* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PDEV-1018 AMATEUR RADIO OPERATOR INTRODUCTION
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Cavity magnetron wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Vacuum tube wikipedia , lookup
Photomultiplier wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
List of vacuum tubes wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
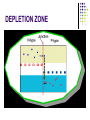
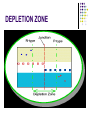
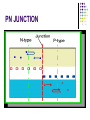
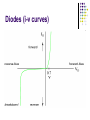
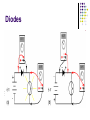
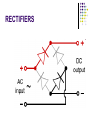
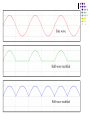
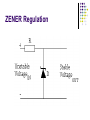
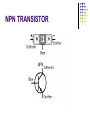
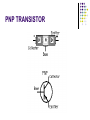
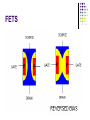
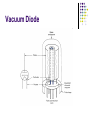
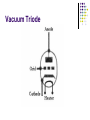
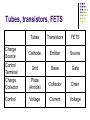
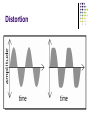
AMATEUR RADIO OPERATOR INTRODUCTION January 2013 Active Devices Diodes, Transistors, and Tubes AGENDA Diodes TRANSISTORS/FETS TUBES QUESTIONS SEMICONDUCTORS VERY STABLE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE SILICON & GERMANIUM MOST COMMON SILCON ATOMS SHARE VALENCE ELECTRONS (8 ELECTRONS) CAN BE GOOD INSULATOR INTRINSIC- PURE MATERIAL, NO FREE CHARGE CARRIERS EXTRINSIC – MATERIAL DOPED WITH EXTRA CARRIERS DOPING JUNCTIONS N TYPE – EXTRA ELECTRON (- CHARGE) P TYPE – MISSING ELECTRON (+ CHARGE) PN JUNCTION DEPLETION ZONE DEPLETION ZONE PN JUNCTION FORWARD BIAS DIODES 2 TERMINAL PN JUNCTION ANODE – P CATHODE - N Diodes (i-v curves) Diodes DIODE APPLICATIONS SWITCH RECTIFICATION DEMODULATION REGULATION LIGHT EMITTING (LED) RECTIFIERS ZENER DIODES Used to regulate voltages Behaves normally when forward biased When reversed biased, non destructive voltage breakdown ZENER Voltage ZENER Regulation TRANSISTORS 3 TERMINAL DEVICE 2 JUNCTIONS P-N-P N-P-N ALSO KNOWN AS “BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR” BASE CURRENT CONTROLS EMITTER/COLLECTOR CURRENT NPN TRANSISTOR PNP TRANSISTOR FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR TWO TYPES JUNCTION FIELD EFFECT or JFET METAL OXIDE SILICON FIELD EFFECT or MOSFET A CONDUCTIVE CHANNEL WITH 2 JUNCTIONS N-CHANNEL P-CHANNEL FETS TRANSISTOR - FET EMITTER, BASE, COLLECTOR FOR BIAS INCREASES CURRENT CURRENT CONTROLS LOW INPUT Z SOURCE, GATE, DRAIN REV BIAS DECREASES CURRENT VOLTAGE CONTROLS HIGH INPUT Z VACUUM TUBES Developed in late 1800’s and early 1900’s Still used in applications requiring high power or high voltages (power amplifiers) Tube Construction Thermionic emission Filament (Heater) used to heat cathode Cathode made of tungsten and thorium Heated cathode emits an electron cloud Positive potential placed on Plate (Anode) to attract electrons Negative potential Grid used to control electron flow Vacuum Diode Vacuum Triode Tubes – Take Aways Grid current – minimal or zero as long as Grid is negative relative to cathode Grid is usually a mesh Grid is closer to cathode Heater is farthest from Plate Used in high power applications Inside of envelope is a vacuum Tubes, transistors, FETS Charge Source Control Terminal Charge Collector Control Tubes Transistors FETS Cathode Emitter Source Grid Base Gate Plate (Anode) Collector Drain Voltage Current Voltage AMPLIFICATION Produce an output which is an enlarged reproduction of the input. Device is called an AMPLIFIER An accurate reproduction is called “LINEAR” Imperfections in reproduction are called “DISTORTION” Tubes, Transistors, and FETs can all be amplifiers. Typically gain is measured in dB Amplifier Applications AF (Audio Frequency) RF (Radio Frequency) IF (Intermediate Frequency) PA (Power Amplifier) Current, Voltage and or Power can all be amplified Distortion Homework Review Class Notes and Handouts Read ahead for next week QUESTIONS???? THANK YOU!!!!!!!!