* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
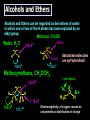
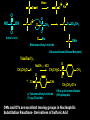
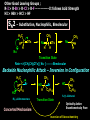
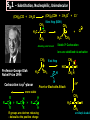
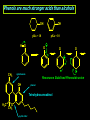
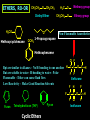
Biological Chemistry FIRST YEAR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Lecture Six Alcohols and Ethers Convenor : Dr. Fawaz Aldabbagh Alcohols and Ethers Alcohols and Ethers can be regarded as derivatives of water in which one or two of the H atoms has been replaced by an alkyl group Methanol, CH3OH Water, H2O H O 0.96 Ao o 0.96 A H C H O H H H 104.5o o 1.43 A O C H H H H H 109.5o 111.7o 1.43 A Saturated molecules are sp3 hybridized 108.5o Methoxymethane, CH3OCH3 H C o 1.10 Ao - I (net dipole) O H3C H Electronegativity of oxygen causes an unsymmetrical distribution of charge Alcohols are found to have much higher bpt than those of alkanes or haloalkanes of comparable size, e.g. Methanol (65 oC), Chloromethane and Methane are gases ; Ethanol (78.5 oC), Chloroethane (12 oC) and Ethane is a gas Methanol and Ethanol are classed as Polar Molecules (Hydrophilic) – They are Infinitely Soluble in Water Why? Answer – Hydrogen R H Bonding H R O H O H O H H O H R H O O H H-bonds weaker than covalent bonds, although these bonds can be continually broken and reformed – a highly ordered structure results – H-Bonding to water can also occur Water (mw = 18) is a liquid, bpt 100oC – otherwise a gas Ethanol H H 1-Pentanol H C C O H C C C C C O H H Hydrophilic end H H H H H H H H H H H H As R-group increases in size, so does the solubility in nonpolar solvents Hydrophobic end As the number –OHs increases so does solubility in water Bpt increase with chain length and number of –OHs Methanol, CH3OH In the Liver - Solvent in varnishes, paint - Racing Car Fuel (easy to put out flames) - Highly Toxic – “Blindness” Formaldehyde In Ethanol, CH3OH -Drinking Alcohol - 50% Ethanol is flammable H3C O OH H C H Alcohol Dehydrogenase the Liver CH3CH2OH O H3C Alcohol Dehydrogenase C O [O] H Acetaldehyde OH O [O] H C H3C C OH Acetic Acid Odour on your breath Symptoms - Hang-over Ethanol content; Beer, 3-9% ; Wine, 11-13% ; Whisky, 40-45% ; Vanilla Extracts, 35% ; Night Nurse, 25% ; Listerine, 25% Preparation of Ethanol - Fermentation of Sugar – Break down of sugar to CO2 and Ethanol by Yeast Enzymes - Industrial Process – Hydration of Ethene H H H2O CH3CH2OH H H3PO4 , 300C H Naming Alcohols hydroxy or alcohol group CH3 OH CH3 CH2 OH Methyl alcohol Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) (methanol) CH3 CH OH CH3 Isopropyl alcohol CH3 CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 OH Propyl alcohol (propanol) CH CH2 CH3 CH2 OH 2-Ethyl-1-butanol Naming Alcohols Polyhydroxy alcohols are alcohols that possess more than one hydroxyl group CH2 CH2 HO CH2 CH3 CH CH2 HO OH OH HO CH CH2 HO OH 1,2,3-Propanetriol (glycerol) 1,2-Propanediol (propylene glycol) 1,2-Ethanediol (ethylene glycol) Harmless Extremely Toxic Calcium Oxalate crystallises in the kidney leading to renal problems CH3 O CH2 HO CH2 OH HO C Liver Enzymes HO OH H3C C Liver Enzymes C OH Oxalic acid O CH CH2 O O C OH Pyruvic acid CH3 H CH3 H3C C OH H3C C OH H H Primary (1o) Alcohol H3C C OH CH3 o Secondary (2 ) Alcohol Tertiary (3o) Alcohol Alcohols are weak Acids H R O H Alcohol O H H + R O Alkoxide Relative Acidity ; H2O > ROH > R H O H C C H > RH pKa CH3OH (15.5), H2O (15.74), CH3CH2OH (15.9), (CH3)3COH (18.0) The Conjugate base of an alcohol is an alkoxide ion Because most alcohols are weaker acids than water ; they’re respective alkoxide is a stronger base than hydroxide ion OH - 2 CH3CH2OH + 2 Na 2 CH3CH2 Vigorous Reaction Na O + H2 Sodium Ethoxide -OH is a Poor Leaving Group Weak acids make Poor Leaving Groups in Organic Reactions Strong Acids have Conjugate Bases that are Good Leaving Groups in Organic Reactions H C O H + H A + C O H A Strong Acid Protonated Alcohol H C O H Nu C Nu + H2O We have to convert OH into a Good Leaving Group Base C O H O Na C O O HO S OH C O Cl O Sulfuric Acid Cl C O SO2CH3 S CH3 O Ms C OMs Methanesulfonyl chloride Alkanesulfonate(Alkane Mesylate) Similiarly, O NaOH , - HCl CH3CH2O H CH3CH2O S O + Cl S CH3 O CH3 O p-Toluenesulfonyl chloride (Tosyl Chloride) CH3CH2-OTs Ethyl-p-toluenesulfonate (Ethyltosylate) OMs and OTs are excellent leaving groups in Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions- Derivatives of Sulfuric Acid Other Good Leaving Groups ; R-I > R-Br > R-Cl > R-F -------------It follows Acid Strength HI > HBr > HCl > HF SN2 – Substitution, Nucleophilic, Bimolecular H3C Nu H C OTs H CH3 Nu C OTs H H CH3 Nu H H Transition State Rate = k [CH3CH2OTs] [ Nu- ] ---------Bimolecular Backside Nucleophilic Attack – Inversion in Configuration H3C HO H C Br C6H13 R-(-)-2-Bromooctane Concerted Mechanism CH3 CH3 HO C Br H C6H13 Transition State HO H C6H13 S-(+)-2-Octanol Optically Active Enantiomericaly Pure Inversion of Stereochemistry SN1 – Substitution, Nucleophilic, Unimolecular (CH3)3COH + 2 H3O+ + Cl Slow Step (RDS) CH3 CH2 Cl H3C C Cl + H3C CH3 CH3 (CH3)3CCl + 2 H2O Aided by polar Solvent Stable 3o Carbocation ions are stabilized via solvation CH2 CH3 Fast Step H 3C C O H Professor George Olah Nobel Prize 1994 H3C CH3 O H H Front or Backside Attack Carbocation is sp2-planar CH3 H - H+ more stable R R C > > R C R H H R CH3 H3C C O H R C H R groups are electron releasing - delocalise the positive charge CH3 tert-Butyl alcohol Evidence for SN1 is Racemization of an optically active compound H3CH2CH2C CH2CH3 HO C CH3 CH2CH2CH3 - HBr H3C C Br H3CH2C H3CH2CH2C S-3-Bromo-3-methylhexane The Carbocation intermediate is attacked by water from either side by the same rate Much high bpt, because of H-Bonding (e.g. Phenol, 182C, toluene, 111C Phenol + H3C C OH H3CH2C 1:1 Mixture of R- and S-3-Methyl-3-hexanol Phenols OH OH OH 1-Naphthol H3C 2-Naphthol OH 4-Methylphenol Phenols are much stronger acids than alcohols OH OH pKa = 18 H O CH3 O cyclohexene OH pKa = 10 O CH3 cyclic ether O Resonance Stabilised Phenoxide anion phenol Tetrahydrocannabinol H3C O ETHERS, RO-OR CH3CH2 O CH2CH3 Diethyl Ether H3CO O Methoxycyclohexane Methoxy group H3C O Ethoxy group CH3CH2 O Non-Flammable Anaesthetics OCH 3 1-Propoxypropane Methoxybenzene Cl F F Bpt are similar to alkanes – No H-bonding to one another H C C O C H But are soluble in water- H-bonding to water - Polar F F F Flammable – Ether can cause flash fires Enflurane Low Reactivity – Make Good Reaction Solvents F F O Furan O Tetrahydrofuran (THF) Cyclic Ethers O Pyran H F C C O C H F Cl F Isoflurane