* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download polymer - MrSimonPorter
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
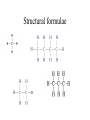
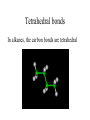
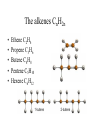
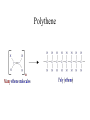
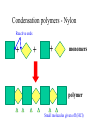
Topics 3abc – Alkanes, alkenes and ethanol Topics 5bc – natural oil and gas and synthetic polymers Crude oil (Petroleum) • A mixture of hydrocarbons (chemicals which contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms) Fractional distillation • Separation of liquids with different boiling points Fractional distillation The mixture can be split into simpler fractions by fractional distillation Welcome to a new family The alkanes Methane (CH4) Ethane (C2H6) Propane (C3H8) Butane (C4H10) The alkanes • • • • • • • Methane Ethane Propane Butane Pentane Hexane Octane CH4 C2H6 C3H8 C4H10 C5H12 C6H14 C8H18 General formula The alkanes CnH2n + 2 • • • • • • • Methane Ethane Propane Butane Pentane Hexane Octane CH4 C2H6 C3H8 C4H10 C5H12 C6H14 C8H18 Homologous group – similar chemical properties, structures and functional groups General formula The alkanes CnH2n + 2 • • • • • • • Methane Ethane Propane Butane Pentane Hexane Octane CH4 C2H6 C3H8 C4H10 C5H12 C6H14 C8H18 Homologous group – similar chemical properties, structures and functional groups Generally unreactive, but burn exothermically. Longer chains burn less easily. Structural formulae Alkanes are saturated compounds No double bonds Tetrahedral bonds In alkanes, the carbon bonds are tetrahedral Chlorinated methane Methane can be chlorinated. Trichloromethane is commonly known as chloroform. Isomers Same formula, but different structures We have slighty different physical properties (longer chains have higher boiling points) Combustion Combustion Hydrocarbons burn producing carbon dioxide and water CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O Incomplete combustion • When there is insufficient oxygen, carbon monoxide is also formed It reduces the blood’s oxygen carrying capability Another family! The alkenes CnH2n • • • • • Ethene C2H4 Propene C3H6 Butene C4H8 Pentene C5H10 Hexene C6H12 The alkenes • Unsaturated (contain a double bond) • More reactive • Can “add” atoms – addition reactions Alkenes - equilateral The bonds on a double bonded carbon in an alkene point towards the corners of an equilateral triangle Test for alkenes • Decolourises bromine water ethene Bromine (brown) Dibromoethane (colourless) Alcohols - ethanol Alcohols • • • • • • Methanol CH3OH Ethanol C2H5OH Propanol C3H7OH Butanol C4H9OH Pentanol C5H11OH Hexanol C6H13OH Ethanol Can be made by the addition reaction of water to ethene – when you have plenty of oil Phosphoric acid Ethanol - Fermentation of sugars You can make ethanol for industry this way when you have lots of sugar cane Ethanol and sodium 2C2H5OH + 2Na 2C2H5ONa + H2 Hydrogen and sodium ethoxide formed Oxidation of ethanol Ethanol can be oxidised to form ethanoic acid (acetic acid = vinegar!) Dehydration of Ethanol Ethanol + carboxylic acids Ethanol + ethanoic acid ethyl ethanoate + water An ester (they normally smell nice!) Polymers Polymers – addition polymerisation Molecules of ethene can be joined together to form polyethene ← monomers ← polymer Polythene Polypropylene – Strong and resistant to chemicals poly(chloroethene) - PVC Condensation polymers - Nylon Reactive ends + + + monomers polymer Small molecules given off (HCl) Cracking! Too many long molecules Crude oil contains too many of the long (and not so useful molecules) Cracking Luckily we can break the long molecules into shorter ones by “cracking” The long molecules are passed over hot broken pot (ceramic) and split up into smaller molecules. A catalyst can also be used Cracking Cracking an alkane produces smaller alkanes and also alkenes.