* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 2B - Financial Crisis of 2008
Syndicated loan wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Securitization wikipedia , lookup
Peer-to-peer lending wikipedia , lookup
Federal takeover of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac wikipedia , lookup
Financialization wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
Public finance wikipedia , lookup
Interbank lending market wikipedia , lookup
United States housing bubble wikipedia , lookup
1998–2002 Argentine great depression wikipedia , lookup
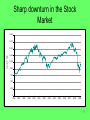
Section 2B Financial Crisis of 2008 1 Overview • Key events of the economic crisis • The four causes of the economic crisis • 3 lessons we should learn from economic crisis 2 Key Events of the Economic Crisis This economic downturn was characterized by: • • • • The boom and bust of the housing market Rising default and foreclosure rates Sharp downturn in the stock market Soaring energy prices 3 Boom and bust of the housing market 20 15.7 15 Percent Change 12.1 10 7.5 8.6 7.4 9.3 11.5 8.0 4.8 4.3 5 8.6 10.6 2.7 1.2 1.7 2.4 2.8 0.2 0 -2.1 -2.8 -5 -10 -11.2 -15 -20 1987 1989 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999 2001 2003 2005 -18.8 2007 4 Mortgage Default Rates 6 5 Percent 4 3 2 1 0 1979 1981 1983 1985 1987 1989 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999 2001 2003 2005 2007 5 Foreclosure Rates 1.4 1.2 Percent 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 1979 1981 1983 1985 1987 1989 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999 2001 2003 2005 2007 6 Sharp downturn in the Stock Market 1,800 1,600 S and P 500 1,400 1,200 1,000 800 600 400 200 0 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 7 What caused the economic crisis of 2008? 1. Regulations that lowered mortgage lending standards 2. Prolonged low interest rate policy of the Fed during 2002-2004 3. Increased debt to capital ratio of lending institutions 4. High and growing debt to income ratio of American households 8 1. Regulations Lowered Lending Standards A. Government Sponsored Enterprises (GSE’s): Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac B. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) required them to extend loans to low and moderate income households C. Community Reinvestment Act (CRA) also pushed banks to extend loans to high risk borrowers 9 1. Regulations Lowered Lending Standards Subprime loans: loans made to borrowers with a blemished credit history Alt-A loans: loans extended to borrowers with a poorly documented credit history 10 1. Regulations Lowered Lending Standards Share of Mortgages Originated (percent) 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 Subprime + Alt-A 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Subprime 11 2. Low interest rate policy of the Fed • The Fed kept interest rates low in 20022004 to stimulate the economy. – This increased the attractiveness of Adjustable Rate Mortgages (ARM loans) • The Fed pushed interest rates back up in 2005-2006 to combat inflation. 12 2. Low interest rate policy of the Fed Interest Rate (percent) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 Federal Funds 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 1 year T-bill 13 2. Low interest rate policy of the Fed When interest rates on ARM loans increased, so did the foreclosure rates (for both subprime and prime loans) 14 2. Low interest rate policy of the Fed When interest rates on ARM loans increased, so did the foreclosure rates (for both subprime and prime loans) 15 3. Increased Debt to Capital Ratio A. In 2004, SEC regulations allowed banks to leverage their capital and extend more loans B. So banks bundled mortgages together into “AAA” securities. C. This led to the collapse of investment banks and other financial institutions 16 3. Increased Debt to Capital Ratio 17 4. High and growing debt to income ratio of American households A. The debt to income ratio of households has risen sharply since the early 1980s. 18 4. High and growing debt to income ratio of American households Debt to Disposable Personal Income Ratio (percent) 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 1953 1958 1963 1968 1973 1978 1983 1988 1993 1998 2003 2008 19 4. High and growing debt to income ratio of American households B. Because mortgage and home equity loans are tax deductible, but other forms of debt are not, household debt is concentrated in housing assets C. As a result, housing is hit especially hard when economic conditions weaken 20 Lessons from the Financial Crisis 1. Be careful with regulations: They can create perverse incentives. 2. Monetary policy should focus on price stability, rather than trying to stimulate or slow the economy. 3. American households should probably carry less debt relative to their income 21 Review 1. Know the key events surrounding the 2008 economic crisis. 2. Know the four causes of the economic crisis. 3. Understand the lessons we should take from the mistakes made leading up to the economic crisis (and don’t repeat them). 22