone fentanyl finasteride gleevec haloperidol irinotecan LAAM lidocaine methadone odanestron pimozide propranolol quinine salmeterol sildenafil sirolimus tamoxifen taxol terfenadine trazodone vincristine zaleplon zolpidem Inhibitors 1A2 2B6 2C19 2C9 2D6 2E1 3A4,5,7 amiodarone cimetidine fluoroquinolones fluvoxamine furafylline interferon? methoxsalen mibefradil ticlopidine thiotepa ticlopidine cimetidine felbamate fluoxetine fluvoxamine indomethacin ketoconazole lansoprazole modafinil omeprazole paroxetine probenicid ticlopidine topiramate amiodarone fluconazole fluvastatin fluvoxamine isoniazid lovastatin paroxetine phenylbutazone probenicid sertraline sulfamethoxazole sulfaphenazole teniposide trimethoprim zafirlukast amiodarone buproprion celecoxib chlorpromazine chlorpheniramine cimetidine clomipramine cocaine doxorubicin fluoxetine halofantrine red-haloperidol levomepromazine metoclopramide methadone mibefradil moclobemide paroxetine quinidine ranitidine ritonavir sertraline terbinafine dithiocarbamat e disulfiram HIV Antivirals: delaviridine indinavir nelfinavir ritonavir saquinavir amiodarone NOT azithromycin cimetidine ciprofloxacin clarithromycin diethyldithiocarbamate diltiazem erythromycin fluconazole fluvoxamine gestodene grapefruit juice itraconazole ketoconazole mifepristone nefazodone norfloxacin norfluoxetine mibefradil verapamil DHB Increase the amount of prohormones your body absorbs by 500% with a DHB Anabolic Amplifier! Over 500% more active Testosterone to your bloodstream with your Current Prohormone dose Attacking the CYP and P450 Enzymes is the most inexpensive and effective way of protecting testosterone. DHB Supplement Amplifier™ is designed to compete with the substrate hormone to attach itself to the enzyme. The body then washes the enzyme harmlessly out of the body! . The enzymes CYP and P450 are responsible for metabolizing and destroying steroids and prohormones. They can be removed from your body, paving the way for anabolic hormones to flood your bloodstream to yield massive muscle growth like never before!

















































![[4-20-14]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003097962_1-ebde125da461f4ec8842add52a5c4386-150x150.png)
