* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download sadc - Amazon Web Services
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
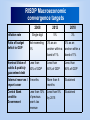
SADC Monetary Union Presentation to PCOF 11September 2007 Introduction The Theory of Monetary Integration Definitions (2) : Nana-Sink-am (1978) Monetary integration is the monetary unification of participating countries in an economic union which involves the adoption of: - common currency - harmonised fiscal and monetary policies - co-ordinated exchange rate policies. Corden(1992) Monetary integration is process that can be envisaged during the final stages of economic integration and it involves : (1) An Exchange Rate Union – an area within which exchange rates bear a permanently fixed relationship to each other. Even though the rates may in unison vary relative to other non union currencies (2) Convertibility - The permanent absence of all exchange controls, whether for current or capital transactions within the area. Monetary union eventually entails: - Adoption of fixed exchange rate margins among the members - Common Currency - Pooling of Foreign Exchange Reserves - Harmonised Fiscal and Monetary policies - Factor Mobility e.g. labour and capital - Common Central Bank This experience has been observed in the EU and The West African Monetary zone where Euro and ECB and the CFA and BCEAO exist. Background 1980 - Organisation of African Union (OAU) adopted the Lagos Plan of Action which culminated in signing of the Abuja Treaty to promote closer economic relations 1999 - African Union (AU) was established to further advance to the objectives specified in the Abuja Treaty Regional Economic Communities (RECs) were formed to become building blocks for continental integration New Partnership for Africa's (NEPAD) designated RECs as agencies for its programme Development implementing Regional Indicative Strategic Development Plan (RISDP) Economic integration within SADC is driven by the RISDP which provides a clear direction for SADC policies and programmes Implementing programmes on achieving: • Free Trade Area - 2008 • SADC Customs Union - 2010 • SADC Common Market – 2015 • SADC Monetary Union – 2016 (thus a SADC Central Bank) RISDP Macroeconomic convergence targets Inflation rate 2008 2012 2018 Single digit 5% 3% Ratio of budget deficit to GDP Not exceeding 5% 3% as an anchor within a band of 1% 3% as an anchor within a band of 1% Nominal Value of public & publicly guaranteed debt Less than 60% of GDP Less than 60% of GDP Less than 60% of GDP External reserves / 3 months import cover More than 6 months Sustained Central Bank credit to Government Less than 5% by 2015 Sustained Less than 10% of previous year’s tax revenue Macroeconomic convergence Member States agreed to achieve maintain macroeconomic stability and Member States should converge on stabilityoriented economic policies which, among other, includes: • Restricting inflation to low and stable levels Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) lays the foundation for the formation of a monetary union in the region Committee of Central Bank Governors (CCBG) CCBG established in August 1995 Deals with the development of well-managed financial institutions and markets, and co-operation regarding international and regional financial relations Various projects, among others: ̶ Development of national payment, clearing and settlement systems for SADC countries ̶ Legal and operational frameworks of SADC central banks – preparation of draft Model Central Bank legislation (to be finalised 2006) Annexes ANNEXES include: • Co-operation in the Area of Information and Communication Technology • Payment, Clearing and Settlement Systems • Co-operation and Co-ordination of Exchange Control Policies • Co-operation among Member Stock Exchanges • Harmonisation of Legal and Operational Frameworks of SADC Central Banks • Banking Regulation and Supervision (in progress) • Co-operation among member associations (in progress) banking Common Monetary Area (CMA) CMA is the only sub-regional formation using a single currency (Rand) Study – CMA regional central bank Rand remains a default currency in most SADC countries CMA Governors meet 4x per year to discuss policy strategies and exchange current economic developments in their respective countries Institutional Issues in Monetary Union Macro Economic Convergence - Basis for stable economies in SADC - Progress in achieving convergence - MEC Reports have been completed Problem: - Institutional mechanism overseeing reports, assessing and monitoring progress is unavailable. - Process of establishing mechanism is slow - Lack of commitment from member states - Cooperation among stake-holders Institutional Issues in Monetary Union Speedy establishment of the Peer Review Mechanism is necessary Guided by principles that ensures equality of participants Including the protection of Central Bank independence Acceptance of the special role Central banks play in the economy Statistical Issues While CCBG have made an effort to collect data and compile publications e.g. - Recent Economic Developments and the Integrated paper updated annually There are still conflicting ideas about the accuracy of data among stakeholders Timelines of data is a problem Lack of cooperation in verifying or supplying data between stakeholders Results: Gaps continue in Reports. More coordination and cooperation is required at national level by stakeholders Statistics Agencies should be involved with the process of Regional Integration SADC statistics office should be revived to oversee and initiate workshops to deal with statistics challenges Other Institutional issues Legal committee - Draft model bill has been concluded will be finalized by April 2008 It set out the environment under which a regional central bank will operate - Next is the development of a road map towards Monetary union - In which a decision on whether other institutions will be identified which will undertake further work towards a monetary union These could include the establishment of a SADC Monetary Institute which will carry on with the preparatory work - Payment, clearing and settlement committee There are 10 countries on RTGS and hopefully the rest will adopt the system which could eventually be linked into a regional systems which can allow for cross border payments. Problem: some countries are slow in modernizing their systems – financial Banking Supervision Discussions still have to happen on whether this function will remain with central banks or an independent regional body will be established. Conclusions Earnest discussions should begin on the road map towards the realization of a monetary union at summit level Peer review mechanism could be the body that will decide conditions for entry into Monetary union and reporting into Summit Consideration should be given of existing institutions e.g. CMA and SACU as building blocks Conclusions Thanks