* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 2 PPt 1 Basic Theories
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
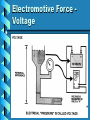
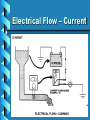
ATM 202 Automotive Electricity Instructor : Matthew Pence Email: [email protected] Book:Automotive Electricity & Electronics 2nd Ed. Barry Hollembeak Hours: Monday 6:00pm – 9:30pm Wednsday 6:00pm – 10:00pm • The Atomic Structure •What is an Atom? • An atom is the smallest particle on any element. • Element – oxygen (O) or hydrogen (H) • Compound – two or more elements combined together – water (H2O) • Molecule – Smallest particle of a compound • Atom Basics • Valence Ring • Free Electrons Conductor • Supports the flow of electrons • Popular Conductors: – Copper, Silver, gold, iron, aluminum – Each have three or less free electrons in it’s valence ring. Insulators • Cannot support the flow of electrons • Five of more free electrons in it’s valence ring • Popular insulators: – Glass, plastic, rubber, paper, wood Semiconductors • Not good conductors or insulators • Four free electrons in valence ring. • Silicon most popular, made from sand Electricity • Electricity is the flow of electrons through a conductor. • The human body runs on electrical impulses • The human body conducts electricity!!! Electrical Theories • Electron theory – electrons moving from negative to positive • Conventional theory – electrons flow from positive to negative • Does it make a difference? Electromotive Force Voltage Electrical Flow – Current AC/DC – Highway to Hell • Alternating current – Voltage that moves from positive to negative at a frequency that can vary • Direct Current – Voltage stays the same in moves in one direction Electrical Restriction – Resistance Review • Voltage – Electrical pressure, potential, measured in Volts • Current – Flow of electrons past a certain point in a given time, measured in Amps: 6.25 Billion Billion electrons per second = 1 amp • Resistance – Opposition to current flow, load or work, consumes voltage, measured in ohms