* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy - nnhschemistry
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
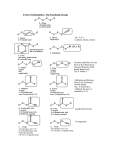
and Chemistry? Joules or calories Joules or calories Joules or calories Joules or calories Evidence of Energy Motion Heat Light Sound Energy Units joule ≡ energy exerted by a force of one Newton acting to move an object through a distance of one meter (SI unit) calorie ≡ the amount of energy required to heat 1 gram of water 1oC Calorie = 1000 calories 1Joule = 0.2390 cal How much is 1 Joule of energy? the energy required to lift a small apple one meter straight up. the energy released as heat by a quiet person, every hundredth of a second. the kinetic energy of an adult human moving a distance of about 6 inches every second. Types of Energy Chemical Heat Light Sound Electrical Magnetic Motion Nuclear Gravitational Chemical Thermal Kinetic Light E Acoustic Nuclear Electromagnetic Energy Transformations Gravitational Chemical Thermal Kinetic Light E Acoustic Nuclear Electromagnetic Energy Transformation Either or Energy Energy can be sorted into one of two categories – either – kinetic (the “doing the work” phase) or – potential (the getting ready to do work or the “stored” phase) Energy examples Potential Kinetic Mechanical Energy Mechanical Energy and and ? ? Forms of Kinetic Energy Electrical – movement of electrons Electromagnetic – moving electro magnetic waves (light, x-rays, gamma rays, radio waves) Thermal – vibrations and movements of particles in a substance Mechanical – movement of objects Sound – movement of particles as energy travels through a medium Potential Energy Chemical – energy stored in the bonds of molecules Stored mechanical – energy stored in an object based on its position relative to some reference state (i.e. a wound springs, a stretched rubber band, a boulder perched on the edge of a cliff) Nuclear – energy stored in nucleus of an atom Gravitational – energy stored based on relative position of two objects How much energy is stored in glucose? C6H12O6 1 gram of carbohydrate releases 4 Calories when burned 1 gram of fat releases 9 Calories when burned Chemical Energy Energy is stored in the bonds between atoms. When chemical reactions occur, bonds are broken and formed. The amount of energy released / absorbed during a chemical reaction can be measured and calculated from the bond energies Bond Energy Energy is absorbed by atoms when their bonds break. (+ΔH) ≡ heat of bond breaking Energy is released when bonds form between atoms. (-ΔH) ≡ heat of bond formation Bond Energy - Analogy Imagine stretching a rubber band until it breaks. You must do work to stretch the band because the tension in the band opposes your efforts. You lose energy; the band gains it. Something similar happens when bonds break in a chemical reaction. The energy required to break the bonds is absorbed from the surroundings. Bond Energy 436 kJ is stored in H-H 436 kJ is released when H-H is broken Bond Energy (kJ/mol) H-H 436 C-H 413 N-H 393 The higher the bond energy, the more work is required to break the bond, the more stable it is Bond Energy Bond Energy (kJ/mol) Bond Energy (kJ/mol) H-H 436 N-N 160 C-H 413 N=O 631 N-H 393 N triple N 941 P-H 297 N-O 201 C-C 347 N-P 297 C-O 358 O-H 464 C-N 305 O-S 265 C - Cl 397 O - Cl 269 C=C 607 O-O 204 C=O 805 C-F 552 O=O 498 C-S 259 Bond Energy Energy is absorbed when bonds break. Energy is released when bonds form. Energy is absorbed or released when the heat capacities of the products and reactants differ. Calculating Energy of a Reaction H2 + Cl2 2HCl Breaking H bond = 436 kJ/mol Breaking Cl bond = 242 kJ/mol H-Cl bond forming = -431 kJ/mol Reactions and Energy If heat is generated during a reaction ≡ exothermic If heat is absorbed during a reaction ≡ endothermic Calculating Energy of a Reaction H2 + Cl2 2HCl Moles of Bonds Broken Energy absorbed Moles of Bonds (kJ) Formed Energy released (kJ) 1 H-H @ 431.2 kJ 436 854 1 Cl-Cl @ 243 2 H-Cl @427 kJ 679 854 Heat of Reaction is 679 – 854 = -175kJ; energy is released during the reaction Endothermic or exothermic? Chemical Reactions and Energy Energy released H2 + Cl2 Bonds are broken HCl Calculating chemical energy N2 + O2 2NO Breaking one N bond = 946 kJ/mol Breaking one O bond = 498 kJ/mol Forming 2 N-O bonds = 2 x 631 kJ/mol = 1262 kJ/mol Net energy released = (946 + 498) + 2(-631) = +182 kJ/mol Endothermic or exothermic? Chemical Reactions and Energy Energy absorbed N2 + O2 Bonds are broken NO Calculating chemical energy 2H2 + O2 2H2O Endothermic or exothermic? Calculating chemical energy CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) Endothermic or exothermic? Food – the ultimate potential energy C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + energy ATP + heat Do I need energy? Where does energy come from? What is energy? Where does the energy in food come from? sun CO2 + H2O + energy C6H12O6 + O2