* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Multi-functional Packaged Antennas for Next
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
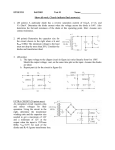
Ideal Diode Model Analysis of Ideal Diode Circuits: 1 12 out of 33 students got higher marks in Quiz 2 than HW2 Grade in Quiz2 - Grade in Hw2 100 75 50 25 0 -25 -50 -75 -100 BDR FM HD MR PM Identity of Students SA Example: Circuit Solution by assumed diode states Solution: 1. Assume that the D1 is on, and D2 is off, and determine the states of the diodes 2. Assume D2 is on and D1 is off, and determine the states of the diodes 3. Find out which assumption is correct, and proceed to solve the circuit from there 4 More examples Find V and I as marked. (a) D1 ON, D2 OFF. V = 10 volts, I = 0 (b) D1 ON, D2 OFF. V = 6 volts, I = 6 mA (c) D1 ON, D2 ON. V = 30 volts, I = 33.6 mA 5 Half wave rectifiers The current is conducted by the diode when it has a positive voltage across it, i.e. it is forward biased. Only then the voltage appears across the load. In reverse bias, the diode blocks the voltage, i.e. acts as an open circuit. Thus the voltage across the load becomes zero. For ideal diodes, the voltage drop in forward bias is zero. For real diodes the voltage drop is usually few tenths of a volt. The drop for a Si diode is usually assumed to be 0.7 V in forward bias. 6 Half-wave rectifier with smoothing capacitor Figure 3.2 Half-wave rectifier with smoothing capacitor Determining the value of the smoothing capacitor (3.2) (3.3) (3.4) IL is the load current, and T is the time period of the ac voltage. Vr is the peak-to-peak ripple voltage and C is the capacitance The average voltage supplied to the load is approximately midway between the maximum and minimum voltages, making VL as (3.5) 7 Full wave rectifier circuits 1. In a full wave rectifier circuit, usually a transformer is used to isolate the load from the ac power line, and provide out of phase input voltages. 2. It also allows the designer to choose the input to the rectifier circuit from the turns ratio. 8 Diode-bridge full-wave rectifier Note that the capacitor is half compared to a half-wave rectifier circuit, as the capacitor needs to discharge for only half the time. The output voltage can be further “smoothed out” by using a regulator circuit. 9 Diode circuit problem Ans: Peak voltage is 10 V, turns ratio = 15.6, C = 833 uF 10