* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transistors
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
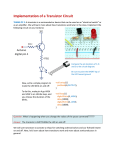
1 Digital Logic Structures: Chapter 3 COMP 2610 Dr. James Money COMP 2610 Transistors Most microprocessors are constructed out of what are called MOS transistors MOS stands for metal-oxide semiconductor For us, we just assume these work according to their specs Transistors The Pentium IV CPU has over 32 millions MOS transistors The IBM PowerPC 750 FX has 38 millions MOS transistors We are going to study how these connect together to get larger units Transistors There are two types of transistors – p-type – n-type These both work logically similar to wall switches in our homes Transistors Let’s first consider the wall switch example: Transistors Instead of the wall switch, you could insert a n-type or p-type MOS transistor: Transistors In (a), the MOS transistor is by itself In (b), it is combined with the wall switch circuit Note there are three terminals in the diagram Transistors Three terminals: – Source – input voltage – Drain – output voltage – Gate – controls output of transistor, depends on types of MOS Transistors What is important is for a n-type transistor, if the gate is supplied with 2.9 volts, the source to drain acts like a closed circuit That is, the drain is 2.9 volts If the n-type transistor gate has 0 volts, this is an open circuit and connection between source and drain is broken Transistors To conclude, for n-type MOS transistor in figure (b): – If Gate has 2.9 volts or on, then voltage is suppiled and the light comes on – If Gate has 0 volts or off, the voltage is not supplied and the light is off Transistors Figure (c) is the shorthand version of the circuit we will normally use We only show the terminals of the power supply The triangle represents source and the horizontal line represents drain Transistors A p-type transistor works in the opposite fashion: – If Gate has 2.9 volts, the circuit is broken and drain has 0 volts – If Gate has 0 volts, the circuit is closed and the drain has 2.9 volts Transistors p-type transistor diagram: Transistors Note that n-type and p-type act in complementary ways Circuits with both types of MOS transistors are called CMOS circuits because of this CMOS – complementary metal-oxide semiconductor