* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Medical Errors: Definition, Causes, and Prevention
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
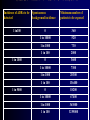
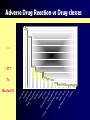
Iran ADR Center Detection, Assessment & Prevention of ADRs in Human. Ref: World Health Organization. Adverse Drug Reaction WHO definition: Any response to a drug which is Noxious and Unintended, and which occurs at doses used in man for prophylaxis, diagnosis or treatment. Why Should We Learn about Adverse Drug Reactions (ADR)? Over 2 MILLION serious ADRs yearly 100,000 DEATHS yearly 6.7% of hospitalized patients have an ADR with a fatality of 0.32, Ref: U.S. Food and Drug Administration . Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Annual death rates in USA AIDS Breast cancer Highway accidents 16,516 42,297 43,458 ADR 100,000 percentage of hospital admissions due to adverse drug reactions: USA UK France Norway 28% 15.6% 12.6% 11.5% Costs Associated with ADRs $ 136 BILLION yearly (related to morbidity and mortality) Greater than total costs of cardiovascular or diabetic care. Mean length of stay, cost and mortality ADR patients are DOUBLE that for control group of patients without ADR. ADRs cause 1 out of 5 injuries or deaths per year to hospitalized patients. Ref: U.S. Food and Drug Administration . Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Since 1995 the costs associated with drug-related problems (DRPs) have more than doubled. The total cost of drug-related morbidity and mortality exceeds the cost of the medications themselves. Ref: Ernst Frank R, Grizzle Amy J. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2001; 41: 192-9 The cost of adverse drug events: estimated lost patient activity days per year in hospitalised patients Country US Germany UK Australia Sweden Serious ADRs 700,000 206,000 148,000 48,000 22,000 Lost Activity Days 1,218,000 358,440 257,520 83,520 38,280 ADR has financial and social effects: 1- Unreliability on manufacturer 2- Unreliability on health system (Physician, Pharmacist & Nurse) 3- Unreliability on governments in saving the social safety 4- Causing mortality & morbidity So many prescriptions! Tow-thirds of patients visits result in a prescription 2.8 BILLION outpatients prescriptions were filled in the year 2000 (about 10 prescriptions per person in the U.S.) ADRs increase exponentially with 4 or more medications Ref: U.S. Food and Drug Administration . Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Even more, dramatic situation with drug safety is in developing countries (IRAN) • They often have older, cheaper drugs which may be more toxic. • Health professional have less opportunity for postgraduate education on clinical pharmacology. • Useful,easily available, balanced information on adverse effects and their management is absent or not enough. • Ref:World Health Organization Assessment the quality of medications Assessment of drug safety Detection of occurrence rate of ADR Decreasing the risk of occurrence of adverse events How Knowledge About ADRs Is Created? 1-Animal experiments 2- Clinical trials 3- Epidemiological methods Spontaneous reporting Cohort studies Case-control studies Limitations of Clinical Trials Limited size Narrow population Narrow indications Short duration • Ref: J. Russell May. Adverse drug Reactions and interaction, In: Pharmacotherapy, A pathophysiologic Approach. 1997, Appleton & Lange. وزارت بهداشت درمان و آموزش پزشكي،معاونت غذا و دارو- دفتر تحقيق و توسعه،مركز ثبت و بررس ي عوارض ناخواسته داروها Incidence of ADRs to be detected 1 in100 1 in 1000 1 in 5000 Spontaneous background incidence Minimum number of patients to be exposed 0 360 1 in 10000 520 1 in 1000 730 1 in 100 2000 0 3600 1 in 10000 7300 1 in 1000 20300 1 in 100 136400 0 18200 1 in 10000 67400 1 in 1000 363000 1 in 100 3255000 How many patients one needs to treat to see with high probability the reaction? Pre-marketing studies are carried out in limited number of patients: “The law of three” – In order to detect for sure SAE that occurs as 1 event per 2000 patients treated we need to treat • 6000 patients • 9600 patients • 13000 patients for 1 case for 2 cases for 3 cases • The number of patients involved in pre-marketing studies has been increasing but is still limited in comparison with the exposure to the drug in post-marketing phase Some drugs cause serious ADRs at very low frequencies bromfenac hepatotoxicity 1 in 20,000 patients, removed from the market in 1998, less than 1 year after it was introduced). • Ref: U.S. Food and Drug Administration . Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Adverse reaction Pulmonary embolism Myocardial infarction Death fro asthma Jaundice Colitis Colitis Aplastic anemia Drug Time lag(yr) Oral contraceptive Oral contraceptive Sympathomimetic Halothane Lincomycin Clindamycin Phenylbutazone 3 5 4 7 6 5 6 Ref: J.Russel May.Adverse Drug Reactions and interactions,In:Pharmacotherapy, a pathophysiologic approach.1997, Appleton & Lange. “yellow cards” Spontaneous Reporting Large population All medicines Hospital and out-patient care Long perspective Patient analysis possible Non-interventional Cheap Recent trends: enlarging the scope of pharmacovigilance Pharmacovigilance concerns have been widened to include: – herbal medicines – traditional and complementary medicines – blood products – biologicals – vaccines – medical devices Pharmacovigilance Major Aims Early detection of unknown reactions and interactions Detection of increase in frequency Identification of risk factors Quantifying risks Preventing patients from being affected unnecessarily RATIONAL AND SAFE USE OF DRUGS Ref: World Health organization. The ultimate goal of pharmacovigilance is improving pharmacotherapy Ref:World Health Organization History of drug safety (1) 2003 - 155 years of pharmacovigilance 29.01.1848 15 year old Hannah Greener died in course of routine anaesthesia with chloroform (problem: ingrown nail of toe; fibrillation of ventricles?). Lancet’i initiated foundation of a (required, that the pharmaceuticals should be “pure” and “free of any contamination”, nothing was said about the efficacy) 1936 - USA-s 107 lethal cases (diethylenglycol was solubilize sulphanilamides); the law was used to amended in 1938 History of drug safety after thalidomide eradication 1961 : Dr William McBride (Australia)( thalidomide 4000 cases) 1964 : UK started “yellow cards” system 1968 : start of WHO Programme for International Drug Monitoring Drug Classes Responsible for ADRs Drug Class Frequency Antibiotics Antitumor agents Anticoagulants Cardiovascular agents Anticonvulsant agents Antihypertensives Analgesics Antiasthmatics Sedative/hypnotics Antidepressants Antipsychotics Peptic ulcer therapy Most frequent Least frequent Ref: J. Russell May. Adverse Drug Reactions and Interactions, In: Pharmacotherapy, A pathophysiologic Approach. 1997, Types of Drug-Related Effects by Frequency Type of adverse event Frequency Marrow suppression Bleeding Central nervous system Allergic/cutaneous Metabolic Cardiac Gastrointestinal Renal Respiratory Most frequent Least frequent Ref: J. Russell May. Adverse Drug Reactions and Interactions, In: Pharmacotherapy, A pathophysiologic Approach. 1997, Appleton & Lange. Preventing ADR Over 75% of all ADR are dose-dependent Many ADR arise from failure to tailor the dosage of drugs to widely different individual needs. Ref:World Health Organization • Patient’s specification • Patient’s drug history • Pharmacology of prescribed drugs • Prescription of minimum effective dosage Essential factors causing ADRs: Factors related to patient: Sex Age (weight) Genetic (PHARMACOGENOMICS) Drug allergy Lack of knowledge in patients Concomitant drugs Factors related to patient: • • • • • Non-compliance - underestimated Route of Administration - bioavailability Food - protein malnutrition Pollutants - smoking/herbicide residues Timing - chronopharmacology Essential factors causing ADRs: Factors related to drug: Route of administration Dosage Duration of treatment Problems with drug: 1-Formulation 2-Problems with preparing of drug 1936 • USA : 107 lethal cases diethylenglycol was used to solubilize sulphanilamides Drugs cause hospitalization Digoxin Aspirin Prednisone Warfarin n Guanethidine 41 24 15 9 5 Aspirin Digoxin Warfarin HCTZ Prednisone 25 24 12 11 8 Type of Alerting Order • One time stat dose • • PRN orders Short course therapy Example Sub-cutaneous epinephrine, corticosteroids, dextrose 50%, sodium polystyrene sulfate Antihistamins, topical corticosteroids Oral corticosteroids (eg.20 mg prednisone p.o 7 days) • aminoglycosides, antiarrhythmic agents, anticonvulsants • Theophylline, phenytoin, aminoglycosides, Drug interactions (eg. Digoxin-verapamil, cimetidine-theophylline) Stool guiac, prothrombin time Abrupt decrease in dose Followed by a stat • Serum level State laboratory tests فوايد وجود برنامه ADRدر بيمارستان -1افزايش كيفيت درمان -2جلوگيري از شكايات حقوقي -3ارزيابي مشكالت دارويي -4ارزيابي مشاهدات پزشكان و ديگر حرف پزشكي -5ارتقاء دانش دارويي دست اندركاران درمان داليلي كه باعث كاهش گزارشات ADRميگردد: -1عدم اطالع از مكانيزم موجود براي ارسال گزارش -2عدم دسترس ي به فرم مربوطه -3عدم اهميت عارضه ازنظرگزارشگر -4نداشتن وقت -5دررابطه با فرم مربوطه -6اجتناب ازدرگيري دركارهاي اداري -7ترس ازشكايات حقوقي ,كيفري -8عدم اطمينان ازبوجود آمدن ADRتوسط دارو Misconceptions about ADR Reporting All serious ADRs are documented by the time a drug is marketed About patient receiving multiple medications,it is difficult to determine if a drug is responsible for the ADR ADRs should only be reported if absolutely certain One reported case can’t make a different Ref: U.S. Food and Drug Administration . Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Report of Iranian ADR monitoring center The numbers of reports, registered in ADR center of Iran •From the year 1377 to Mordad 83 , 5861 cases of Adverse Drug Reaction have been sent to Iranian ADR Center Pharmacovigilance Activities in Iran Accepted as a full member of WHO International Drug Monitoring Program in July 1998. Implemented Spontaneous Reporting System in Iran. Collected more than 6000 ADR reports from different parts of the country. Issued 38 Alert Letters on drug safety sending to the health professionals. Pharmacovigilance Activities in Iran Has published 24 monthly reports in Razi journal. Has published 9 issues of national ADR Bulletin. Has over 150 workshops and seminars all over the country. Has trained over 8000 health professionals on ADRs. en tis t U th er s nk no w n O ph ar m ac is t D nt s ur se Pa tie N Sp ec ia lis t io ne r al pr ac tit lin ic al en er C G Ph ar m ac is t Reporters WHO Drug Monitoring Programme Participating countries 1999 58 countries have joined the programme Official member countries Associate member countries International Vigilance Every healthcare professional in the world should be constantly alert for adverse effects or potentional new hazards and reporting them to their National Centers. Countries with the best reporting rates generate: • Over 200 reports per 1,000,000 inhibitants per year. • Over 150 reports per 1000 physicians per year. N S A ge Mordad 83 A nt s nt ib C io ar tic B di lo o va s od sc & ul C ar oa gu la tio M is n al le no us H or m El on ec e G t ro Va IA s ly cc ge te in & nt e M s & et im A a bo nt m in un e o lic ol pl og as ic m al s pr od uc Sk ts in A Sm EE ge oo nt N th s T m A ge us cl nt e s re la xa nt Vi ta m in s C Adverse Drug Reaction vs Drug classes From: 1377 To Site of Reaction (CNS agents ) From: CNS 77 GI Body as a whole To Skin & apprndages Application site Cardiovascular Psychiatric Respiratory Autonomic Musculoskeletal Urinary Vision Heart rate & rhythm Mordad 83 C B a C r& S ep ro du ct iv e Sy s Vi si on bi lia ry oa gu la tin g R N w ho le I es pi ra to ry Li ve R as G Ap pe nd ag es od y & 77 Sk in From: Site of Reaction (Antibiotics) To Mordad 83 Diclofenac Na Above 100 Cases of Foot drop Withdrawal from Iranian Pharmacopoeia Streptokinase Bupivacaine 4 Cases of Para-plegia following IT injection 2 of them led to Death Tramadol? • From 04.81 to 05.83, 289 cases of adverse effects of Tramadol have reported to ADR center • Among them : 81 cases have been in Male & 208 cases have been in Female Age groups (Reaction of Tramadol): 0-10 11-20 21-30 31-40 41-50 51-60 61-70 71-80 >80 Unknown 3 7 86 61 51 29 18 11 3 20 Rout of administration (In patients with Tramadol adverse effects) . % . . % IM PO IV ID Unknown % . % . % Adverse Reaction of Tramadol from 04.81 to 03.83 6 Major Adverse Effects of Tramadol: •Nausea 125 •Vomiting 116 •Vertigo 109 •Asthenia 57 •Dyspnoea 42 •Hypotension 41 Adverse effects of Tramadol from 04.81 to 03.83 Reaction Number Reaction Number Sweating 24 Myalgia 7 Headache 21 Pale 7 Agitation 20 Ataxia 6 Somnolence 17 Vision disorders 6 Pruritus 16 Paraesthesia 6 Rigors 15 Injection site reaction 6 Flushing 11 Delusion 6 Urticaria 11 Tachycardia 6 Bronchospasm 10 Respiratory depression 6 Hallucination 9 Palpitation 5 Convulsion 9 Rash 4 Hypertension 8 Cold extremity 4 Confusion 8 Apnoea 3 Abdominal pain 8 Anxiety 3 Dry mouth 7 Stupor 3 Adverse effects of Tramadol from 04.81 to 03.83 Reaction Number Reaction Number Cardiac arrest 3 Back pain 1 Anorexia 3 Arrhythmia 1 Shock 3 Bradycardia 1 Allergic reaction 2 Lacrimation abnormal 1 Cyanosis 2 Myocardial Ischemia 1 Constipation 2 Diarrhea 1 GI disorders 2 Depression 1 Leg pain 2 Erythem 1 Dysphagia 2 Coma 1 Speech disorders 2 Edema 1 Urinary retention 2 Hearing decrease 1 Chest pain 2 Facial pain 1 Fever 2 Withdrawal syndrome 1 Syncope 2 Foot drop 1 Insomnia 2 Tremor 1 Sildenafil •Sildenafil has cardiac related side effect. •Some cases of myocardial infarction were reported to ADR center due to this drug. The following tips must be reminded when using Sildenafil: • Cardiovascular adverse effects such as atrial fibrillation, cardiomyopathy, flushing, hypotension, myocardial infarction, thrombosis, ventricular tachycardia have been reported with Sildenafil. • Concomitant use of Sildenafi with following drugs are forbidden: Organic nitrates (eg. Nitroglycerin) Nitrates & Nitric donors (eg. Nitroproside) Lamotrigine Common adverse effects: Skin reaction: rash ,Steven's Johnson syndrome, TEN Women more than men Onset Caution Adverse events causing hospitalization Weight limitation Age Limitation • Not effective & safe in children under 16 years old • Person younger than 16 years old: • Risk factor for severe skin reactions Lindane •*This drug has entered to the world drug market since 1901. •*Since the year 1990 Lindane has been introduced as a second line treatment. Suggestion: Single dose of use Second line of treatment Labeling Contraindication Precaution FDA alert (2003) •Systemic adverse effects of Lindane •70% of adverse effects have been the CNS adverse events,including: •Seizure,Vertigo,Headache,Parasthesia •17 cases of death have been reported to FDA, •IN 3 cases an established relationship between the events and using of drug were found Celecoxib Labelling Changes • Celecoxib Long-term Arthritis Safety Study (Class) did not show a safety advantage of upper GI events for celecoxib compared with diclofenac or ibuprofen. Hypiran Drug Interaction with: • Indinavir • OCPs • Antidepressants • Digoxin, Warfarin, Theophylline, Cyclosporin Risperidone Extrapyramidal Reactions: Rabbit Syndrome 1 Case in the USA 2 Cases in the English- Language Literature 4 Cases reported to IADRMC IV IG . 2 Cases of Death following Administration of Vials with Unusual Color Benzyl benzoate . 5 Cases of Sever Systemic Side Effects following Topical Administration 3 of them led to Death مرگ ناشی از تزریق سرم حیوانی به جای سرم انسانی درود -آبان 1381 Salmeterol 3 cases of Asthma attack 1382 بهمن ماه-تهران 3مورد مرگ ناشی از تزریق اشتباه ÷تاسیم کلراید به جای مترونیدازول تیر ماه 1384 One case of Death Promethazin + Hyoscin+Dicyclomin 1385 اردیبهشت محلولهای دیالیز صفاقی ساخت شرکت ثامن 250مورد ÷ریتونیت شیمیایی اردیبهشت 1385 Contribution of Drug Interactions to the Overall Burden of preventable ADRs Drug interactions represent 3-5% of preventable inhospital ADRs. Drug interactions are an important contributor to number of emergency departments visits and hospital admissions. Ref: U.S. Food and Drug Administration . Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Comparison Type A and Type B A B Pharmacologically predictable Yes No Dose-dependent Yes No Incidence and morbidity High Low Mortality Low High Treatment Adjust dose Stop MedWatch The FDA Safety Information and Adverse Event Reporting Program: www.fda.gov/medwatch/ Safety alerts Recalls Withdrawals Important labeling changes Biologicals, Drugs, Dietary supplements معاونت غذا و دارو www.fdo.ir دبيرخانه تحقيقات كاربردی مركز ثبت و بررسی عوارض ناخواسته دارويی Iranian Adverse Drug Reaction Monitoring Center مركز ثبت و بررس ي عوارض ناخواسته داروها دفتر تحقيق و توسعه-معاونت غذا و دارو وزارت بهداشت درمان و آموزش پزشكي تلفن6405569: نمابر6417252: E-mail: [email protected] Case II خانم 35ساله اي با سابقه افسردگي و فشار خون تحت درمان با ترانيل سيپرومين، اناالپريل و هيدروكلرتيازيد مي باشد .ايشان به دليل جراحي اورژانس ،تحت بيهوشي با هالوتان و پتيدين قرارمي گيرد .پس از جراحي براي بيمار در اطاق Recovery فشار خون 210/120و انقباضات ميوكلونيك ثبت مي شود .بيمار به دليل عدم هوشياري كامل و به دليل فشار خون اورژانس به ICUمنتقل و تحت درمان با نيترو پروسايد قرار مي گيرد.پس از اقدام به كاهش ويا قطع نيتروپروسايد ،فشار خون بيمارمجددا افزايش مي يابد .كليه آزمايشات پاراكلينيك بيمار طبيعي مي باشد. سوال :به نظر شما علت افزايش فشار خون بيمار چيست؟ Ccase III بيمار پسر بچه 4ساله اي است كه با تشخيص اوتيت مدياي حاد تحت درمان با آموكسي سيلين قرار گرفته است .شكايت اوليه بيمار تب – بي قراري و درد گوش بوده است 2 .روز بعد از شروع دارو تب بيمار قطع شده و حال عمومي بهتر شده است 4 .روز بعد از شروع درمان ،كودك دوباره تب كرده است ولي حال عمومي خوب بوده و Toxicنمي باشد .مادر بيمار ذكر مي نمايد كه آموكسي سيلين را به موقع داده است و هنوز درمان ادامه دارد. پزشك در منطقه اي كه طبابت مي كند تجربه اوتيت مقاوم به آموكسي سيلين را نداشته و بيمار نيز سابقه مصرف آنتي بيوتيك در يك ماه اخير و اوتيت مكرر را نمي دهد. در معاينه اخير راشهاي ماكولوپاپوالر بر روي تنه مشاهده مي شود .در CBCاخير بيمار : WBC = 9000 PMN = 57% L= 30% E=10% M=2% B= 1% پزشك تصمیم به قطع داروي آموكسي سیلین و ادامه درمان با اریترومایسین مي گیرد. 48ساعت بعد از قطع آموكسي سیلین تب بیمار قطع شده و راشهاي جلدي محو مي شود. لطفا در مورد این بیمار به سواالت زیر پاسخ دهید: -1تشخیص شما در مورد مشكل بیمار چیست؟ -2چه نكات مثبتي به تشخیص شما كمك مي كند؟ -3تشخیص هاي افتراقي در این بیمار كدامند؟ -4درمان مشكل اخیر بیمار چیست؟



























































































![Is It Making a Difference? [PDF, 8.72MB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008253928_1-59943b7d1c0ee9fe2fc49012bcc3e283-150x150.png)
