* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
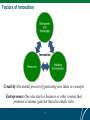
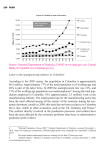
Pursuing Growth through Innovation Mohsen A. Khalil Bogotá, Colombia July 24, 2012 Global Challenges Growing Young Population Depletion of Natural Resources Global Financial Crisis Climate Change …Doing More with Much Less 2 Increased resource scarcity necessitates a departure from the business-as-usual growth model Interlinked resources (climate capacity for GHG, energy, water and land) in combination with… …drive increasing real prices and volatility… …rising resource demand due to increasing populations and wealth… …primarily impacting the world’s poorest people… …requiring much greater resource productivity increases 3 Innovation will be required to reach necessary resource productivity levels for economic growth Percent Historical growth rate 1995-2008 Energy GDP/BTU Materials GDP/Tonnes Water1 GDP/m3 Required growth rate 2008-2030 1.7 0.8 3.2 1.3 2.5 Food/feed Yield/hectare 1.4 Carbon2 GDP/tCO2e 1.3 Technical potential 3.2 ▪ While technically possible, current solutions will be prohibitively expensive for adoption in much of the developing word 3.3 ▪ Investment in innovation will be required in order to bring these price points down 1.5 3.7 1.5 4.0 5.3 6.4 1 Additional infrastructural investment for supply above BAU level is necessary to fully close the gap 2 All greenhouse gases SOURCE: GDP: Global Insight; Water: McK global supply-demand model; GHGs: IPCC; Oil: IEA WEO 2008 reference scenario; Power: IEA WEO 2008 (historic) and McKinsey Global Abatement Cost Curve v2.0(2030); Food/feed: FAO 2008; IIASA 4 Breakthrough innovations will disrupt billion dollar markets, creating new opportunities to capture value Disruption area Renewable 1 power generation 2 Energy efficiency Innovation in 3 fossil fuel Overhauling 4 power infrastructure 5 New mobility Disruption scenarios ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ 6 Materials ▪ ▪ 7 Water 20% of power from renewables by 2020 30% reduction in energy use Ban of incandescent bulbs 30 240 15% of new car sales to be xEV in 2015 Biofuels 5% of liquid fuels by 2020 >10x energy efficient building material 8% of chemicals biobased by 2012 90% of world population with water shortage 1,100 29 90 118 120 2,460 3,100 Declining business ▪ Wind, geothermal, biomass to heat and power, solar power equipment and services Grid energy storage ▪ Coal, oil burning power plant building, and operation Heat reflective windows/films LEDs and lighting controls Energy service companies Advanced HVAC CHP/micro CHP LNG growth Biomass fuel Advanced CCS SmartMeters High voltage DC technology In home energy management Grid IT Battery and electric motors Power electronics Charging infrastructure/comms Biofuels production Carbon negative cement Gel based insulation Bio-based chemicals and plastics ▪ ▪ Traditional light bulb Power/energy company ▪ ▪ Oil refinery Petrochemical ▪ ▪ Traditional meters Meter reading services ▪ ▪ Gasoline stand Traditional power train companies ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Traditional windows High emission cement Fiber glass insulation Fossil based plastics Existing agricultural region Manufacturing plants (textile, chemical, semiconductors, etc) ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ 147 470 5 Total addressable market Growth business 214 470 2-10x increases in US natural gas capacity from 88 shale discoveries SmartMeters in all homes by 2020 Grid energy storage proliferates Current CleanTech market Market size $ billions, 2010 Advanced pipes, pumps, valves Desalination plants Efficient irrigation systems Korea - Innovation Leader • By 2007, Korean investment in R&D was at least five times greater than Colombia. • Multiple nation-wide policies driving technology research. • International leader in broadband penetration rates. Singapore - Innovation Leader • Facilitated multiple-sector cooperation to develop innovation economy. • International leader in internet penetration rates and gov’t prioritization of innovation. Why Innovation Matters Innovation Productivity and Competitiveness 6 Growth and Development Factors of Innovation Innovation Creativity: the mental process of generating new ideas or concepts Entrepreneur: One who starts a business or other venture that promises economic gain but that also entails risks 7 Types and Models of Innovation Types of Innovation • High Level (e.g., Research & Development) • Process Innovation (e.g., assembly line) • Product Innovation (e.g., mobile banking) Innovation Models • • • • • Corporate R&D: Technology Transfer versus Home-Grown Business Incubation Technology Parks Open Collaboration Model driven by Resource Scarcity 8 Innovation, enabled by new information technologies that are transformative and disruptive. • • • • • • Reversing the flow of goods and services High degree of economic interdependence Shorter and sharper economic cycles Greater participation by emerging economies and companies Reversing brain drain Emerging countries leading innovation and becoming global trendsetters • Improved governance, transparency and empowerment • Changing business models • Emerging new platforms for distribution of social and business services 9 Resource scarcity and global climate change are driving worldwide innovation, unlike previous innovation cycles. 2030 GHG emissions tCO2e per capita 0-5 10-15 5-10 >15 Key areas for climate adaptation Major innovation hub during industrial revolution Major innovation hub during IT revolution Growing innovation hub in cleantech Source: McKinsey global cost curve; World Development Report 2010; Oregon State University, Resource Conservation and Food Security, Climate Change Impact on Agricultural Yields team analysis; US and European patent offices; World Intellectual Property Organization 10 How does LAC compare globally? Source: World Bank DataBank. July 2012. 11 Colombia at a Glance Strategic Sectors for Innovation: • Agribusiness (Forestry, Biofuels) • Industry (Oil & Gas, Manufacturing, Biotechnology, Clean Energy) • Manufacturing (Automotive, Building Materials, Textiles) • Services (Software and IT, Business Process Outsourcing, Tourism)5/13/11 mbia at a glance o pm e nt Indic a t o rs Share of Total Latin American R&D Expenditure mid-year (millio ns) (tho usand sq. km) ro wth (%) atio n (% o f to tal po pulatio n) etho d, US$ billio ns) a (A tlas metho d, US$ ) a (P P P , internatio nal $ ) (%) ita gro wth (%) Co lo mbia Latin A merica & Carib. Upper middle inco me Age distribution, 2009 Male Other Key Indicators 46.3 572 1,002 Unemployment 10.8% 1,142 20,422rate:48,659 1.4 1.1 0.9 75 79 75 23% Youth unemployment rate: Female 75-79 60-64 45-49 30-34 229.4 4,003 Urban population: 5,050 6,993 8,600 10,315 75%7,508 of total 7,495 12,466 Population in poverty: 37.2% 15-19 0-4 6 4.3 Economic 2.9 -1.8 growth: -2.9 -2.5 4.5% -3.3 4 2 0 2 4 percent of total population e nt e s t im a t e , 2 0 0 3 – 2 0 0 9 ) dco unt ratio at $ 1.25 a day (P P P , %) dco unt ratio at $ 2.00 a day (P P P , %) 12 16 28 8 17 .. .. Under-5 mortality rate (per 1,000) 6 Colombia Opportunities Challenges • Proactive public sector • Inadequate infrastructure • Public corporations • Security issues • Large domestic market • Informality • Natural resources • Inequality • Favorable business environment • Capital markets only for big firms • Encouraging to FDI and trade • Inefficient judiciary progress on Intellectual Property protection • Connectivity rates exceed regional averages • Growth in Capital Markets and PE networks • Low value on entrepreneurs • Poor quality education • High level educational enrollment with a large proportion of science and technology graduates 13 Colombia – Some Recommendations • Take advantage of land and biodiversity to develop new and unique products to sell around the world. • Train human capital to be able to bring foreign companies to invest in Colombia, create jobs with added value, especially in services sectors, especially for export-oriented outsourcing services. • Build Research/Develop/Innovation Centers to enhance studies to create new technologies and products to increase exports and bring the eyes of the world to Colombia. 14 Colombia – Some Recommendations • Establish incentives, vehicles, and institutions fostering grassroot innovation and entrepreneurship that can support employment creation, equality, and social inclusion. • Forge partnerships with global partners with: • Corporations to support technology transfer and adaptation in key strategic sectors; and • Technology and innovation networks that can support entrepreneurs to develop and commercialize concepts as well as link to global knowledge centers and markets. 15 What is Required? …an Innovation and Entrepreneurship Ecosystem 16