* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth`s+Layers+Worksheet+PowerPoint
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Diamond anvil cell wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
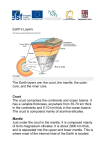
Earth’s Layers Crust Thin rigid layer that surrounds the earth Two types of crust Continental – granite Oceanic – basalt Oceanic Crust is more dense than continental crust but thinnest type of crust Crust Thin rigid layer that surrounds the earth Two types of crust Continental – granite Oceanic – basalt Oceanic Crust is more dense than continental crust but thinnest crust Earth’s Layers Mantle Mantle is less dense near the crust and more dense near the core Solid and liquid mix Mantle is the thickest layer Outer edge is cool and rigid Contains asthenosphere & part of lithosphere Crust Thin rigid layer that surrounds the earth Earth’s Layers Mantle Mantle is less dense near the crust and more dense near the core Mantle is the thickest layer Two types of crust Continental – granite Oceanic – basalt Oceanic Crust is more dense than continental crust Outer edge is cool and rigid Contains asthenosphere & part of lithosphere Outer Core Lower pressure allows the outer core to remain liquid & move around inner core causes Earth’s magnetic field Made up of metals Temperature and pressure are lower in the outer core than the inner core Outer core is less dense than the inner core Crust Thin rigid layer that surrounds the earth Two types of crust Continental – granite Oceanic – basalt Oceanic Crust is more dense than continental crust Outer Core *Lower pressure allows the outer core to remain liquid & move around the inner core causing Earth’s magnetic field *Temperature and pressure are lower in the outer core than the inner core *Outer core is less dense than the inner core Earth’s Layers Mantle Mantle is less dense near the crust and more dense near the core Mantle is the thickest layer Outer edge is cool and rigid Inner Core Intense pressure makes the inner core a solid even though it is very hot Inner core is made up of metals (iron & nickle) Inner core has the highest/greatest temperature, pressure and density Crust Thin rigid layer that surrounds the earth Two types of crust Continental – granite Oceanic – basalt Oceanic Crust is more dense than continental crust Outer Core Lower pressure allows the outer core to remain liquid Temperature and pressure are lower in the outer core than the inner core Outer core is less dense than the inner core Earth’s Layers Mantle Mantle is less dense near the crust and more dense near the core Mantle is the thickest layer Outer edge is cool and rigid Inner Core Intense pressure makes the inner core a solid even though it is very hot Inner core is made up o f metals (iron & nickle) Inner core has the highest/greatest temperature, pressure and density Lithosphere Crust & top rigid layer of mantle Broken into tectonic plates (19) “Litho” – stone We “li”ve on the “li”thosphere Asthenosphere Hot, soft rock of mantle Flows, plasticity Magma Convection currents which move tectonic plates Moving from the CRUST to the CORE Lowest Temperature Lowest Pressure Least Dense All the above INCREASES as you go down Highest Temperature Highest Pressure Greatest Density Convection Currents CONTINUOUS MOVEMENT Most Dense Sinks ( Cools) Molecules are CLOSER together Less Dense Rises (heats) Molecules are FARTHER apart Heat Source