* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Development Economics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
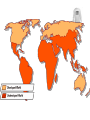
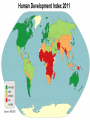
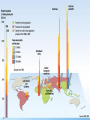
Development Economics: the International Perspective Why are some countries rich while others are poor? Objective: Given Theory of Development 4 Types of Economic Systems the student will distinguish these systems by discussing, writing, and presenting a response to the 3 economic questions, with 100% accuracy. Pineda 1 Development is… The sustained, concerted actions of policymakers and communities that promote the standard of living and economic health of a specific area. The scope of economic development includes the process and policies by which a nation improves the economic, political, and social well-being of its people Standard of Living A level of material comfort as measured by the goods, services, and luxuries available to an individual, group, or nation. Specifically, DEVELOPMENT is concerned with 3 Key Questions: 1. What Should Be Produced? 2. How Should It Be Produced? 3. For Whom Should It Be Produced? Why not just live “naturally?” – live off the earth, as Adam and Eve did! PowerPoint Conclusion Address the 3 Key Economic Questions: 1. What Should Be Produced? 2. How Should It Be Produced? 3. For Whom Should It Be Produced? The Four Types of Economic Systems or Models of Development Four very different types of Economic Systems have evolved as different societies have placed different emphasis on different goals and priorities in their efforts to answer the Three Key Economic Questions. How do you go from here to here? I. Traditional Economy Family or community based economic system that relies on custom and ritual to make its choices. Examples: Aborigines (Australia) Yanomami (Amazon) Tribes (Africa/Asia) Any Subsistence Economy II. Market Economy Individual or consumer based economic system that relies on the consumption choices of consumers. Examples: The U.S.A. (Remember this during Food, Inc.) Japan Most of Latin America III. Command Economy Centrally controlled economy where the government makes all decisions. Examples: Cuba North Korea, China Any Communist Country or Dictatorship IV. Mixed Economy Command & Free Market Economic system that incorporates some governmental involvement into a market based economy. Examples: Germany Japan Mexico China Theory of DEVELOPMENT To achieve development countries MUST: -allocate resources effectively, -ensure the optimal growth of resources, -create markets, -educate its people, -ensure the flow of economic benefits (employment; income; retirement) 1. Developed – A nation where the average income is higher than in developing nations, where the economy relies on many export goods, and where farming is conducted by advance methods. -High GDP, Exports, Diversification, Education 2. Developing - A nation where the average income is lower than in industrial nations, where the economy relies on a few export crops, and where farming is conducted by primitive methods. -Low GDP, Exports, Diversification, Education GDP - total dollar value of all final goods and services produced in a nation in a single year. Exports – goods sold to other countries. Diversification – spreading of investments among several different types of accounts to lower overall risk. Education- the act or process if imparting or acquiring general knowledge, developing the powers of reasoning and judgment, and generally of preparing one self or others intellectually for mature life. Crop – the cultivated produced of the ground; i.e. wheat crop Primitive – being the first or earliest in existence Objective: Given Relate development to our society & the 3rd World Define 1st and 3rd World Explain poverty the student will compare and contrast development in our society and the 3rd World by creating a comparison chart listing characteristics for each, with 100% accuracy. Pineda 14 Objective: Given Definitions of 1st and 3rd World Free market solutions Barriers of Development Marx’s class struggle TSWBAT write a three paragraph essay on 1st and 3rd world, barriers of development, free market vs. command, or Marx’s class struggle, with 90% accuracy. Pineda 15 UN, Human Development Index, 2009 Defining the 1st and 3rd World Sao Paolo, Brazil The World Divided 1. First World – refers to developed or industrialized nations such as US; most of Europe; & some of Asia 2. Third World – developing nations such as some LatAm; most Africa; parts of Asia Pineda 20 Characteristics of rd the 3 World 1. Low standard of living: low incomes, inequality, poor health and inadequate education 2. Low level of productivity: low education standards, low levels of health care, lack of investment 3. High rates of population growth and high dependency ratios i.e. proportion of the popular under 15 and over 64 who are supported by people between 15 and 64 4. High unemployment and underemployment Pineda 21 Calcutta, India Four Barriers to Growth 1. Institutional and Political Factors 2. International Financial Barriers 3. International Trade Barriers 4. Social and Political Factors Pineda 24 I. Institutional & Political Factors (reasons) a. Ineffective Tax Systems b. Political Corruption / Instability c. Unequal Distribution of Income d. Informal Market e. Lack of Infrastructure Political Instability 27 USA GB France Germany Japan Italy Canada Pineda Russia II. International Financial Barriers a. Debt b. Non-Convertible Currency c. Capital Flight 29 Pineda III. International Trade Barriers a. Single Crop Economy b. Minimal Exports c. Maximum Imports IV. Social & Cultural Barriers a. Religion b. Culture c. Tradition Market Economics Ways out of poverty: I. Natural Factors: abundance or natural resources especially land. II. Human Factors and Human Capital: skills, experience, education and health of the population III.Physical Capital: Accumulation of factors of production especially infrastructure IV.Institutional Factors: banking and finance Pineda 32 ☻The Communist Manifesto 33 (1848) Marx & Engels argued that human history…is the story of social classes and their struggles with each other: bourgeoisie (have) and the Karl Marx & proletariat (have not). Frederick ☻As long as poor and rich exist, Engels on equality = dream. Society & ☻Communism: a system in which Its all property and wealth is owned Problems in a classless society by all the members of that society. Pineda ☻Society’s problems stem from class struggle – owners of production vs. workers. 34 ☻Businesses seek to monopolize resources to maximize profit. ☻Workers are doomed under Capitalism. ☻Solution to society’s problems: workers take hold of the means of production. ☻How: proletarian revolution to establish new Gov’t with a Command Economy ☻Under CE: production is commanded to serve the interests of the people. ☻Free-Market or Command Economy??? Pineda Karl Marx on Society & its Problems Models of Development Short Essay Exam Directions: on a blank sheet of paper, in the best writing possible, answer one of the following questions in 1-3 paragraphs. Define the first and third world. Provide and explain at least three characteristics of each. Explain the four barriers of development or growth. Explain the “Market Economy” or “Free Market Economic” model AND how this model offers to move nations out of poverty or towards development. Explain Karl Marx’s “class struggle.” Of the four models of development, explain his model and how it will bring an end to the class struggle.