* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Кредитный Value-at-Risk
Socially responsible investing wikipedia , lookup
Stock market wikipedia , lookup
Hedge (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Market sentiment wikipedia , lookup
Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act wikipedia , lookup
International monetary systems wikipedia , lookup
Efficient-market hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
2010 Flash Crash wikipedia , lookup
Financial crisis of 2007–2008 wikipedia , lookup
Currency intervention wikipedia , lookup
Systemic risk wikipedia , lookup
European Union financial transaction tax wikipedia , lookup
Patriot Act, Title III, Subtitle A wikipedia , lookup
Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission wikipedia , lookup
Systemically important financial institution wikipedia , lookup
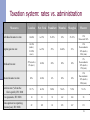
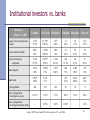
Developing international financial centers in Russia, India, and China based on a report for the Ministry of Economic Development of Russian Federation Alexei Goriaev New Economic School / CEFIR 1 What is an IFC? Financial center: Concentration of asset demand from individual and institutional investors Broad range of financial instruments (asset supply) Effective infrastructure and financial intermediation International financial center: Focus on the foreign capital, investors and intermediaries Transnational operations: fund raising, asset management, risk management, tax management, exchange trading, project financing (e.g., for PPP) 2 Why do RIC countries need an IFC? Additional funding for national companies at a lower cost More efficient asset allocation for local investors More risk management opportunities Making ruble/rupia/yuan a reserve and settlement currency Deeper economic integration with other countries Diversification of the national economy Directly: raising the share of financial sector in GDP Indirectly: stimulating young, growing industries …at a cost of higher sensitivity to global risks 3 IFC competitiveness index (2007) Leading IFC’s Place Rating London 1 795 New York 2 Hong Kong Emerging IFC’s Place Rating Dubai 24 585 786 Shanghai 31 554 3 695 Mumbai 48 481 Singapore 4 675 Moscow 56 423 Zurich 5 665 Frankfurt 6 642 Geneva 7 640 Chicago 8 637 Tokyo 9 628 Sidney 10 621 Source: Report “The Global Financial Centers Index 3” by the Z/Yen Group for the City of London. 4 Best practice of leading IFC’s Flexible legislation Stimulating taxation of financial operations Unified regulation system for all segments Efficient legal system (often, a specialized court) Modern centralized financial infrastructure Global integration, openness to foreign market participants Developed financial intermediaries Broad range of instruments Large and flexible labor market Favorable business environment Stable and positive macroeconomic situation 5 Traditional IFC’s: London, New York Strong national economy (EU region for London) Democracy and rule of law Anglo-Saxon legal system Multinational, multilingual workforce Easy to develop connections to the countries of origin Strong financial intermediaries and institutional investors Language Openness, no capital controls UK: unified, flexible, principles-based regulation US: business education and research, innovations 6 Young IFC’s: Singapore, Hong Kong State-driven development of the financial sector Globally oriented strategy (due to relatively small size of the national economy), no capital controls Mostly focused on the Asian region Efficient infrastructure Trading, transport, communications,… Workforce relying largely on expatriates Regulatory and fiscal incentives to foreign institutions HK: has profited from its role as a gateway to China 7 Emerging IFCs in RIC countries Increasing financial globalization and competition Either national financial centers become internationally competitive or concede to leading IFCs The ongoing financial crisis questions the current financial system …and leadership of traditional financial centers Large, dynamic national economy (f)needs development of active, efficient financial markets IFC requires reforms in legislation, regulation, infrastructure, labor market, and business environment Develop long-term institutional investors and attract population Impose more transparency and disclosure requirements Increase liquidity and scope of financial instruments Need to overcome bureaucracy, corruption 8 Russia: Moscow The concept of creating an IFC was adopted (only) in October 2008 Most developed financial market in the region, but …cap and liquidity are concentrated in the blue chips (mostly oil&gas) Segmented, non-flexible legislation and regulation system Tax pressure on financial companies and operations due to high effective tax rates and inefficient administration Lack of efficient and transparent legal system Low standards of information disclosure Segmented financial infrastructure, not well-integrated into global capital markets (no central depository, RTGS, DVP+3 trading) Tough access for foreigners (inefficient visa and migration regime) Low level of social and business environment 9 Shanghai and Mumbai Gradual development of national financial markets as IFC For foreigners, access granted only to qualified institutional investors Narrow market for qualified local labor, rely on ‘brain drain’ reversal The infrastructure needs to be further developed India: Anglo-Saxon legal system and rule of law Unified regulator of financial markets (SEBI) High corporate governance standards, compulsory IFRS reporting English language and links to the UK Over 9,000 stocks are listed, but most are illiquid; active equity futures trading China: More conservative approach, controlled by the state Enormous potential for the internal market Separate regulators for financial markets, banks, insurance companies Slow-to-change codified legal system, bureaucracy 10 Regulation system: protecting investors vs. enforcing contracts Measures London New York Frankfurt Mumbai Shanghai Moscow Rule of Law, World Bank, 2007, from 0 to 100 92.9 91.9 94.3 56.2 42.4 16.7 Regulatory quality, World Bank, 2007, from 0 to 100 98.1 90.8 92.7 46.1 45.6 35.0 Ease of doing business (rank from 178 countries, IFC, 2008), incl. 6 place 3 place 20 place 120 place 83 place 106 place Protecting investors 9 place 5 place 83 place 33 place 83 place 83 place Enforcing contracts 24 place 8 place 15 place 177 place 20 place 19 place Paying taxes 12 place 76 place 67 place 165 place 168 place 130 place 11 Taxation system: rates vs. administration Measures London Individual income tax rate 10-40% Capital gain tax rate 10-18% (indiv.) 21-28% (inst.) Dividend tax rate 25% (indiv.) 0% (inst.) New York Frankfurt to 35% to 35% 0-30% 15-45% 25% 20% Mumbai Shanghai Moscow 30% 25-33% 13% Non-resid: 30% 33% 13% Non-residents: 30% (indiv.) 24% (inst.) 10% 9% Non-residents: 30% (indiv.) 15% (inst.) 10-40% 20% 20% 0-30% 0% 20% 10% 13% Non-residents : 30% (indiv.) 20% (inst.) 35.7% 46.2% 50.8% 70.6% 73.9% 51.4% # tax payments, IFC 2008 10 21 39 162 104 58 Time spent on tax reporting (hours/year), IFC 2008 22 122 65 105 167 151 Interest income tax rate Total tax rate (% from the firm’s profit), IFC 2008 12 Financial markets: cap vs. trading Measures ($bln) (% GDP) London New York Frankfurt Mumbai Shanghai Moscow Stock market cap in a country 3 851.7 139% 15 650.8 113% 2 105.2 63% 1 819.1 166% 3 694.3 113% 1 221.5 95% Annual equity trading volume in the exchanges 10 334 373% 29 910 216% 4 325 130% 344 31% 4 069 125% 1 261 98% Volume of IPOs 50.4 76.5 10.4 17.6 63.3 26.7 Face value of exchangetraded bonds 3 782 136% 29 240 211% 5 335 161% 468 43% 1 565 48% 243 19% Face value of exchangetraded corporate bonds 453.2 16% 17 418.7 126% 1 146 34% 38.3 3% 486.7 15% 50.2 4% Trading volume of bonds at the exchanges 3 603.1 130% - 315.6 10% 60.4 5.5% 26.3 8% 115 9% Open positions of options 172 848 6 234% 402 235 2 906% 33 242 1 001% 397 36% 0 0% 52 4% Open positions of futures 451 757 16 294% 857 278 6 193% 137 581 4 141% 2 557 233% 0 0% 240 19% 13 Source: BIS Quarterly Review (as of end-2007) Institutional investors vs. banks Measures ($bln) (% GDP) London New York Frankfurt Mumbai Shanghai Moscow Assets of non-state pension funds 1 763 78.5% 13 310* 100.5% 116* 4.0% 33 4.2% 38 1.7% 19.2 1.5% Assets of mutual funds 820* 34% 12 496 100.5% 348* 12% 36 4.6% 56 2.5% 32 2.5% Assets of insurance companies 2 184 97.9% 6 074* 45.9% 1 224 43.8% 104 13.3% 141 6.3% 9* 0.9% Bank deposits 2 930 122% 10 028 76% 3 033 104% 640 73% 4 469 169% 415 32% Bank loans 3 289* 140% 8 278 71% - 278 41% 4 018 208% 426* 33% 486 253 106 29 74 71 21.6% 11.3% 5.7% 0.6% 5.6% 0.4% - 15.5% 9.8% 0.4%* - 1.2% # foreign banks Share of population investing into stocks Share of population investing into mutual funds Source: OECD (as of end-2007, with exception of * as of 2006) 14 General competitiveness: freedom vs. political risk Measures London New York Frankfurt Mumbai Shanghai Moscow Human development index (from 177 countries, UNDP 2008) 16 place 12 place 22 place 128 place 81 place 67 place Global competitiveness index (from 131 countries, WEF 2008) 9 place 1 place 5 place 48 place 34 place 58 place Index of economic freedom (from 157 countries, Heritage 2008) 10 place 5 place 23 place 115 place 126 place 134 place Index of press freedom, from 0 to 100 (WB 2008) 93.8 85.1 94.7 58.7 5.8 20.2 Government effectiveness index, from 0 to 100 (WB 2008) 93.8 91.5 92.4 57.3 61.1 42.2 12 place 20 place 16 place 72 place 72 place 143 place 66.3 55.8 81.3 17.8 32.2 23.1 Corruption perception index (from 180 countries, Transparency Intl 2007) Index of political risk, from 0 to 100 (WB 2008) 15 Conclusions for RIC countries The crisis exposed weaknesses of RIC markets …but also gave them a chance to avoid mistakes of the traditional financial centers Need unified risk-based regulation approach across different countries and types of financial services Hedge funds, sovereign wealth funds,… Minimize infrastructural and legal risks CSD, contract enforcement, role of offshores,… Make financial engineering transparent Put more responsibility and disclosure requirements on financial intermediaries Revise the role of the state 16